
Interpretation:
The equilibrium concentration of iodine gases has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Equilibrium concentration: If Kc and the initial concentration for a reaction and calculate for both equilibrium concentration, and using the (ICE) chart and equilibrium constant and derived changes in respective reactants and products.
Equilibrium constant: Concentration of the products to the respective molar concentration of reactants it is called equilibrium constant. If the K value is less than one the reaction will move to the left side and the K values is higher (or) greater than one the reaction will move to the right side of reaction.
Kp and Kc: This equilibrium constants of gaseous mixtures, these difference between the two constants is that Kc is defined by molar concentrations, whereas Kp is defined by the partial pressures of the gasses inside a closed system.
Vaporized equilibrium: This conversion of liquid in gaseous phase is known as vaporization process. At starting the rate of condensation is less than the rate of evaporation but as evaporation continues the concentration of gaseous molecule in the vapour phase increase.
Answer to Problem 15.34QP
Explanation of Solution
To find: The each reactant product equilibrium concentration should be identified given the gas phase reaction.
Write and Analyze the given gas phase
The given equilibrium reaction has a homogenous process, then the equilibrium constant can also be represented by Kp, were the Kp represents partial pressure. Then the product molecule partial pressure 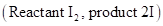 is derived in step-2.
is derived in step-2.
To find: Calculate equilibrium concentration (Kp) values for given the statement of equilibrium reaction.
Calculate and analyze the (Kp) values at
We derived here (Kp) values of (I2) dissociation reaction
First we derived the initial concentration of (I2) is
We consider the equilibrium expression in terms of the equilibrium concentration.
The obtained second (x) values are negative concentration, this physically impossible so we omitted this values. First (x) value is correct one.
The given iodine dissociation equilibrium reaction the respective reactant to give the two moles of products in the gas phase and this equilibrium reaction expression contains single conditions like gases phase, the equilibrium constant can also be represented by Kp, were the “P” partial pressure. The each molar concentration values are Kp derived given the gas phase reaction at
The molar concentration (M) values are derived given the iodine
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for General Chemistry: The Essential Concepts
- Match the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forwardCan you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward
- 2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forwardconsider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





