
(a)
The explanation for variation in the number of daylight hours due to the inclination of and constant orientation of earth’s axis.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1CQ
Due to the inclination and orientation of the axis of the earth, the intensity of sunlight on a particular location changes as the earth rotates. This causes a variation in the number of daylight hours.
Explanation of Solution
The axis of the earth is tilted and always points towards the North Star. As a result the orientation of the axis of the earth changes throughout the year as it revolves around the sun. At some instant the axis points towards the sun and at the other instance it points away from the sun.
As the orientation of the earth’s axis changes throughout the year, the distribution of sunlight also changes across different latitude. This causes a seasonal variation in the number of hours of daylight. The variation in intensity is due to the angle at which the sun’s rays hit the earth and it changes throughout the year.
(b)
The explanation for variation in seasons throughout the year due to the inclination of and constant orientation of earth’s axis.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1CQ
Due to the inclination and orientation of the axis of the earth the intensity of sunlight on a particular location changes as earth rotates. This causes variation in seasons throughout the year.
Explanation of Solution
The axis of the earth is tilted and always points towards the North Star. As a result the orientation of the axis of the earth changes throughout the year as it revolves around the sun. At some instant, the northern hemisphere is towards the sun and at the other instance the southern hemisphere is away from the sun.
Seasons change occurs throughout the year due to the variation of sunlight falling on the earth. The hemisphere close to the sun experiences winter while the other experiences summer and vice versa.
The following figure shows the position of the earth throughout a year.
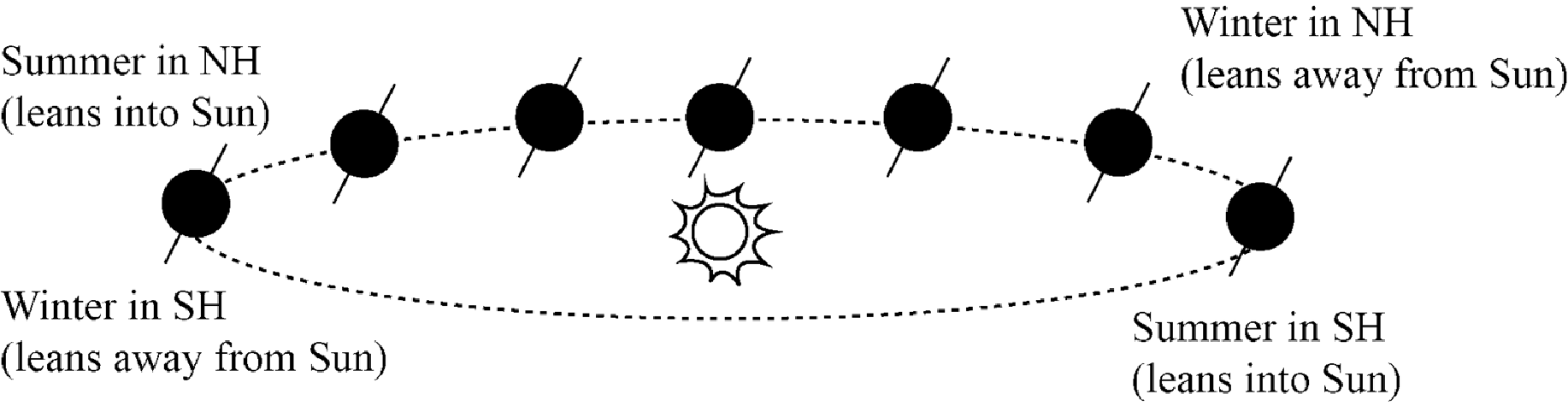
Figure-(1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Integrated Science
- A 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardFind the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forwardWhat is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forward
- What is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forward
- Can someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forward
- Portfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 4. Consider two identical springs, each with natural length and spring constant k, attached to a horizontal frame at distance 2l apart. Their free ends are attached to the same particle of mass m, which is hanging under gravity. Let z denote the vertical displacement of the particle from the hori- zontal frame, so that z < 0 when the particle is below the frame, as shown in the figure. The particle has zero horizontal velocity, so that the motion is one dimensional along z. 000000 0 eeeeee (a) Show that the total force acting on the particle is X F-mg k-2kz 1 (1. l k. (b) Find the potential energy U(x, y, z) of the system such that U x = : 0. = O when (c) The particle is pulled down until the springs are each of length 3l, and then released. Find the velocity of the particle when it crosses z = 0.arrow_forwardIn the figure below, a semicircular conductor of radius R = 0.260 m is rotated about the axis AC at a constant rate of 130 rev/min. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.22 T fills the entire region below the axis and is directed out of the page. R Pout (a) Calculate the maximum value of the emf induced between the ends of the conductor. 1.77 v (b) What is the value of the average induced emf for each complete rotation? 0 v (c) How would your answers to parts (a) and (b) change if the magnetic field were allowed to extend a distance R above the axis of rotation? (Select all that apply.) The value in part (a) would increase. The value in part (a) would remain the same. The value in part (a) would decrease. The value in part (b) would increase. The value in part (b) would remain the same. The value in part (b) would decrease. × (d) Sketch the emf versus time when the field is as drawn in the figure. Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. (e) Sketch the emf…arrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning






