
Concept explainers
Types of kinematic surveys.
Answer to Problem 15.1P
Types of kinematic
1. Real time kinematic survey
2. Post process kinematic survey
Explanation of Solution
Surveying plays is an important role in all engineering projects. By measuring the horizontal and vertical direction and angle, it is an art and science to find the relative position of various valuable points or stations on the earth's surface. We prepare plans, maps, or layout by these points.
The most effective and fastest survey technique is Kinematic surveying. The relative positioning technique is used for the observation of the carrier phase shift. The cinematic survey can provide the coordinate of the points with the fastest values while the receiver is motionless or in motion.
The two types of kinematic survey are:
1. Real time kinematic survey
The Real time kinematic survey (RTK) is also referred to as the relative positioning technique that measures the position in real time using two global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). One is placed at a static point with established coordinates and is known as the base station. It carries a large frequency radio to the second unit (known as the rover) with its raw observation and the rover carries both observations to determine a position relative to the base location in real time.
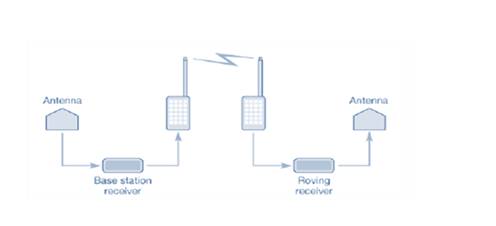
RTK surveying requires positive communication between base and rover units and works best with short baselines as the accuracy of measurements or analysis of RTK decreases as the length of the baseline increases.
2. Post process kinematic survey
A post process kinematic survey requires a base receiver that collects data at the same time rate as the rover. In the Kinematic survey of post processes, the identified coordinates should be stored in the survey controller and the observations of the raw global navigation satellite system (GNSS) are saved in the recipient until the fieldwork is completed. The data are then processed by the same software and processing techniques used in static surveys in the office.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
ELEMENTARY SURVEYING LL W/MASTERING ENGR
- nent 6-Transverse Shear & Deflection ↓ 2 of 2 -+ Automatic Zoom 4.) The built-up wooden beam shown is subjected to a vertical shear of 8 kN. Knowing the the nails are spaced longitudinally every 60 mm at A and every 25 mm at B, determine the shear force in the nails at A and B. (5 points) 50 300- 400 A 50 A C 150 B A 100 50 200 A B Dimensions in mm 5.) A 2.5 inch x 5.5 inch rectangular Southern pine section (E=1.8 x 103 ksi) is used in an 8 ft cantilever span subjected to the loads shown. Compute the deflections at point A. (4 points) Дarrow_forwardE:/school%20pack/BENG%202/EG231/STATICS/LECTURE%20NOTES/PRACTICE%20QUESTIONS/EG%20231%20Chap-5%20Practice%20Que PDF 豆豆豆豆豆豆 aw V Aa | Ask Copilot - + 4 of 8 D 3. Calculate the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shaded area. 74 mm y 3232 mm mm DELL 32 mm -x F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 prt sc F10 home end F11 F 2 W E3 $ 4 € 95 % & 6 7 8 * 00 R T Y כ 9 O Parrow_forward*8-60. The 2-in.-diameter rod is subjected to the forces shown. Determine the state of stress at point B, and show the results on a differential element located at this point. Probs. 8-59/60 B 8 in. 600 lb 12 in. 500 lb 800 lbarrow_forward
- find SFD and BMD by using slope deflection methodarrow_forwardThe following relates to Problems 4 and 5. Christchurch, New Zealand experienced a major earthquake on February 22, 2011. It destroyed 100,000 homes. Data were collected on a sample of 300 damaged homes. These data are saved in the file called CIEG315 Homework 4 data.xlsx, which is available on Canvas under Files. A subset of the data is shown in the accompanying table. Two of the variables are qualitative in nature: Wall construction and roof construction. Two of the variables are quantitative: (1) Peak ground acceleration (PGA), a measure of the intensity of ground shaking that the home experienced in the earthquake (in units of acceleration of gravity, g); (2) Damage, which indicates the amount of damage experienced in the earthquake in New Zealand dollars; and (3) Building value, the pre-earthquake value of the home in New Zealand dollars. PGA (g) Damage (NZ$) Building Value (NZ$) Wall Construction Roof Construction Property ID 1 0.645 2 0.101 141,416 2,826 253,000 B 305,000 B T 3…arrow_forwardfind SFD and BMDarrow_forward
- The data needed to answer this question is given by this link: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1vzb03U7Uvzm7X-by3OchQNwYeREzbP6Z-xzZMP2tzNw/edit?usp=sharing if it is easier to make a copy of the data because it is on view only then feel free to do so.arrow_forwardThe data needed to answer this question is given in the following link (file is on view only so if you would like to make a copy to make it easier for yourself feel free to do so) https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1aV5rsxdNjHnkeTkm5VqHzBXZgW-Ptbs3vqwk0SYiQPo/edit?usp=sharingarrow_forwardA k 000 6 ft A kips Bl D ft C C kips 10 ft 12 ft E B k/ft D E ft tarrow_forward
- H.W: show that the equations 1. (x+y)dy+(x-y)dx = 0 2. x²dy+(y²-xy)dx = 0 are homogeneous and solve:arrow_forwardH.W: Solve the differential equation y' - (1+x)(1 + y²) = 0arrow_forwardThe benchmark is 00.00. The backsights are 6.00, 9.32 and 13.75 and 14.00 The foresights are 6.00, 9.00 and 3.22. What is the height of the instrument? H.I. - 100.00 - 124.85 - 43.07- 24.85arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





