
Measures of liquidity, solvency, and profitability
The comparative financial statements of Marshall Inc. are as follows. The market price of Marshall common stock was $82.60 on December 31, 20Y2.
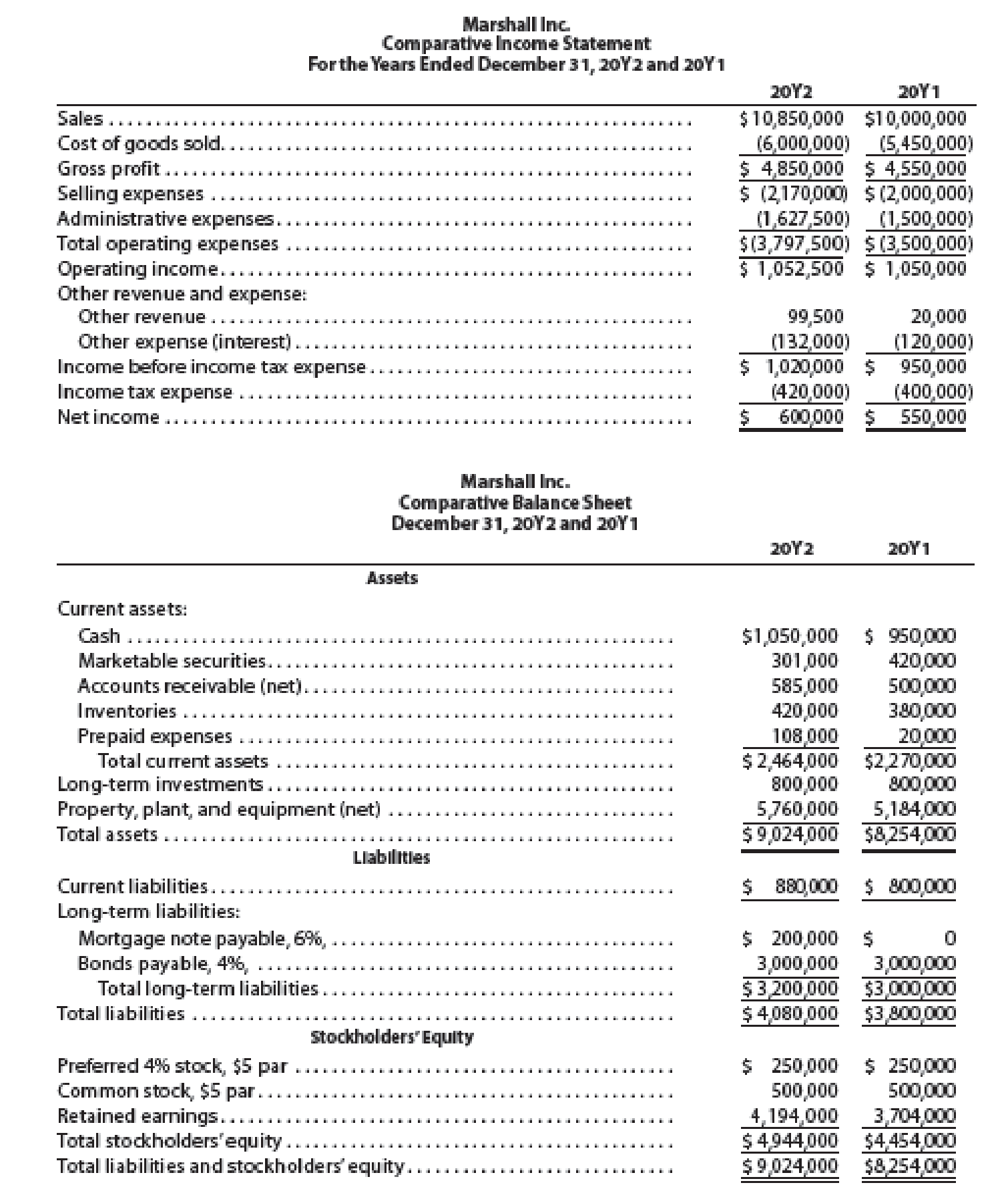
Instructions
Determine the following measures for 20Y2 (round to one decimal place, including percentages, except for per-share amounts):
- 1.
Working capital - 2.
Current ratio - 3. Quick ratio
- 4.
Accounts receivable turnover - 5. Number of days’ sales in receivables
- 6. Inventory turnover
- 7. Number of days’ sales in inventory
- 8. Ratio of fixed assets to long-term liabilities
- 9. Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity
- 10. Times interest earned
- 11. Asset turnover
- 12. Return on total assets
- 13. Return on stockholders’ equity
- 14. Return on common stockholders’ equity
- 15. Earnings per share on common stock
- 16. Price-earnings ratio
- 17. Dividends per share of common stock
- 18. Dividend yield
1 (1)
Determine the working capital.
Explanation of Solution
Financial Ratios: Financial ratios are the metrics used to evaluate the capabilities, profitability, and overall performance of a company.
.Working capital
Working capital is determined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
Formula:
1(2)
Determine the current ratio of M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio
Current ratio is used to determine the relationship between current assets and current liabilities. The ideal current ratio is 2:1. Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments, net, accounts and notes receivables, net, inventories, and prepaid expenses and other current assets. Current liabilities include short-term obligations and accounts payable.
Formula:
1 (3)
Determine the quick ratio of M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
.Quick ratio
Acid-Test Ratio is the ratio denotes that this ratio is a more rigorous test of solvency than the current ratio. It is determined by dividing quick assets and current liabilities. The acceptable acid-test ratio is 0.90 to 1.00. It is referred as quick ratio. Use the following formula to determine the acid-test ratio:
1 (4)
Determine accounts receivable turnover for M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
Accounts receivable turnover
Accounts receivables turnover ratio is mainly used to evaluate the collection process efficiency. It helps the company to know the number of times the accounts receivable is collected in a particular time period. Main purpose of accounts receivable turnover ratio is to manage the working capital of the company. This ratio is determined by dividing credit sales and sales return.
Formula:
Average accounts receivable is determined as follows:
1(5)
Determine number of days’ sales in receivables of M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
Number of days’ sales in receivables
Number of days’ sales in receivables is used to determine the number of days a particular company takes to collect accounts receivables.
Formula:
Average daily sales are determined by dividing sales by 365 days.
1 (6)
Determine inventory turnover ratio for M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
Inventory turnover ratio is used to determine the number of times inventory used or sold during the particular accounting period.
Formula:
Average inventory is determined as below:
1(7)
Determine number of days’ sales in inventory ratio of M Incorporation.
Explanation of Solution
Number of days sales in inventory ratio
Number of days’ sales in inventory is determined as the number of days a particular company takes to make sales of the inventory available with them.
Formula:
Average daily cost of goods sold are determined by dividing cost of goods sold by 365 days. Thus, average daily cost of goods sold are determined as follows:
1 (8)
Determine ratio of fixed assets to long-term liabilities.
Explanation of Solution
Ratio of fixed assets to long-term liabilities is determined by dividing fixed assets and long-term liabilities.
Formula:
1 (9)
Determine ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity.
Explanation of Solution
Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity
Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity is determined by dividing liabilities and stockholders’ equity.
Formula:
1 (10)
Determine times interest earned ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio
Times interest earned ratio quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense. First, determine the sum of income before income tax and interest expense. Then, divide the sum by interest expense.
Formula:
1 (11)
Determine asset turnover ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Asset turnover ratio
Asset turnover ratio is used to determine the asset’s efficiency towards sales.
Formula:
Working notes for average total assets are as follows:
1 (12)
Determine return on total assets.
Explanation of Solution
Return on total assets
Return on assets determines the particular company’s overall earning power. It is determined by dividing sum of net income and interest expense and average total assets.
Formula:
1 (13)
Determine return on stockholders’ equity.
Explanation of Solution
Return on stockholders’ equity
Rate of return on stockholders’ equity is used to determine the relationship between the net income and the average equity that are invested in the company.
Formula:
Average stockholders’ equity is determined as follows:
1 (14)
Determine return on common stockholders’ equity.
Explanation of Solution
Return on common stockholders’ equity
Rate of return on stockholders’ equity is used to determine the relationship between the net income and the average common equity that are invested in the company.
Formula:
Average common stockholders’ equity is determined as follows:
1(15)
Determine earnings per share on common stock.
Explanation of Solution
Earnings per share on common stock
A portion of profit that an individual earns from each share is referred to earnings per share.
Formula:
1 (16)
Determine price earnings ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Price earnings ratio
Price/earnings ratio is used to determine the profitability of a company. This ratio is abbreviated as P/E.
Formula:
17.
Determine dividend per share of common stock.
Explanation of Solution
Dividend per share of common stock
Dividend per share of commons stock is determined by dividing dividend per common stock and shares of common stock.
Formula:
18.
Determine dividend yield ratio.
Explanation of Solution
Dividend yield ratio
Dividend yield ratio is determined to evaluate the relationship between the annual dividend per share and the market price per share.
Formula:
Thus, summary table of determined ratios are below:
| S.No | Particulars | Ratios |
| 1. | Working capital | $1,584,000 |
| 2. | Current ratio | 2.8 |
| 3. | Acid test ratio | 2.2 |
| 4. | Accounts receivable turnover ratio | 20.0 |
| 5. | Number of days’ sales in receivables | 18.3 |
| 6. | Inventory turnover ratio | 15.0 |
| 7. | Number of days sales in inventory | 24.3 |
| 8. | Ratio of fixed assets to long-term liabilities | 1.8 |
| 9. | Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity | 0.8 |
| 10. | Times interest earned ratio | 8.7 |
| 11. | Asset turnover ratio | 1.3 |
| 12. | Return on total assets | 8.5% |
| 13. | Return on stockholders’ equity | 12.8% |
| 14. | Return on common stockholders’ equity | 13.3% |
| 15. | Earnings per share | $5.90 |
| 16. | Price earnings ratio | 14.0 |
| 17. | Dividend per share of common stock | $1.00 |
| 18. | Dividend yield | 1.2% |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting
- 17 If a company provides a non-contributory pension plan, who makes the contributions? Question 17 options: Only the employee. Both the employer and employee. No one. Only the employer.arrow_forward9 Assume that on January 15, 2025, Ariel agrees to purchase US$500,000 for C$550,000 for delivery on January 15, 2026. The exchange rate at its December 31 year-end is US$1 = C$0.95 and on January 15, 2026, the exchange rate is US$1 = C$0.97. What is the foreign exchange gain or loss recognized on January 15, 2025? Question 9 options: 0 $75,000 gain. $75,000 loss. $65,000 loss.arrow_forward18 Stranger Things Inc. (STI) had 80,000 ordinary shares outstanding on January 1, 2026. Transactions throughout 2026 affecting its shareholdings follow. • February 1: STI issued 200,000, $10, cumulative 10% preferred shares.• March 1: STI issued 40,000 ordinary shares.• April l: STI declared and issued an 8% stock dividend on the ordinary shares.• July 1: STI repurchased and cancelled 30,000 ordinary shares.• October 1: STI declared and issued a 3-for-l stock split on the ordinary shares.• December 31: STI declared $99,600 in dividends on the ordinary shares.• Net income for the year ended December 31, 2026, was $600,000. Its tax rate was 40%.Required1. What was weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding in 2026?2. What was basic EPS in 2026?arrow_forward
- 16 Which of the following best describes a "defined benefit plan"? Question 16 options: A pension plan that specifies how much funds the employee needs to contribute. A plan that requires the employer to contribute $10 per hour worked by an employee. A plan that specifies how much in pension payments employees will receive in their retirement. High returns in the pension plan result in higher benefit payments to the employees in the future.arrow_forwardPlease provide problem with accounting questionarrow_forward3 Which statement is correct about financial leverage? Question 3 options: Leverage can increase an investor's returns but also increases the risk of loss. Leverage decreases the debt level relative to a company's equity base. Leverage can decrease an investor's returns and also decrease the risk of loss. Leverage decreases the payments that a company makes on an ongoing basis.arrow_forward
- The comparative balance sheets and an income statement for Raceway Corporation follow. Balance Sheets As of December 31 Year 2 Year 1 Assets Cash $ 6,300 $ 48,400 Accounts receivable 10,200 7,260 Inventory 45,200 56,000 Prepaid rent 700 2,140 Equipment 140,000 144,000 Accumulated depreciation (73,400) (118,000) Land 116,000 50,000 Total assets $ 245,000 $ 189,800 Liabilities Accounts payable (inventory) $ 37,200 $ 40,000 Salaries payable 12,200 10,600 Stockholders’ equity Common stock, $50 par value 150,000 120,000 Retained earnings 45,600 19,200 Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity $ 245,000 $ 189,800 Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 Sales $ 480,000 Cost of goods sold (264,000) Gross profit 216,000 Operating expenses Depreciation expense (11,400) Rent expense (7,000) Salaries expense (95,200) Other operating expenses (76,000) Net income $ 26,400 Other Information Purchased…arrow_forwardPlease help holy tamale I have been staring at this for hours.arrow_forwardCould you explain the steps for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forward
- I need help with this General accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





