
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
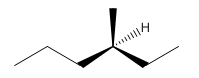
Explanation of Solution
Since alkanes consist of only carbon and hydrogen, the lowest molecular weight alkane can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, ethyl group, and propyl group.
So the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Hexane.
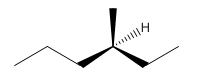
3-Methyl-Hexane.
(b)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
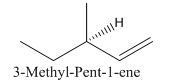
Explanation of Solution
Since alkenes consist of only carbon and hydrogen, with a double bond, the lowest molecular weight alkene can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, vinyl group, and ethyl group.
So the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Pent-1-ene.
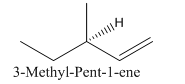
(c)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
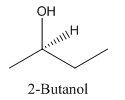
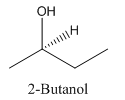
Explanation of Solution
Since alcohol consist of carbon and hydrogen and oxygen, the lowest molecular weight alcohol can have four different groups attached to it namely- hydrogen, methyl group, hydroxyl group, and ethyl group.
So, the molecule so formed is: 2-Butanol.
(d)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
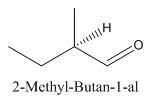
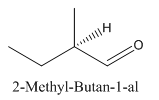
Explanation of Solution
Since
So the molecule so formed is: 2-Methyl-Butan-1-al.
(e)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
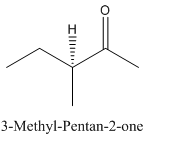
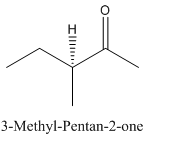
Explanation of Solution
Since
So, the molecule so formed is: 3-Methyl-Pentan-2-one.
(f)
Interpretation:
To write the structural formula of the lowest molecular weight chiral molecule of alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
A molecule is said to be chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image and if it does not possess an alternate axis of symmetry.
A carbon atom bonded in a tetrahedral structure to four different substituents in a molecule, it is called as a chiral centre or stereocentre.
If an organic molecule has more than one chiral carbon or chiral centre then the molecule may be achiral or chiral and it is depend upon whether the molecule has element of symmetry or not.
The elements of symmetry are-
- A plane of symmetry
- A centre of symmetry
- n-fold alternating axis of symmetry.
Answer to Problem 15.18P
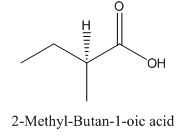
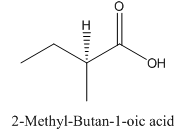
Explanation of Solution
Since
So, the molecule so formed is: 2-Methyl-Butan-1-oic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th
- Using the table of Reactants and Products provided provide the correct letter that corresponds with the Carboxylic acid that is formed in the reaction below. 6 M NaOH Acid-workup WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES A) Pool of Reagents for Part B CI B) OH C) E) CI J) racemic F) K) OH N) OH P) G) OH D) HO H) L) M) HO Q) R) CI Aarrow_forwardIn the table below, the exact chemical structures for Methyl salicylate can be represented by the letter WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES CI B) A) E) Cl racemic F) J) CI K) N) OH P) Pool of Reagents for Part B OH OH G) L) OH D) HO H) M) HO Q) R) CIarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forward
- Part I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward
- Show the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

