
Organic Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780321803221
Author: Paula Y. Bruice
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.21, Problem 39P
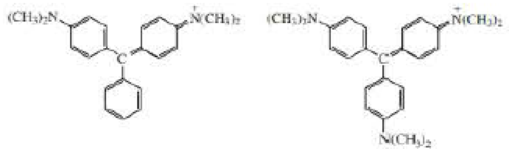
a. At pH = 7 one of the ions shown here is purple and the other is blue. Which is which? (Hint: refer to the color spectrum in figure 13.8 on page 584.)
b. What would be the difference in the colors or the compounds at pH = 3?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A solution of 14 g of a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte compound in 0.10 kg of benzene boils at
81.7°C. If the BP of pure benzene is 80.2°C and the K, of benzene is 2.53°C/m, calculate the
molar mass of the unknown compound. AT₁ = Km (14)
Please help me answer the following questions. My answers weren't good enough. Need to know whyy the following chemicals were not used in this experiment related to the melting points and kf values. For lab notebook not a graded assignments.
Draw the arrow pushing reaction mechanism. DO NOT ANSWER IF YOU WONT DRAW IT. Do not use chat gpt.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 14.1 - Which of the following fragments produced in a...Ch. 14.2 - What distinguishes the mass spectrum of...Ch. 14.2 - What is the most likely m/z value for the base...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 14.3 - If a compound has a molecular ion with an...Ch. 14.3 - a. Suggest possible molecular formulas for a...Ch. 14.3 - Identify the hydrocarbon that has a molecular ion...Ch. 14.4 - Predict the relative intensities of the molecular...Ch. 14.5 - Which molecular formula has an exact molecular...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 14.6 - Sketch the mass spectrum expected for...Ch. 14.6 - The mass spectra of 1-methoxybutane,...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 14PCh. 14.6 - Identify the ketones responsible for the mass...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 16PCh. 14.6 - Using curved arrows, show the principal fragments...Ch. 14.6 - The reaction of (Z)-2-pentene with water and a...Ch. 14.9 - Prob. 19PCh. 14.9 - Prob. 20PCh. 14.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 14.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 14.14 - Which occur at a larger wavenumber: a. the C O...Ch. 14.14 - Prob. 24PCh. 14.14 - Prob. 25PCh. 14.14 - Rank the following compounds from highest...Ch. 14.14 - Which shows an O H stretch at a larger...Ch. 14.15 - Prob. 28PCh. 14.15 - a. An oxygen-containing compound shows an...Ch. 14.15 - Prob. 30PCh. 14.15 - For each of the following pair of compounds, name...Ch. 14.16 - Which of the following compounds has a vibration...Ch. 14.16 - Prob. 33PCh. 14.17 - A compound with molecular formula C4H6O gives the...Ch. 14.19 - Prob. 35PCh. 14.19 - Prob. 36PCh. 14.20 - Predict the max of the following compound:Ch. 14.20 - Prob. 38PCh. 14.21 - a. At pH = 7 one of the ions shown here is purple...Ch. 14.21 - Prob. 40PCh. 14.22 - Prob. 41PCh. 14.22 - Prob. 42PCh. 14 - In the mass spectrum of the following compounds,...Ch. 14 - Prob. 44PCh. 14 - For each of the following pairs of compounds,...Ch. 14 - Draw structures for a saturated hydrocarbon that...Ch. 14 - a. How could you use IR spectroscopy to determine...Ch. 14 - Assuming that the force constant is approximately...Ch. 14 - In the following boxes, list the types of bonds...Ch. 14 - A mass spectrum shows significant peaks at m/z. =...Ch. 14 - Prob. 51PCh. 14 - Prob. 52PCh. 14 - Prob. 53PCh. 14 - How can you use UV spectroscopy to distinguish...Ch. 14 - Rank the following compounds from highest...Ch. 14 - Rank the following compounds from highest...Ch. 14 - What peaks in their mass spectra can be used to...Ch. 14 - Each of the IR spectra shown below is accompanied...Ch. 14 - Prob. 59PCh. 14 - Prob. 60PCh. 14 - How can IR spectroscopy distinguish between...Ch. 14 - 62. Draw the structure of a carboxylic acid that...Ch. 14 - Prob. 63PCh. 14 - Give approximate wavenumbers for the major...Ch. 14 - Prob. 65PCh. 14 - Prob. 66PCh. 14 - Prob. 67PCh. 14 - The IR spectrum of a compound with molecular...Ch. 14 - Which one of the following live compounds produced...Ch. 14 - Prob. 70PCh. 14 - Phenolphthalein is an acid-base indicator. In...Ch. 14 - Which one of the following five compounds produced...Ch. 14 - The IR and mass spectra for three different...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete the following esterification reaction by drawing the structural formula of the product formed. HOH HO i catalyst catalyst OH HO (product has rum flavor) (product has orange flavor)arrow_forwardThe statements in the tables below are about two different chemical equilibria. The symbols have their usual meaning, for example AG stands for the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction and K stands for the equilibrium constant. In each table, there may be one statement that is faise because it contradicts the other three statements. If you find a false statement, check the box next to t Otherwise, check the "no false statements" box under the table. statement false? AG"1 no false statements: statement false? AG-0 0 InK-0 0 K-1 0 AH-TAS no false statements 2arrow_forwardComplete the following esterification reactions by drawing the line formulas of the carboxylic acid and alcohol required to form the ester shown. catalyst catalyst catalyst apricot fragrancearrow_forward
- Show the saponification products of the following ester: You don't need to draw in the Na+ cation. catalyst, A catalyst, A catalyst, Aarrow_forwardWhat would happen if the carboxylic acid and alcohol groups were on the same molecule? In essence, the molecule reacts with itself. Draw the structure of the products formed in this manner using the reactants below. If two functional groups interact with one another on the same molecule, this is called an “intramolecular" (within one) rather than "intermolecular" (between two or more) attack. OH OH catalyst OH HO catalyst catalyst HO OHarrow_forwardQ3: Write in the starting alkyl bromide used to form the following products. Include any reactants, reagents, and solvents over the reaction arrow. If more than one step is required, denote separate steps by using 1), 2), 3), etc. H OH racemic OH OH 5 racemicarrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure of the SO3-O(CH3)2 complex shown in the bottom right of slide 2in lecture 3-3 (“Me” means a CH3 group) – include all valence electron pairs and formal charges.From this structure, should the complex be a stable molecule? Explain.arrow_forwardPredict all organic product(s), including stereoisomers when applicable.arrow_forwardQ5: Propose a reasonable synthesis for the following decalin derivative. using only decalin and alkanes of 3 or fewer carbons. Decalin H3C HO க CH3arrow_forward
- 2Helparrow_forwardplease add appropriate arrows, and tell me clearly where to add arrows, or draw itarrow_forwardWhat I Have Learned Directions: Given the following reaction and the stress applied in each reaction, answer the question below. A. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) Stress applied: Decreasing the pressure 1. What is the Keq expression? 2. What will be the effect in the number of moles of HCl(g)? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? B. Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) + heat 53 Fe(s) + 4 H₂O(g) Stress applied: Increasing the temperature 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the volume of water vapor collected? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? C. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + heat Stress applied: Increasing the volume of the container 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the amount of H₂O? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Acid-base Theories and Conjugate Acid-base Pairs; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hQLWYmAFo3E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
COMPLEXOMETRIC TITRATION; Author: Pikai Pharmacy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EQxvY6a42Dw;License: Standard Youtube License