
Concept explainers
a)
Profit maximizing
a)
Explanation of Solution
Therefore, profits are,
Differentiating the profit equation with respect to
Second order condition, proves that this price and quantity maximizes the profits for a monopolist.
And profits given this price and quantity is,
b)
Nash equilibrium output for two firms operating in Cournot model. Also to compute
market output, price and firms profits.
b)
Explanation of Solution
From the demand function, we get,
Also,
So, profit for the firm 1 ,
Differentiating with respect to
And similarly, profit equation of the firm 2 reveals,
Solving 1 and 2 we get,
Market output will be,
And market price is,
So, at
The profits for firm 1 is,
The profit for firm 2 is,
c)
To find Nash
c)
Explanation of Solution
In case of a Bertrand model, undercutting of prices by both the firms leads to price becoming approximately nil in the given scenario. Hence the price will tend to zero, and quantity will become tending to 150 .
So, price
And Quantity
As there are no cost to production so firms will undercut to a level that at the end of the day both firms will be willing to provide the quantity at price 0 .
Profits for the firm
And market output is,
However the maximum demand is only for 150 units, therefore market output is 150 .
d)
To graph the demand curve for cases in parts (a), (b), (c).
d)
Explanation of Solution
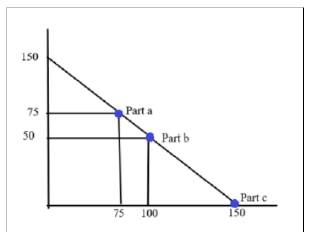
In the above diagram, Price is measured on
In part
In part c, the two firms follows Bertand
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Bundle: Microeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions, 12th + MindTap Economics, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- how commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
- Outline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning


 Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305260948Author:Irvin B. TuckerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305260948Author:Irvin B. TuckerPublisher:Cengage Learning





