
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept-Introduction:
Lewis structure
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
According to VSEPR theory, the geometry is predicted by the minimizing the repulsions between electron-pairs in the bonds and lone-pairs of electrons. The VSEPR theory is summarized in the given table as,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Outer valence electrons of Selenium and Florine are six and seven respectively.
Draw Lewis structure of Selenium tetrafluoride:
The Lewis structure of Selenium tetrafluoride follows as,
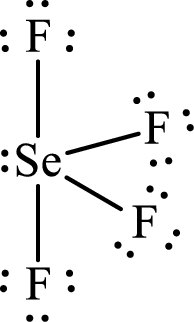
After the distribution of electrons, Selenium atom gets a lone pair of electrons.
Selenium has
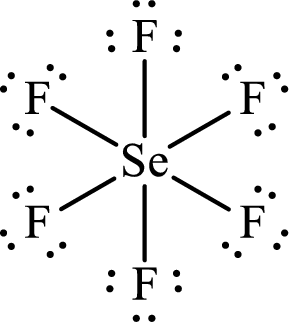
Draw Lewis structure of Selenium hexafluoride:
Selenium has
The Lewis structure of Selenium hexafluoride follows as,
(b)
Interpretation:
Change in orbital hybridization of the central
Concept-Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Geometry of a molecule can be predicted by knowing its hybridization.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Selenium tetrafluoride and Fluorine reacts to form Selenium hexafluoride.
The geometry of
In
In
During the reaction the hybridization of Selenium changes from
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
CONNECT ACCESS CARD FOR CHEMISTRY: MOLECULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND CHANGE
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forward35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward21) The rate of reaction depends upon: a. the concentration and nature of reactants b. the temperature of the reaction C. whether or not a catalyst was used d. all of the above 22) A Maxwell-Boltzmann curve shows the distribution of molecular energies in a reaction system. When the temperature in this system is increased, the peak is a. higher and further to the right. b. higher and further to the left. c. lower and further to the right. d. lower and further to the left. 23) Which of the following correctly describes the reaction represented by the reaction below? CaCO3 (s) + energy → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) a. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the reactants than the products. b. c. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. It is endothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. d. It is endothermic and the potential energy is equal for the products and reactants.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





