
(a)
Identify the
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Table-1 shows the data of quantity demanded and quantity supplied as follows:
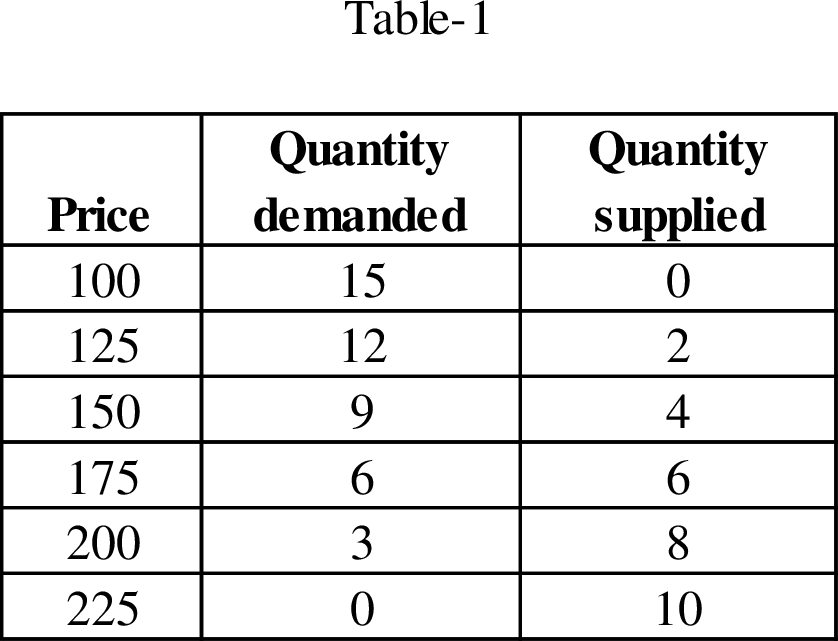
According to the equilibrium condition, the number of the container of roses is produced where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied and the price is charged at the corresponding equilibrium quantity level. Since the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied, Country U produces 6 million containers per year. In this
(b)
Identify the
(b)
Explanation of Solution
According to Table-1, the price charged by Country U is $175 per container. The wholesalers brought roses at auction from Countries A and H for $125 per container. The cost of production of roses in Country U is higher than that of Countries A and H. Therefore, the rest of the world has a comparative advantage in producing roses than Country U.
Comparative advantage: Comparative advantage is a term in economics that explains the ability of a country to produce an output or production of goods and services in an economy at a minimum
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Macroeconomics
- As indicated in the attached image, U.S. earnings for high- and low-skill workers as measured by educational attainment began diverging in the 1980s. The remaining questions in this problem set use the model for the labor market developed in class to walk through potential explanations for this trend. 1. Assume that there are just two types of workers, low- and high-skill. As a result, there are two labor markets: supply and demand for low-skill workers and supply and demand for high-skill workers. Using two carefully drawn labor-market figures, show that an increase in the demand for high skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers. 2. Using the same assumptions as in the previous question, use two carefully drawn labor-market figures to show that an increase in the supply of low-skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers.arrow_forwardPublished in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curves facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. a. Calculate the values of profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss, and illustrate these on the graph. b. Repeat the calculations in part a, but now assume the monopoly is able to practice perfect price discrimination.arrow_forward
- how commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
 Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





