
(a)
Calculate the stiffness co-efficient K.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1P
The stiffness co-efficient K is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The modulus of elasticity (E) is 30,000 ksi.
The vertical displacement of joint A
The vertical load acting at joint A is 24 kips.
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the structure as in Figure (1).
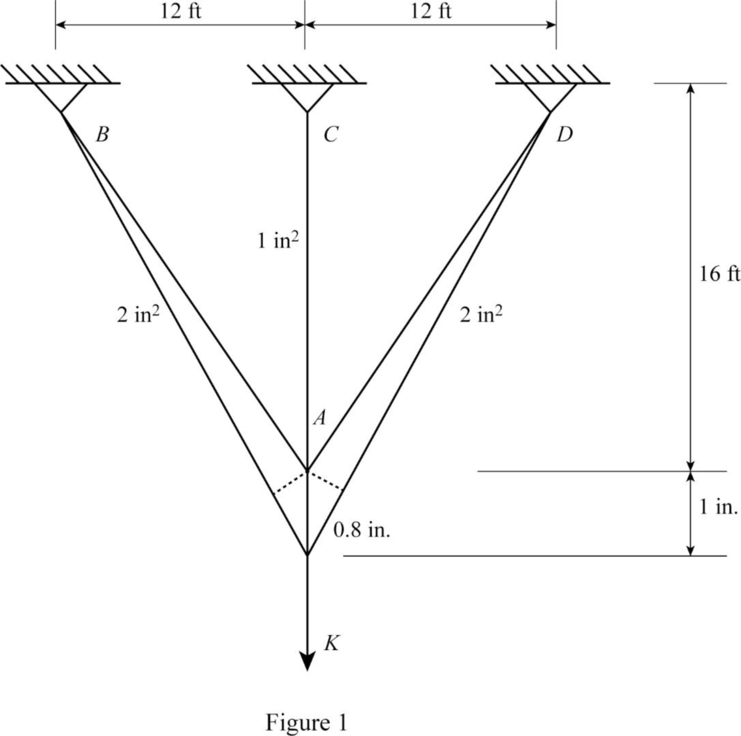
Refer Figure (1),
Find the force in the member AC using the relation;
Find the angle in the member;
Find the inclined displacement of joint A;
Find the force in the member AB using the relation;
Find vertical force in the member AB;
Find horizontal force in the member AB;
Show the free body diagram of the joint A as in Figure (2).
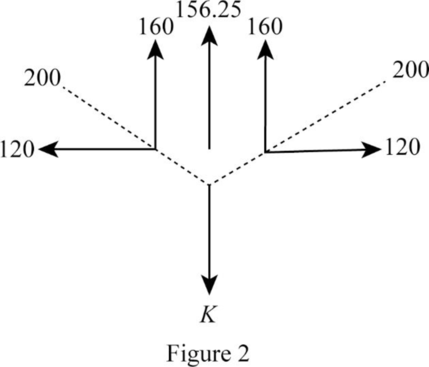
Refer Figure (2),
Consider the upward force is positive and downward force is negative.
Find the stiffness coefficient;
Summation of forces along y-direction is equal to 0.
Thus, the stiffness co-efficient K is
(b)
Calculate the vertical displacement at A.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1P
The vertical displacement at A is
Explanation of Solution
Find the vertical displacement at A;
Thus, the vertical displacement at A is
(c)
Calculate the axial forces in all bars.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1P
The axial force in the member AC is
The axial force in the member AB and AD is
Explanation of Solution
Find the axial force in the member AC using the relation;
Thus, the axial force in the member AC is
Find the force in the member AB and AD using the relation;
Thus, the axial force in the member AB and AD is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Structural Analysis:
- Can you please do with hand calcs and answer the following: a Determine the global stiffness matrix (K) of the beam including indicating correct degrees-of freedom (dof) b i) Calculate vectors D and Q ii) Show partition and solve KD=Q for D iii) Calculate all reactions c BMD & max BM, deflected shape d i) Solve the problem using Strand7 (model) ii) Display the deflected shape and BMD e Comparisons of reactions + Max BM including commentsarrow_forward5-1. Determine the force in each member of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression.arrow_forwardI have the correct answer provided, just lookng for a more detailed breadown of how the answer was obtained thanks.arrow_forward
- Q1. Statically indeterminate beam analysis. a) Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w kN/m. L1= 0.4L. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I=250x106 mm². Use the values of w = 50 kN/m and L = 6 b) Draw the shear force and bending diagrams for the entire beam. c) Calculate the BMs at all the joints of the same beam shown in Fig.1 using the slope deflection method. d) Compare the values of BMs obtained using the two methods a) and c) and comment. w kN/m £1m Lm m Fig 1. Beam for Q1arrow_forwardI have the answer provided for the question, just looking for a more detailed breadown of how it was obtained thanks.arrow_forwardQ5.--Finite-element-modelling. a) → Draw-a-2D-element-and-show-the dots (degrees of freedom). Draw-all-the-2D-elements. used-in-Strand 7..Explain the differences between-these-elements-in-terms-of-the-no..of. nodes-and-interpolation/shape-functions used. b)→A-8-m-x-8-m-plate (in-the-xx-plane)-with-8-mm-thickness, is fixed-at-all-the-edges.and.is. loaded-by-a-pressure-loading-of-4 kN/m2.-in-the-downward-(-2)-direction.-The-plate.is. made-of-steel-(E=-200 GPa, density-7850-kg/m3). Explain-the-steps-involved-in-setting. up-a-Strand 7-model-for-this-problem. Your-explanation-should-include-how-the-given. input-data-for-this-problem-will-be-used-in-Strand 7-modelling. Explain how you would. determine the maximum-deflection-from-the-Strand 7-output.-1 11arrow_forward
- I need Help some hw for AutoCAD please use measure front top and side viewarrow_forwardCalculate the discharge of the system shown below. Neglecting minor losessarrow_forwardQ3. Statically determinate or indeterminate beam analysis by the stiffness method a) Determine the global stiffness matrix of the beam shown in Fig. 3. Assume supports at 1 and 3 are rollers and the support at 2 is a pinned support. Indicate the degrees- of freedom in all the stiffness matrices. El is constant. Use the values of w = 50 kN/m and L1 = 2.0 m Note, L2-3L1. b) Determine the rotations at all the nodes of the beam and reactions at the supports. Show all calculations. c) Draw the BMD of the beam on the compression side showing the salient values. What are the maximum bending moments of the beam? Draw the deflected shape of the beam. d) Solve the problem using the Strand7. Assume any suitable value of El (state the value you have used for El). Show the model with all the nodes, element numbers and boundary conditions. Display the deflected shape and BMD. e) Show a table comparing the stiffness method (manual calculations) of the all the reactions and the maximum bending moment…arrow_forward
- Using AutoCAD. I need help please to exact measurearrow_forwardDraw Isometric view of this multiview of object.arrow_forwardREMINDER: The truss must be cut into two different sections. You can choose either one to solve as you will get the same answer. Since there are three equations available, you can't cut more than three members 6.25 Determine the force in members BD, CD, and CE of the truss shown. BO C 36 kips 36 kips D F H 7.5 ft E G 4 panels at 10 ft = 40 ftarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





