
(1)
Trading securities: These are short-term investments in debt and equity securities with an intention of trading and earning profits due to changes in market prices.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
To journalize: The stock investment transactions in the books of Company Z
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 4,800 shares of Company AP, at $26 per share, and a brokerage commission of $192.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| February | 14 | Investments–Company AP Stock | 124,992 | ||
| Cash | 124,992 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (1)
- Investments–Company AP Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AP’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 2,300 shares of Company
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| April | 1 | Investments–Company AR Stock | 43,792 | ||
| Cash | 43,792 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (2)
- Investments–Company AR Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AR’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 600 shares of Company AP, at $32, with a brokerage of $100.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| June | 1 | Cash | 19,100 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Investments | 3,476 | ||||
| Investments–Company AP Stock | 15,624 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Loss on Sale of Investments is a loss or expense account. Since losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company AP Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company AP for 4,200 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | |||||
| June | 27 | Cash | 840 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 840 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company AP’s stock.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
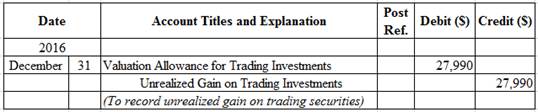
Figure(1)
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was increased (gain) to $181,150 from the cost of $153,160.
- Unrealized Gain on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and increase stockholders’ equity value, and an increase in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of the portfolio of the trading investment.
| Security | Number of Shares | Fair Market Value | = | Fair Market Value of Investment | |
| Company AP | 4,200 shares | $33.00 | = | $138,600 | |
| Company AR | 2,300 shares | 18.50 | = | 42,550 | |
| Total | $181,150 | ||||
Table (5)
Step 2: Compute the cost per share of Company AP.
Step 3: Compute the cost per share of Company AR.
Step 4: Compute the cost of the portfolio of the trading investment, as on December 31, 2016.
| Security | Number of Shares | Cost per Share | = | Cost of Investment | |
| Company AP | 4,200 shares | $26.04 | = | $109,368 | |
| Company AR | 2,300 shares | 19.04 | = | 43,792 | |
| Total | $153,160 | ||||
Table (6)
Note: Refer to Steps 3 and 4 for cost per share of Company AP and Company AR.
Step 5: Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, 2016.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Trading investments at fair value, December 31 (From Table-5) | $181,150 |
| Less: Trading investments at cost, December 31 (From Table-6) | (153,160) |
| Unrealized loss on trading investments | $27,990 |
Table (7)
Prepare journal entry for the purchase of 1,200 shares of Company AT, at $65 per share, and a brokerage commission of $120.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| March | 14 | Investments–Company AT Stock | 78,120 | ||
| Cash | 78,120 | ||||
| (To record purchase of shares for cash) | |||||
Table (8)
- Investments–Company AT Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of cash paid to purchase Company AT’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for the dividend received from Company AP for 4,200 shares.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| June | 26 | Cash | 882 | ||
| Dividend Revenue | 882 | ||||
| (To record receipt of dividend revenue) | |||||
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received on Company AP’s stock.
Prepare journal entry for sale of 480 shares of Company AT at $60, with a brokerage of $50.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2017 | |||||
| July | 30 | Cash | 28,750 | ||
| Loss on Sale of Investments | 2,498 | ||||
| Investments–Company AT Stock | 31,248 | ||||
| (To record sale of shares) | |||||
Table (10)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Loss on Sale of Investments is an expense account. Since expenses and losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Investments–Company AT Stock is an asset account. Since stock investments are sold, asset value decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Calculate the realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Step 1: Compute cash received from sale proceeds.
Step 2: Compute cost of stock investment sold.
Step 3: Compute realized gain (loss) on sale of stock.
Note: Refer to Steps 1 and 2 for value and computation of cash received and cost of stock investment sold.
Prepare adjusting entry for valuation of trading securities transaction.
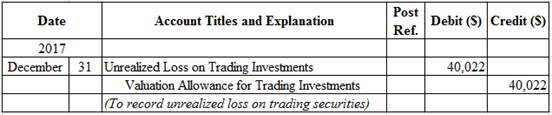
Figure (2)
- Unrealized Loss on Trading Investments is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses decrease stockholders’ equity value, and a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited.
- Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments is a contra-asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased (loss).
Working Notes:
Compute the unrealized gain (loss) as on December 31, 2017.
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Unrealized loss as on December 31, 2017 | $12,032 |
| Add: Unrealized gain as on December 31, 2016 (From Table-7) | 27,990 |
| Unrealized loss on trading investments | $40,022 |
Table (11)
(2)
To indicate: The presentation of trading investments on the current assets section of the
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet presentation:
| Company Z | ||
| Balance Sheet (Partial) | ||
| December 31, 2017 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | ||
| Trading investments (at cost) | $200,032 | |
| Less valuation allowance for trading investments | (12,032) | |
| Trading investments (at fair value) | $188,000 | |
Table (12)
(3)
To discuss: The reporting of trading investments on the financial statements
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Unrealized gain or loss is the result of change in trading investments cost and fair values, and reported as Other Revenues (Losses) on the income statement. The unrealized gain will be added to the net income and unrealized loss will be deducted from the net income. In 2016, Company Z would report $27,990 of unrealized gain as Other Income on the income statement. In the 2017, Company Z would report $40,022 of unrealized loss as Other Losses on the income statement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Accounting, Loose-Leaf Version, 26th + CengageNOWv2, 2 term Printed Access Card
- What is the net income percentage ?arrow_forwardCan you please answer the financial accounting question?arrow_forwardidentify the key factors that contributed to the collapse of Northern Rock bank. Compile documents and analysis of regulations (magazine articles, newspapers, online sources, working papers from different organizations, activity summaries, results reports, legal regulations, speeches, public statements, press conferences, etc.). Apply, in a practical and theoretical way, what has been learned in class about the financial world, regulation and risk management.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning





