
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The class of given cycloocta-1,4-diene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as isolated diene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given diene is shown in figure 1.
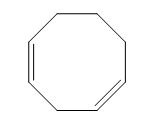
Figure 1
It is conferred from the above structure of
(b)
Interpretation: The class of given cycloocta-1,3-diene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as conjugated diene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given diene is shown in figure 2.
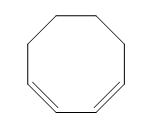
Figure 2
It is conferred from the above structure of
(c)
Interpretation: The class of given cycloocta-1,2-diene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as cumulated diene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given diene is shown in figure 3.
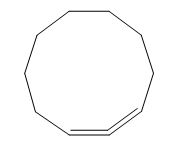
Figure 3
It is conferred from the above structure of
(d)
Interpretation: The class of given cycloocta-1,2,5,7-tetraene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as conjugated polyene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given polyene is shown in figure 4.
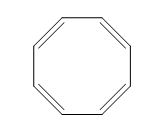
Figure 4
It is conferred from the above structure of
(e)
Interpretation: The class of given cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(e)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as conjugated polyene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given polyene is shown in figure 5.
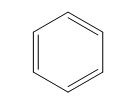
Figure 5
It is conferred from the above structure of
(f)
Interpretation: The class of given penta-1,2-4-triene as isolated, conjugated, cumulated, or a combination is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Conjugated systems have alternate single and double bonds that results in lower the energy and increase the stability of a molecule. Isolated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that comprise double bonds at the large distances separated by more than one single bond, whereas cumulated dienes or polyenes are the compounds that do not possess any single bond in between the two double bonds.
(f)
Answer to Problem 15.24SP
The given compound is classified as cumulated and conjugated polyene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given polyene is shown in figure 6.
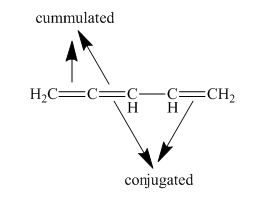
Figure 6
It is conferred from the above structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (9th Edition)
- NAME: 1. Draw the major product of the following E2 reaction. Make sure you pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. To get credit for this question, you must EXPLAIN how you got your answer using STRUCTURES and WORDS. Br NaOCH3 acetone F2 reaction To get credit for thisarrow_forward3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardPlease provide a synthesis for the Ester using proponoic acid, thank you!arrow_forward
- Please help with the curved arrow mechanism of this reaction, thank youarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 Question: Determine the regression equation (a and b coefficients) from first principlesarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forward
- Need help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- 6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forwardDraw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

