
(a)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
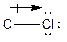
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
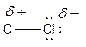
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (a)
(b)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
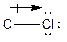
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
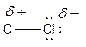
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (b)
(c)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
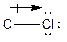
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
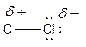
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (c)
(d)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
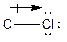
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
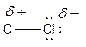
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (d)
(e)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
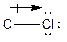
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
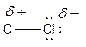
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (e)
(f)
Interpretation: For the given set of compounds the location of the partial charges that results due to inductive effect should be identified.
Concept Introduction: The nature of the bond depends on the electronegativity values of the shared electron pair of the involved atoms.
Electronegativity is the important chemical property of the elements in the periodic table. It is the tendency of the atoms to attract electrons towards it.
If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.5 and 1.7, a bond between two different electronegative atoms becomes polar. Most electronegative atoms get partial negative charge because they attract electrons from least electronegative atom towards it. The least electronegative atoms get partial positive charge because it loses electrons towards most electronegative atoms.
The process of the attraction of electrons from electron-donating atoms (less electronegative atoms) towards electron-withdrawing atoms (most electronegative atoms) is called induction. It can be represented by the following arrow:
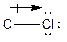
Here, chlorine atom has more electronegative than carbon atom. Chlorine attracts electrons towards it. This difference in electron density is called inductive effect. It can be shown by Greek symbol delta (
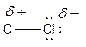
To find: Categorize all polar covalent bonds in the given compound (f)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. and two equivalents of CH2=O draw structure ...arrow_forwardH-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





