
a.
To calculate: The price of the coupon bond when investor purchases a 3 year bond with annual payment of $60 and par value $1000.
Introduction:
b.
To determine: The yield to maturity of the coupon bond
Introduction:
Yield to maturity: In short it is represented as YTM. YTM is supposed to be the total return which is expected from a bond when the bond is held till the maturity date.
c.
To determine: The expected realized compound rate of the coupon bond in the presence of expectations hypothesis theory.
Introduction:
Realized yield: Sometimes, the bonds are sold before its maturity date. The total return from that sort of a bond is called realized yield.
d.
To predict: The expected 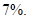
Introduction:
Expected rate of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Investments
- Security market line (SML) Assume that the risk-free rate, RF, is currently 8% and that the market return, rm, is currently 15%. a. Calculate the market risk premium. b. Given the previous data, calculate the required return on asset A having a beta of 0.8 and asset B having a beta of 1.9. a. The market risk premium is ☐ %. (Round to one decimal place.) b. If the beta of asset A is 0.8, the required return for asset A is %. (Round to one decimal place.) If the beta of asset B is 1.9, the required return for asset B is %. (Round to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardRisk and probability Micro-Pub, Inc., is considering the purchase of one of two digital cameras, R and S, each of which requires an initial investment of $4,000. Management has constructed the following table of estimates of rates of return and probabilities for pessimistic, most likely, and optimistic results: a. Determine the range for the rate of return for each of the two cameras. b. Determine the value of the expected return for each camera. c. Which camera purchase is riskier? Why? a. The range for the rate of return for camera R is %. (Round to the nearest whole number.) The range for the rate of return for camera S is ☐ %. (Round to the nearest whole number.) b. The value of the expected return for camera R is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The value of the expected return for camera S is %. (Round to two decimal places.) c. Which camera purchase is riskier? Why? (Select from the drop-down menus.) The purchase of is riskier because it has a range for the rate of return.arrow_forward4 analysts covered the stock of Flooring Chemical. One forecasts a 5% return for the coming year. The second expects the return to be -4%. The third predicts a return of 9%. The fourth expects a 1% return in the coming year. You are relatively confident that the return will be positive but not large, so you arbitrarily assign probabilities of being correct of 33%, 7%, 18%, and 42%, respectively to the analysts' forecasts. Given these probabilities, what is Flooring Chemical's expected return for the coming year?arrow_forward
- Why you would be a quality recipient of the Linda K Crandall Nutrition Scholarship.arrow_forwardIf Image is blurr then tell me . please comment below i will write values. if you answer with incorrect values i will give unhelpful confirm.arrow_forwardNormal probability distribution Assuming that the rates of return associated with a given asset investment are normally distributed; that the expected return, r, is 17.2%; and that the coefficient of variation, CV, is 0.86, answer the following questions: a. Find the standard deviation of returns, or. b. Calculate the range of expected return outcomes associated with the following probabilities of occurrence: (1) 68%, (2) 95%, (3) 99%. a. The standard deviation of returns, or, is %. (Round to three decimal places.) b. (1) The lowest possible expected return associated with the 68% probability of occurrence is %. (Round to two decimal places.) The highest possible expected return associated with the 68% probability of occurrence is decimal places.) (2) The lowest possible expected return associated with the 95% probability of occurrence is decimal places.) %. (Round to two %. (Round to two The highest possible expected return associated with the 95% probability of occurrence is decimal…arrow_forward
- General Finance Please don't answer i posted blurred image mistakely. please comment below i will write values. if you answer with incorrect values i will give unhelpful confirm.arrow_forwardno ai Please don't answer i posted blurred image mistakely. please comment below i will write values. if you answer with incorrect values i will give unhelpful confirm.arrow_forwardFinan Please don't answer i posted blurred image mistakely. please comment below i will write values. if you answer with incorrect values i will give unhelpful confirm.arrow_forward
- see itPlease don't answer i posted blurred image mistakely. please comment below i will write values. if you answer with incorrect values i will give unhelpful confirm.arrow_forwardNo use ai. if image is blurr or data is not showing properly then dont answer i will sure deslike. please comment i will write values.arrow_forwardDon't use ai. if image is blurr or data is not showing properly then dont answer i will sure deslike. please comment i will write values.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

