
To explain:
The difference between short-run and long-run
Explanation of Solution
At natural rate of
The difference between the short-run Philips curve and long-run Philips curve is shown in the diagram below:
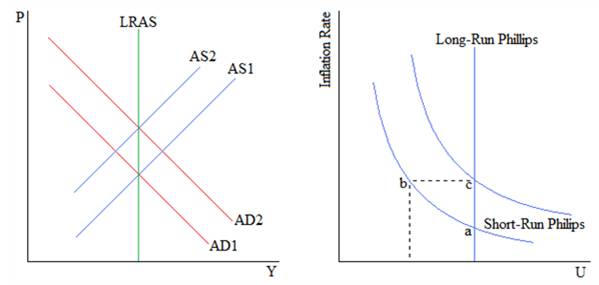
On the left, the Aggregate
On the right, the increases in the price level translate to higher inflation. This leads to lower rates of unemployment (U) in the short run. Starting at a point a, the curve moves to point b. However, as Aggregate Supply decreases, the Short-Run Philips curve shifts up. Moving from point b to point c, the inflation stays high and the unemployment increases. In the long run, the unemployment is fixed with respect to the inflation rate.
Philips Curve:
Phillips curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between inflation rate and unemployment. This curve states that there is an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
Aggregate demand:
Aggregate demand is the total demand for final goods and services at a given time.
Aggregate supply:
Aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services available in a market place.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Consider the figure at the right. The profit of the single-price monopolist OA. is shown by area D+H+I+F+A. B. is shown by area A+I+F. OC. is shown by area D + H. ○ D. is zero. ○ E. cannot be calculated or shown with just the information given in the graph. (C) Price ($) B C D H FIG шо E MC ATC A MR D = AR Quantityarrow_forwardConsider the figure. A perfectly price-discriminating monopolist will produce ○ A. 162 units and charge a price equal to $69. ○ B. 356 units and charge a price equal to $52 for the last unit sold only. OC. 162 units and charge a price equal to $52. OD. 356 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. Dollars per Unit $69 $52 MR 162 356 Output MC Darrow_forwardThe figure at right shows the demand line, marginal revenue line, and cost curves for a single-price monopolist. Now suppose the monopolist is able to charge a different price on each different unit sold. The profit-maximizing quantity for the monopolist is (Round your response to the nearest whole number.) The price charged for the last unit sold by this monopolist is $ (Round your response to the nearest dollar.) Price ($) 250 225- 200- The monopolist's profit is $ the nearest dollar.) (Round your response to MC 175- 150 ATC 125- 100- 75- 50- 25- 0- °- 0 20 40 60 MR 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantityarrow_forward
- The diagram shows a pharmaceutical firm's demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. At its profit-maximizing level of output, it will generate a deadweight loss to society represented by what? A. There is no deadweight loss generated. B. Area H+I+J+K OC. Area H+I D. Area D + E ◇ E. It is not possible to determine with the information provided. (...) 0 Price 0 m H B GI A MR MC D Outparrow_forwardConsider the figure on the right. A single-price monopolist will produce ○ A. 135 units and charge a price equal to $32. B. 135 units and generate a deadweight loss. OC. 189 units and charge a price equal to the perfectly competitive price. ○ D. 189 units and charge a price equal to $45. () Dollars per Unit $45 $32 MR D 135 189 Output MC NGarrow_forwardSuppose a drug company cannot prevent resale between rich and poor countries and increases output from 3 million (serving only the rich country with a price of $80 per treatment) to 9 million (serving both the rich and the poor countries with a price of $30 per treatment). Marginal cost is constant and equal to $10 per treatment in both countries. The marginal revenue per treatment of increasing output from 3 million to 9 million is equal to ○ A. $20 per treatment, which is greater than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ B. $20 per treatment, which is greater than zero and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ C. $30 per treatment, which is greater than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will rise. ○ D. $5 per treatment, which is less than the marginal cost of $10 per treatment and thus implies that profits will fall. ○ E. $30 per treatment, which is less than the marginal revenue of $80 per treatment…arrow_forward
- Consider the figure. A single-price monopolist will have a total revenue of Single-Price Monopolist OA. 84×$13. O B. 92x $13. OC. 84×$33. OD. 92 x $33. C Price ($) $33 $13 MC MR D 84 92 Output The figure is not drawn to scale.arrow_forward10.As COVID-19 came about, consumers' relationship with toilet paper changed and they found themselves desiring more than usual. Eventually, toilet paper producers saw an opportunity to make more money and meet the growing demand. Which best describes this scenario as depicted in Snell's 2020 article? A. The demand curve shifted left and the supply curve shifted left B. The demand curve shifted left and the supply curve shifted right C. The demand curve shifted right and the supply curve shifted left D. The demand curve shifted right and the supply curve shifted rightarrow_forward5. Supply and Demand. The graph below shows supply and demand curves for annual medical office visits. Using this graph, answer the questions below. P↑ $180 $150 $120 $90 $60 $30 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 a. If the market were free from government regulation, what would be the equilibrium price and quantity? b. Calculate total expenditures on office visits with this equilibrium price and quantity. c. If the government subsidized office visits and required that all consumers were to pay $30 per visit no matter what the actual cost, how many visits would consumers demand? d. What payment per visit would doctors require in order to supply that quantity of visits? e. Calculate total expenditures on office visits under the condition of this $30 co- payment. f. How do total expenditures with a co-payment of $30 compare to total expenditures without government involvement? Provide a numerical answer. Show your work.arrow_forward
- 4. The table below shows the labor requirements for Mr. and Mrs. Howell for pineapples and coconuts. Which is the most accurate statement? A. Mrs. Howell has a comparative advantage in coconuts and the opportunity cost of 1 coconut for Mrs. Howell is 4 pineapples B. Mrs. Howell has a comparative advantage in pineapples and the opportunity cost of 1 pineapple for Mrs. Howell is .25 coconuts. C. Mr. Howell has a comparative advantage in pineapples and the opportunity cost of 1 pineapple is 1 coconut. D. Mr. Howell has a comparative advantage in both pineapples and coconuts and should specialize in pineapples. Labor Requirements for Pineapples and Coconuts 1 Pineapple 1 Coconut Mr. Howell 1 hour 1 hour Mrs. Howell 1/2 hour 2 hoursarrow_forward4. Supply and Demand. The table gives hypothetical data for the quantity of electric scooters demanded and supplied per month. Price per Electric Scooter Quantity Quantity Demanded Supplied $150 500 250 $175 475 350 $200 450 450 $225 425 550 $250 400 650 $275 375 750 a. Graph the demand and supply curves. Note if you prefer to hand draw separately, you may and insert the picture separately. Price per Scooter 300 275 250 225 200 175 150 250 400 375425475 350 450 550 650 750 500 850 Quantity b. Find the equilibrium price and quantity using the graph above. c. Illustrate on your graph how an increase in the wage rate paid to scooter assemblers would affect the market for electric scooters. Label any new lines in the same graph above to distinguish changes. d. What would happen if there was an increase in the wage rate paid to scooter assemblers at the same time that tastes for electric scooters increased? 1ངarrow_forward3. Production Costs Clean 'n' Shine is a competitor to Spotless Car Wash. Like Spotless, it must pay $150 per day for each automated line it uses. But Clean 'n' Shine has been able to tap into a lower-cost pool of labor, paying its workers only $100 per day. Clean 'n' Shine's production technology is given in the following table. To determine its short-run cost structure, fill in the blanks in the table. Fill in the columns below. Outpu Capita Labor TFC TVC TC MC AFC AVC ATC 1 0 30 1 1 70 1 2 120 1 3 160 1 4 190 1 5 210 1 6 a. Over what range of output does Clean 'n' Shine experience increasing marginal returns to labor? Over what range does it experience diminishing marginal returns to labor? (*answer both questions) b. As output increases, do average fixed costs behave as described in the text? Explain. C. As output increases, do marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost behave as described in the text? Explain. d. Looking at the numbers in the table, but without…arrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





