
(a)
Effects of higher interest rate on households and firm behavior.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
If the Federal Reserve System rises the interest rates, then the borrowing of items become more costly. Therefore, households will reduce the purchase of durable goods such as auto mobiles and houses. So when the rate of interest rises, consumers spending on durable goods reduce.
In the case of firms, when the rate of interest rises, cost of capital becomes higher. Therefore firms will reduce the spending on investment. So when the rate of interest rises, investment will reduce.
Rate of interest: The rate of interest refers to that percentage at which the money is borrowed or is taken as a loan. The amount to be paid as interest is calculated on this given percentage.
(b)
Effects of higher interest rate on bonds.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
When the rate of interest rises by the Federal Reserve, will fall the existing values of fixed rate bonds. Because, in the case of fixed rate bonds, if the holder paying 7% for the next 10 years is become simply worth less if the potential buyers can now earn 8% by buying a new bond. That’s why, the higher interest rate would decrease the value of existing fixed rate bonds held by the public.
Bonds: Bond refers to the securities, which are traded in the public to raise the capital when needed. It is an investment with a fixed income, where an investor gives money to an entity or individual for a specified period of time at a fixed rate.
(c)
Wealth effect of higher interest rate on consumption.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The below figure illustrates the changes in aggregative demand
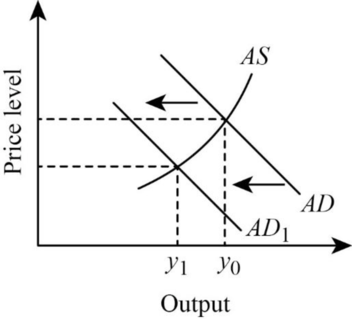
In the figure, vertical axis shows the output and the horizontal axis shows the price level. When the consumption falls the AD curve will shift from AD to AD1. As a result, price level falls and the quantity reduces from Y0 to Y1.
When the rate of interest rises, the cost of borrowing become higher. And also, the investment rate reduces because of the higher rate of capitals. These factors will reduce the wealth of an economy. When wealth reduces, consumers will spend less and they become worse off. In short, higher interest rate will reduce the spending of consumers. Therefore, the aggregative demand curve will shift the left wards. This is higher than the direct effect on investment.
Wealth effect: Wealth effect refers to the effect of a change in the price that has on the wealth of the individual.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write explanation in paragraphs and if you use currency use USD currency: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forwardZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 4. Draw a Keynesian AD curve in P – Y space and list the shift factors that will shift theKeynesian AD curve upward and to the right. Draw a separate Classical AD curve in P – Yspace and list the shift factors that will shift the Classical AD curve upward and to the right.arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 15. How is the Keynesian expenditure multiplier implicit in the Keynesian version of the AD/ASmodel? Explain and show mathematically. (note: this is a tough one)arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 13. What would happen to the net exports function in Europe and the US respectively if thedemand for dollars rises worldwide? Explain why.arrow_forward20. Given the mathematical model below, solve for the expenditure multiplier for a) government spending, G; and b) for consumer taxes, T. (medium difficulty) Y=C+I+G C=Co+b(Y-T) 1 = 10 T=To+tY G = Go+gYarrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 11. What exactly is a rectangular hyperbola and what relevance is it to classical economics?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 9. Explain the difference between absolute and comparative advantage in a family setting, i.e.using parents and children. What can we glean from knowing about comparative andabsolute advantages?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 18. Explain why most economists believe it is absolutely necessary to allow free trade in aneconomy. Why is it harmful (under most circumstances) to have tariffs and trade barriers?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





