
To identify: The expected
Introduction:
Return on Equity:
The return, which is generated on the equity that is invested by the stockholders is known as return on equity.
Explanation of Solution
The capital ratio at 0% and none interest rate.
Compute the expected return on equity.
State-1
Compute the net income.
Given,
The probability is 0.2.
The EBIT is $4,200,000.
Formula to calculate the net income,
Where,
- EBIT is earning before interest and tax.
- I is interest.
- T is tax rate.
Substitute $4,200,000 for EBIT, 0 for I and 0.40 for T.
The net income of state 1 is $2,520,000.
Compute the return on equity of state 1.
The net income is $2,520,000. (Calculated above)
The equity is $14,000,000. (Given)
Formula to calculate the return on equity,
Substitute $2,520,000 for net income and $14,000,000 for equity.
The return on equity of state 1 is 18%.
State-2
Compute the net income.
Given,
The probability is 0.5.
The EBIT is $2,800,000.
Formula to calculate the net income,
Where,
- EBIT is earning before interest and tax.
- I is interest.
- T is tax rate.
Substitute $2,800,000 for EBIT, 0 for I and 0.40 for T.
The net income of state 2 is $1,680,000.
Compute the return on equity of state 2.
The net income is $1,680,000. (Calculated above)
The equity is $14,000,000. (Given)
Formula to calculate the return on equity,
Substitute $1,680,000 for net income and $14,000,000 for equity.
The return on equity on state 2 is 12%.
State-3
Compute the net income.
Given,
The probability is 0.3.
The EBIT is $700,000.
Formula to calculate the net income,
Where,
- EBIT is earning before interest and tax.
- I is interest.
- T is tax rate.
Substitute $700,000 for EBIT, 0 for I and 0.40 for T.
The net income of state 3 is $420,000.
Compute the return on equity of state 3.
The net income is $420,000. (Calculated above)
The equity is $14,000,000. (Given)
Formula to calculate the return on equity,
Substitute $420,000 for net income and $14,000,000 for equity.
The return on equity on state 3 is 3%.
Compute the expected return on equity of 3 states.
The return on equity of state 1 is18%. (Calculated in equation (1))
The return on equity of state 2 is 12%. (Calculated in equation (2))
The return on equity of state 3 is 3%. (Calculated in equation (3))
The probability of state 1 is 0.2. (Given)
The probability of state 2 is 0.5. (Given)
The probability of state 3 is 0.3. (Given)
Formula to calculate the expected return on earnings,
Substitute 0.2, 0.5 and 0.3 for probability and 18%, 12% and 3% for return on earnings.
The expected return on earnings is 10.50%.
Compute the standard deviation.
| State | Probability |
Return on Equity (ROE) |
Expected Return on Equity (EROE) |
Deviation
|
| 1 | 0.2 | 18% | 10.50% | 11.25% |
| 2 | 0.5 | 12% | 10.50% | 1.125% |
| 3 | 0.3 | 3% | 10.50% | 16.88% |
| Variance | 29.25% |
Table (1)
The variance is 29.25%. (Calculated above)
Formula to calculate the standard deviation,
Substitute 29.25% for variance.
The standard deviation is 5.408%.
Compute the coefficient of deviation.
The standard deviation is 5.408%.
The expected return on equity is 10.50%.
Formula to calculate the coefficient of variance,
Where,
- EORE is expected return on equity.
Substitute 5.408% for standard deviation and 10.25% for EROE.
The coefficient of variance is 0.515.
The capital ratio at 10% and interest rateis 9%.
Compute the expected return on equity
Statement to show the computation of return on equity of each state
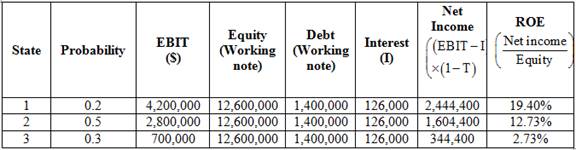
Table (2)
Compute expected return on equity of 3 states.
The return on equity of state 1 is 19.40%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 2 is 12.73%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 3 is 2.73%. (Calculated above)
The probability of state 1 is 0.2. (Given)
The probability of state 2 is 0.5. (Given)
The probability of state 3 is 0.3. (Given)
Formula to calculate the expected return on earnings,
Substitute 0.2, 0.5 and 0.3 for probability and 19.40%, 12.73% and 2.73% for return on earnings.
The expected return on earnings is 11.07%.
Compute the standard deviation
| State | Probability |
Return on Equity (ROE) |
Expected Return on Equity (EROE) |
Deviation
|
| 1 | 0.2 | 19.40% | 11.07% | 13.88% |
| 2 | 0.5 | 12.73% | 11.07% | 1.378% |
| 3 | 0.3 | 2.73% | 11.07% | 20.87% |
| Variance | 36.128% |
Table 3
The variance is 36.128%. (Calculated above)
Formula to calculate the standard deviation,
Substitute 36.128% for variance.
The standard deviation is 6.01%.
Compute the coefficient of deviation.
The standard deviation is 6.01%.
The expected return on equity is 11.07%.
Formula to calculate the coefficient of variance,
Where,
- EORE is expected return on equity.
Substitute 6.01% for standard deviation and 11.07% for EROE.
The coefficient of variance is 0.543.
The capital ratio at 50% and none interest rate is 11%.
Compute the expected return on equity
Statement to show the computation of return on equity of each state
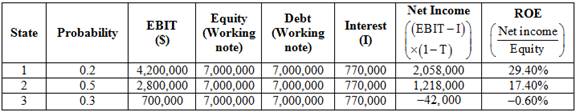
Table (4)
Compute expected return on equity of 3 states.
The return on equity of state 1 is 29.40%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 2 is 17.40%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 3 is
The probability of state 1 is 0.2. (Given)
The probability of state 2 is 0.5. (Given)
The probability of state 3 is 0.3. (Given)
Formula to calculate the expected return on earnings,
Substitute 0.2, 0.5 and 0.3 for probability and 29.40%, 17.40% and
The expected return on earnings is 14.40%.
Compute the standard deviation.
| State | Probability | Return on Equity (ROE) | Expected Return on Equity (EROE) |
Deviation
|
| 1 | 0.2 | 29.40% | 14.40% | 45% |
| 2 | 0.5 | 17.40% | 14.40% | 4.5% |
| 3 | 0.3 |
| 14.40% | 67.5% |
| Variance | 117% |
Table (5)
The variance is 117%. (Calculated above)
Formula to calculate the standard deviation,
Substitute 117% for variance.
The standard deviation is 10.82%.
Compute the coefficient of deviation.
The standard deviation is 10.82%.
The expected return on equity is 14.40%.
Formula to calculate the coefficient of variance,
Where,
- EORE is expected return on equity.
Substitute 10.82% for standard deviation and 14.40% for EROE.
The coefficient of variance is 0.751.
The capital ratio at 60% and none interest rate is 14%.
Compute the expected return on equity.
Statement to show the computation of return on equity of each state,
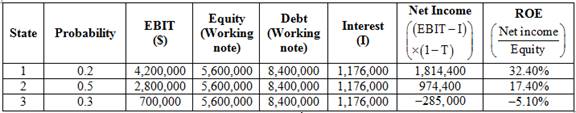
Table (6)
Computation of expected return on equity of 3 states
The return on equity of state 1 is 32.40%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 2 is 17.40%. (Calculated above)
The return on equity of state 3 is
The probability of state 1 is 0.2. (Given)
The probability of state 2 is 0.5. (Given)
The probability of state 3 is 0.3. (Given)
Formula to calculate the expected return on earnings,
Substitute 0.2, 0.5 and 0.3 for probability and 32.40%, 17.40% and
The expected return on earnings is 13.65%.
Compute the standard deviation.
| State | Probability | Return on Equity (ROE) | Expected Return on Equity (EROE) |
Deviation
|
| 1 | 0.2 | 32.40% | 13.65% | 70.31% |
| 2 | 0.5 | 17.40% | 13.65% | 7.031% |
| 3 | 0.3 |
| 13.65% | 105.47% |
| Variance | 182.8% |
Table (7)
The variance is 182.8%. (Calculated above)
Formula to calculate the standard deviation,
Substitute 182.8% for variance.
The standard deviation is 13.521%.
Compute the coefficient of deviation.
The standard deviation is 13.521%.
The expected return on equity is 13.65%.
Formula to calculate the coefficient of variance,
Where,
- EORE is expected return on equity.
Substitute 13.521% for standard deviation and 13.65% for EROE.
The coefficient of variance is 0.99.
Working note:
Compute the value of debt and equity at capital ratio of 10% and interest rate of 9%.
Given,
Thetotal capital structure is 14 million.
The capital structure is 10.
Compute the debt value,
The debt is $1,400,000.
Compute the equity
The total capital is $14,000,000. (Given)
The debt is $1,400,000. (Calculated)
Compute the equity value,
The equity is $12,600,000.
Compute the interest on debt.
The interest rate is 9% or 0.09. (Given)
The debt is $1,400,000. (Calculated)
Compute the interest on debt,
The interest on debt is $126,000.
Compute the value of debt and equity at capital ratio of 50% and interest rate of 11%.
Given,
The total capital structure is 14 million.
The capital structure is 50.
Compute the debt value,
The debt is $7,000,000.
Compute the equity.
The total capital is $14,000,000. (Given)
The debt is $7,000,000. (Calculated)
Compute the equity value,
The equity is $7,000,000.
Compute the interest on debt.
The interest rate is 11% or 0.11. (Given)
The debt is $7,000,000. (Calculated)
Compute the interest on debt,
The interest on debt is $770,000.
Compute the value of debt and equity at capital ratio of 60% and interest rate of 14%.
Given,
The total capital structure is 14 million.
The capital structure is 60.
Compute the debt value,
The debt is $8,400,000.
Compute the equity.
The total capital is $14,000,000. (Given)
The debt is $8,400,000. (Calculated)
Compute the equity value,
The equity is $5,600,000.
Compute the interest on debt.
The interest rate is 11% or 0.11. (Given)
The debt is $8,400,000. (Calculated)
Compute the interest on debt,
The interest on debt is $1,176,000.
Hence, the ROE, standard deviation, and coefficient of varianceat 0% capital ratio are 10.50%, 5.408% and 0.515.
The ROE, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance at 10% capital ratio and 9% interest are 11.07%, 6.01% and 0.543.
The ROE, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance at 50% capital ratio and 11% interest are 14.40%, 10.82% and 0.751.
The ROE, standard deviation, and coefficient of variance at 60% capital ratio and 14% interest are 13.65%, 13.52% and 0.099.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
- The beta of a stock measures: A. Total riskB. Unsystematic riskC. Systematic riskD. Credit riskarrow_forwardGive answer The beta of a stock measures: A. Total riskB. Unsystematic riskC. Systematic riskD. Credit riskarrow_forwardI need help A bond with a face value of $1,000 and a 10% coupon pays: A. $1,000 annuallyB. $10 annuallyC. $100 annuallyD. $110 annuallyarrow_forward
- I want the correct answer with financial accounting questionarrow_forwardAs a finance manager for a major utility company. Thinking about some of the capital budgeting techniques that I might use for some upcoming projects. I need help Discussing at least 2 capital budgeting techniques and how my company can benefit from the use of these tools.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


