
Sub part (a):
Diminishing marginal utility .
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The utility function is
Figure 1 illustrates the diminishing marginal utility.
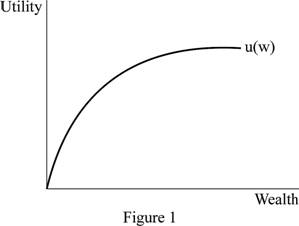
In Figure 1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity of wealth and the vertical axis measures the utility. When the quantity of wealth increases then the additional utility decreases.
Concept introduction:
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub Part (b):
Expected value.
Sub Part (b):
Explanation of Solution
Since the value is sure, the probability is 1. Expected value of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected value of A is $4,000,000.
Expected value of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected value of B is $4,200,000. Thus, B offers higher value.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (c):
Expected utility.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Expected utility of A can be calculated as follows:
Expected utility of A is $2,000.
Expected utility of B can be calculated as follows.
Expected utility of B is $1,800.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Sub part (d):
greaterExpected utility.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
Since the expected utility from B is greater than A, the person should select A.
Concept introduction:
Risk is the future uncertainty about deviation from expected earnings or expected outcome. Risk measures the uncertainty situation that an investor is willing to take to realize a gain from an investment.
Risk aversion: Risk aversion can be defined as it is a dislike of an uncertainty.
Marginal utility: Marginal utility refers to the additional units of satisfaction derived from one more additional unit of goods and services.
Diminishing marginal utility: Diminishing marginal utility refers to a decrease in the additional satisfaction as a result of increasing the consumption.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- How does the change in consumer and producer surplus compare with the tax revenue?arrow_forwardConsidering the following supply and demand equations: Qs=3P-1 Qd=-2P+9 dPdt=0.5(Qd-Qs) Find the expressions: P(t), Qs(t) and Qd(t). When P(0)=1, is the system stable or unstable? If the constant for the change of excess of demand changes to 0.6, this is: dPdt=0.6(Qd-Qs) do P(t), Qs(t) and Qd(t) remain the same when P(0)=1?arrow_forwardConsider the following supply and demand schedule of wooden tables.a. Draw the corresponding graphs for supply and demand. b. Using the data, obtain the corresponding supply and demand functions. c. Find the market-clearing price and quantity. Price (Thousands USD) Supply Demand2 96 1104 196 1906 296 270 8 396 35010 496 43012 596 51014 696 59016 796 67018 896 75020 996 830arrow_forward
- What happens to consumer surplus and producer surplus when the sale of a good is taxed?arrow_forwardEconomics Grade 3 CONDUCT RESEARCH ON (the various) MARKET STRUCTURES Research Project/May Explain the concept market structure and explain why there are perfect and imperfect market structures. (5) • Provide reasons as to why the taxi industry is regarded as operating in a monopolistic competitive structure. (10) • How do monopolies impact consumers and the economy. (10) • Use graph(s) to explain the long run equilibrium price and output in a perfect market. (10) • Evaluate the effectiveness of South Africa's competition policy in curbing anticompetitive tendencies in the market. Make use of practical examples. (10) GRAND TOTAL:50 Please turn Copyrightarrow_forwardUGD KCQ 2: Microeconomic Essentials (page 11 of 20) - Google Chrome mancosaconnect.ac.za/mod/quiz/attempt.php?attempt=1958913&cmid=436375&page=10 MANCOSA Microeconomic Essentials Jan25 Y1 S1 Back Refer to the diagram below to answer the question that follows: Price PH P1 D₁ ㅁ X Quiz navigation 3 4 5 6 Time left 0:58:34 1 2 Question 11 7 8 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 13 33 14 S₁ Flag question Q Q1 Quantity Which of the following may result in a shift of the supply curve from S to S1? OA. An increase in price of the good. B. An increase in wages. O C. A decrease in price of the good. O D. An improvement in the technique of production. https://mancosaconnect.ac.za/mod/quiz/attempt.php?attempt=1958913&cmid=436375&page=10#question-2064270-11 19 20 6 10 10 11 12 15 Question 11- Not yet answered Finish attempt... 7:31 PMarrow_forward
- Euros per U.S. Doler Consider the model below, showing the supply and demand curves for the exchange market of U.S. Dollars and Euros. If the inflation rate in the U.S. increases (and in the European Union stays the same), how will that change the original equilibrium shown in the graph? 1.10- 1.00- 0.90 0.80- 0.70 0.60 0.50- 0.40- 0.30 0.20 E 4.7 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 Quantity of U.S. Dollars traded for Euros (trillionsday) O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknown. O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate increases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknownarrow_forwardIf the US Federal Reserve increases interests on reserves, how will that change the original equilibrium shown in the graph? Euros par US alar 1.10 1.00 0.90- E 0.80- 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40- 0.30 0.20 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 Quantity of US Dollars traded for Euros (trillions/day) It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknown. O It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate increases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknown O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. Question 22 5 ptsarrow_forward1. Based on the video, answer the following questions. • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? Based on the video. • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? Based on the video. • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? Based on the video. • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? Based on the video. • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Based on the video. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forward
- 1. Answer the following questions based on the reference video below: • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Discuss. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forwardExplain the importance of differential calculus within economics and business analysis. Provide three refernces with your answer. They can be from websites or a journals.arrow_forwardAnalyze the graph below, showing the Gross Federal Debt as a percentage of GDP for the United States (1939-2019). Which of the following is correct? FRED Gross Federal Debt as Percent of Gross Domestic Product Percent of GDP 120 110 100 60 50 40 90 30 1940 1950 1960 1970 Shaded areas indicate US recessions 1980 1990 2000 2010 1000 Sources: OMD, St. Louis Fed myfred/g/U In 2019, the Federal Government of the United States had an accumulated debt/GDP higher than 100%, meaning that the amount of debt accumulated over time is higher than the value of all goods and services produced in that year. The debt/GDP is always positive during this period, so the Federal Government of the United States incurred in budget deficits every year since 1939. From the mid-40s until the mid-70s, the debt/DGP was decreasing, meaning that the Federal Government of the United States was running a budget surplus every year during those three decades. During the second half of the 1970s, the Federal Government…arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





