
Plot the following waveform versus time showing one clear. Complete cycle. Then determine the derivative of the waveform using Eq. (14.1) and sketch one complete cycle of the derivative directly under the Original waveform. Compare the magnitude of the derivative at various points versus the slope of the original sinusoidal function.
To plot:
The graph of the waveform versus time for one complete cycle. Calculate the derivative of the waveform and then draw one complete cycle of it. Also, compare the magnitude of the derivative at various points versus the slope of the original sinusoidal function.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given equation is
Calculation:
Let us consider the sinusoidal expression of voltage as:
Standard sinusoidal equation is:
Comparing, we get
Value of frequency will be
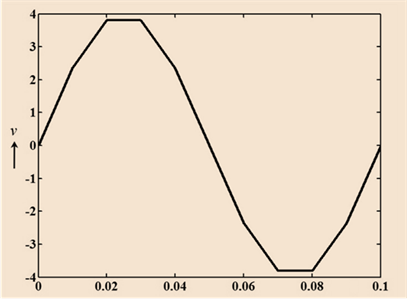
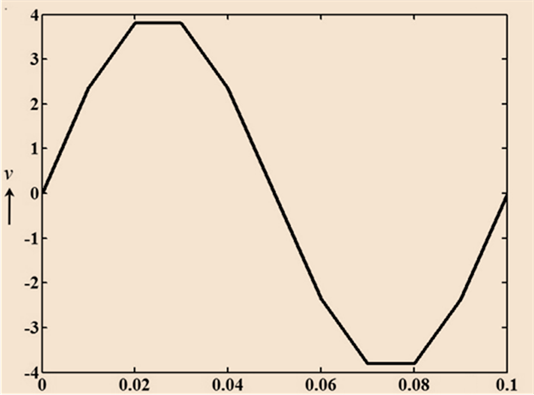
Voltage at
Voltage at
Voltage at
Voltage at
Voltage at
Voltage at
Graph showing voltage versus time
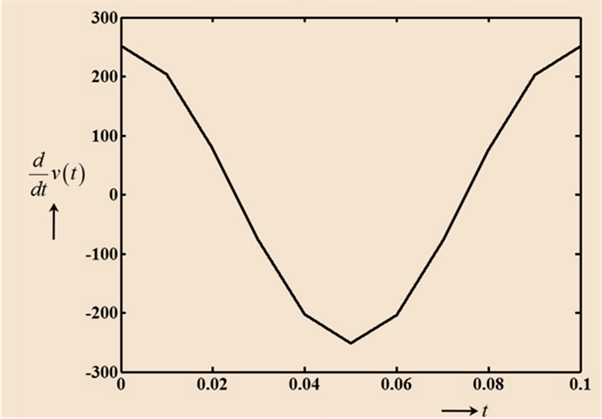
Derivative of standard sinusoidal equation is
Value of derivative of voltage at
Value of derivative of voltage at
Value of derivative of voltage at
Value of derivative of voltage at
Value of derivative of voltage at
Value of derivative of voltage at
Graph of derivative of voltage directly under the original waveform:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Experiencing MIS
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- An FDM is used to multiplex two groups of signals using AM-SSB, the first group contains 25 speech signals, each has maximum frequency of 4 kHz, the second group contains 15 music signals, each has maximum frequency of 10 kHz. A guard bandwidth of 500 Hz is used between each two signals and before the first one. 1. Find the BWmultiplexing 2. Find the BWtransmission if the multiplexing signal is modulated using AM-DSB-LC.arrow_forwardA single tone is modulated using FM transmitter. The SNR; at the input of the demodulator Is 20 dB. If the maximum frequency of the modulating signal is 4 kHz, and the maximum frequency deviation is 12 kHz, find the SNR, and the bandwidth (using Carson rule) at the following conditions: 1. For the given values of fm and Af. 2. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is increased by 80%. 3. If the amplitude of the modulating signal is decreased by 50%, and frequency of modulating signal is increased by 50%.arrow_forwardFM station of 100 MHz carrier frequency modulated by a 20 kHz sinusoid with an amplitude of 10 volt, so that the peak frequency deviation is 25 kHz determine: 1) The BW of the FM signal. 2) The approximated BW if the modulating signal amplitude is increased to 50 volt. 3) The approximated BW if the modulating signal frequency is increased by 70%. 4) The amplitude of the modulating signal if the BW is 65 kHz.arrow_forward
- b) The joint probability function for the random variables X and Y is given in Table below. Find a) the marginal probability function of X and Y. P(Y/X) and P(X/Y). c) P(X ≥ 2, Y ≤ 2) y 1 2 3 10.05 0.05 0.1 P(X, Y) = X 20.05 0.1 0.35 3 0 0.2 0.1arrow_forwardSuppose a random variable X as pmf / Px (x) = { %, x = 1, 2, 3, 0, otherwise. find constand c ①P(X = 1), P(X 7,2), PC1 3) C CDFarrow_forwardSuppose that a coin is tossed three so that the sample space is Let X represent the number of heads that can come up. i) Find the probability function corresponding to the random variable X. Assuming that the coin is fair ii) Find the distribution function for the random variable X. iii) Obtain its graph.arrow_forward
- Q9 A single-phase transformer, 2500 / 250 V, 50 kVA, 50 Hz has the following parameters, the Primary and secondary resistances are 0.8 ohm and 0.012 ohm respectively, the primary and secondary reactance are 4 ohm and 0.04 ohm respectively and the transformer gives 96% maximum efficiency at 75% full-load. The magnetizing component of-load current is 1.2 A on 2500 V side. 1- Draw the equivalent circuit referred to primary (H.V side) and inserts all the values in it 2- Find out Ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter readings on open-circuit and short-circuit test. If supply is given to 2500 V side in both cases. Ans. O.C. Test (Vo= 2500 V, lo=1.24 A, Wo=781.25 w) S.C. Test (Vsc =164.924 V, Isc =20 A, Wsc =800 w )arrow_forwardQ2-A)- Enumerate the various losses in transformer. Explain how each loss varies with (Load current, supply voltage). B)- Draw the pharos diagram at load on primary side.arrow_forwardQ2- What are the parameters and loss that can be determined during open-circuit test of singlephase transformer. Draw the circuit diagram of open-circuit test and explain how can you calculate the Parameters and loss.arrow_forward
- Q2-Drive the condition of maximum efficiency of single-phase transformer. Q1- A 5 KVA, 500/250 V ,50 Hz, single phase transformer gave the following reading: O.C. Test: 250 V,2 A, 50 W (H.V. side open) S.C. Test: 25 V10 A, 60 W (L.V. side shorted) Determine: i) The efficiency on full load, 0.8 lagging p.f. ii) Draw the equivalent circuit referred to primary and insert all the values it.arrow_forwardQ2- Describe various losses in transformer. Explain how each loss varies with load current, supply voltagearrow_forwardQ1-A 12 KVA, 440/ 220 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has 275 secondary turns. The no load current of transformer is 2A at power factor 0.375 when connected to 220 V, 50 Hz supply. The full load copper loss is 198.3 watt. Calculate a) Maximum value of flux in the core. b) Maximum efficiency at 0.8 lagging p.f c) KVA supply at maximum efficiencyarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





