
Concept explainers
PRACTICE PROBLEM 15.1
Show how loss of a proton can be represented using each of the three resonance structures for the arenium ion and show how each representation leads to the formation of a benzene ring with three alternating double bonds (i.e., six fully delocalized
Interpretation:
The loss of protons from three resonating structures of the areniumion, are to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Arrows present in the mechanism of the reaction indicate the electron transfer, starting from negatively charged species and ending at the positively charged species.
Electrophiles attract negatively charged species and nucleophiles attract positively charged species.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution: The loss of protons from the three resonating structures of the arenium ion are shown as follows:

Explanation of Solution
The resonating structures of the arenium ion, formed in the electrophilic substitution reaction of benzene, are shown below:

The removal of proton occurs from the carbon atom where the electrophile is attached and the bond pairs of electrons of
The removal of proton from (I) resonating structure is shown as follows:
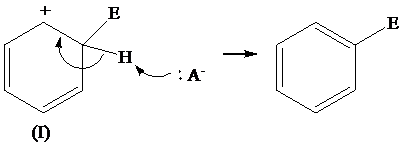
The removal of proton from (II) resonating structure is shown as follows:
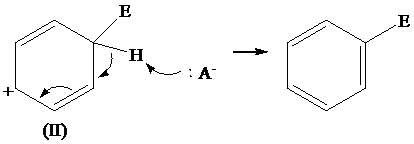
The removal of proton from (III) resonating structure is shown as follows:
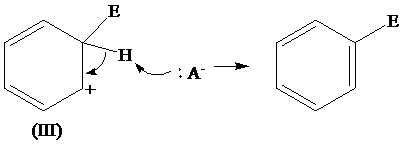
The removal of protons from the arenium ion leads to the transfer of bond pairs to the benzene ring and the delocalization of these electrons on the ring occurs, to form the final product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM. VOL.1+2-W/WILEYPLUS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
