
Concept explainers
Issue of bond at premium:
When the coupon rate or contract rate of a bond is higher than the market interest rate, the bond is being issued at premium. If the bond is issued at premium, the selling price of the bond will be higher than the face value of the bond.
Under straight line amortization method, a specific amount of premium is amortized each period till its maturity period. The period ending amortization amount is computed by dividing the total premium by the number of periods in maturity of the bonds payable.
To determine:
1. Preparation of
2. Computation of (a) the cash payment, (b) the straight-line premium amortization, and (c) the bond interest expense
3. Determine to total bond interest expense to be recognized over the life of the bonds.
4. Prepare the first two years of an amortization table using straight-line method.
5. Prepare the journal entries to record the first two interest payments.
Answer to Problem 3APSA
Solution:
1.
| Date | Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| 2015 | |||
| Jan. 1 | Cash | $4,895,980 | |
| Bonds Payable | $4,000,000 | ||
| Premium on Bonds Payable | $895,980 |
2.
| Semiannual Period | Amount |
| Cash Payment | $120,000 |
| Straight-line discount amortization | $29,866 |
| Bond Interest Expense | $149,866 |
3.
The total bond interest expense to be recognized over the bond’s life is $2,704,020.
4.
| Period Ending | Unamortized Premium | Carrying Value |
| 01/1/2015 | $895,980 | $4,895,980 |
| 06/30/2015 | $866,114 | $4,866,114 |
| 12/31/2015 | $836,248 | $4,836,248 |
| 06/30/2016 | $806,382 | $4,806,382 |
| 12/31/2016 | $776,516 | $4,776,516 |
5.
| Date | General Journal | Debit | Credit |
| 2015 | |||
| Jun. 30 | Interest Expense | $90,134 | |
| Premium on Bonds Payable | $29,866 | ||
| Cash | $120,000 | ||
| Dec. 31 | Interest Expense | $90,134 | |
| Premium on Bonds Payable | $29,866 | ||
| Cash | $120,000 |
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
1. Computation of discount on bonds payable
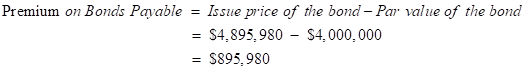
2. Computation of cash payment, straight-line discount amortization, and the bond interest expense

3.
| Computation of total interest expense | |
| Amount to be repaid at maturity: | |
| Total Interest Payment | $3,600,000 |
| Par | $4,000,000 |
| Total amount to be repaid | $7,600,000 |
| Less : Selling Price of the Bonds | $4,895,980 |
| Total Bond Interest Expense | $2,704,020 |
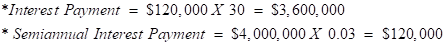
4. The premium amortization amount of $29,866 deducted from both the unamortized premium column and carrying value of the bonds payable for every semiannual period.
5. Under straight line premium amortization, the same amount of interest expense, discount amortized and interest payment is recorded till the maturity of the bonds.
Conclusion:
The discount amortization for every semiannual period is $29,866 and carrying value of the bonds payable for the year ended December 31, 2016 is $4,776,516.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamental Accounting Principles -Hardcover

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





