
(1)
Bonds
Bonds are a kind of interest bearing notes payable, usually issued by companies, universities and governmental organizations. It is a debt instrument used for the purpose of raising fund of the corporations or governmental agencies. If selling price of the bond is equal to its face value, it is called as par on bond. If selling price of the bond is lesser than the face value, it is known as discount on bond. If selling price of the bond is greater than the face value, it is known as premium on bond.
Effective interest rate of amortization bond
Effective interest rate method of amortization is a process of amortizing premium on bond or discount on bond, which allocates the different amount of interest expense in each period of interest payment, but at a constant percentage rate.
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
To Determine: The price value of the bonds as on 1st February 2016.
(1)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the price value of the bonds as on 1st February 2016 as shown below:
Working notes:
Calculation of the present value of the principal amount as shown below:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Face |
$80,000,000 |
| PV factor at an annual market rate of 5% for 8 periods (b) |
|
| Present value of face value of the bonds
|
$54,147,200 |
Table (1)
Note: The present value of $1 for 8 periods at 5% is 0.67684 (refer Table 2 in Appendix).
Hence, present value of the principal amount is $54,147,200.
Calculation of the present value of the interest payment amount as shown below:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Interest payments amount (a) | $3,600,000 |
| PV factor at an annual market rate of 5% for 8 periods (b) |
|
| Present value of interest payments
|
$23,267,556 |
Table (2)
Note: The Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1 for 8 periods at 5% is 6.87396 (refer Table 4 in Appendix).
Hence, the present value of interest payment amount is $23,267,556.
Calculation of the amount of interest payment as shown below:
Hence, the amount of interest payment is $3,600,000.
Therefore, price value of the bonds as on 30th June 2016 is $77,414,756.
(2)
To Prepare: The amortization schedule for Products CM (issuer) and Industries B (Borrower).
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of the amortization schedule for Products CM (issuer) as shown below:
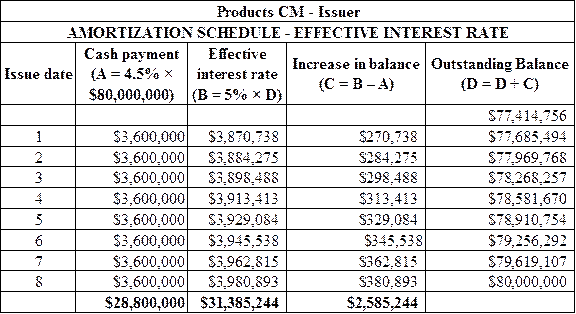
Figure (1)
Calculation of the amortization schedule for Industries B (Borrower) as shown below:
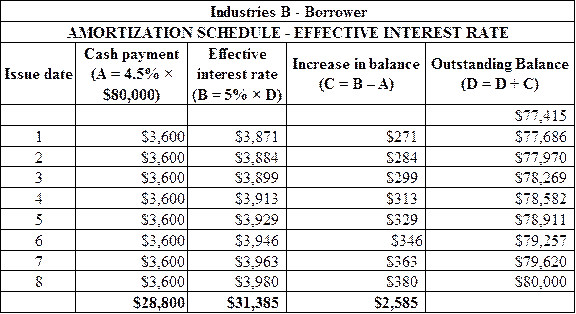
Figure (2)
(3)
To Prepare: The
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of the bonds for Products CM (Issuer) as on 1st February 2016 as show below:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
| 2016 | Cash | 77,414,756 | ||
| February | 1 | |||
| Discount on Bonds Payable | 2,585,244 | |||
| Bonds Payable | 80,000,000 | |||
| (To record the issue of bonds) | ||||
Table (3)
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $77,414,756.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit discount on bonds payable account for $2,585,244.
- Bonds payable is a long term liability, and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $80,000,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of the bonds for Industries B (Borrower) as on 1st February 2016 as show below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
| 2016 | Bonds Investment | 80,000 | ||
| February | 1 | |||
| Discount on Bonds Investment | 2,585 | |||
| Cash | 77,415 | |||
| (To record the purchase of bonds) | ||||
Table (4)
- Bond investment is a non- current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit investment on bonds account for $8,000.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $2,585.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $77,415.
(4)
To Prepare: The journal entry to record all the subsequent events related to the through 31st July 2016 for both the firms.
(4)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record all subsequent events through July 31, 2016 for C (Issuer).
Journal entry to record interest on July 31, 2016 as show below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Interest Expense | 3,870,738 | ||||
| July | 31 | Discount on Bonds Payable | 270,738 | |||
| Cash | 3,600,000 | |||||
| (To record payment of semi-annual interest) | ||||||
Table (5)
Interest expense is a component of
Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $270,738.
Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $3,600,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on December 31, 2016 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Interest Expense | 3,236,896 | ||||
| December | 31 | Discount on Bonds Payable | 236,896 | |||
| Interest Payable | 3,000,000 | |||||
| (To record interest accrued) | ||||||
Table (6)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of interest expense for 5 months a shown below:
Hence, interest expenses amount is $3,236,896.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 5 months a shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable for 5 months amount is $236,896.
Calculation of the interest payable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest payable amount for 5 months is $3,000,000.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expenses account for $3,236,896.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $236,896.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $3,000,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on January 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 2017 | Interest Expense | 647,379 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Interest Payable | 3,000,000 | |||||
| Discount on Bonds Payable | 47,379 | |||||||
| Cash | 3,600,000 | |||||||
| (To record payment of interest) | ||||||||
Table (7)
Working notes:
Calculation of the amount of interest expense for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, interest expenses amount for 1 month is $647,379.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable for 1 month amount is $47,379.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expenses account for $647,379.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $3,000,000.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $47,379.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $3,600,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on July 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Interest Expense | 3,898,488 | |||||
| July | 31 | Discount on Bonds Payable | 298,488 | ||||
| Cash | 3,600,000 | ||||||
| (To record payment of semi-annual interest) | |||||||
Table (8)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders; equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $3,898,488.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $298,488.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $3,600,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 2017 | Interest Expense | 3,261,177 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Discount on Bonds Payable | 261,177 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 3,000,000 | |||||||
| (To record interest accrued) | ||||||||
Table (9)
Working notes:
Calculation of the amount of interest expense for 5 months as show below:
Hence, interest expenses for 5 months amount is $3,261,177.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable for 5 months amount is $261,177.
Calculation of the interest payable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest payable for 5 months amount is $3,000,000.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expenses account for $3,261,177
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $261,177.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $3,000,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on January 31, 2018 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 2018 | Interest Expense (E–) | 652,236 | ||||||
| January | 31 | Interest Payable (L–) | 3,000,000 | |||||
| Discount on Bonds Payable (L+) | 52,236 | |||||||
| Cash (A–) | 3,600,000 | |||||||
| (To record payment of interest) | ||||||||
Table (10)
Working notes:
Calculation of the amount of interest expense for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, an interest expense for 1 month amount is $652,236.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, the discount on bonds payable amount for 1 month is $52,236.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expenses account for $652,236.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $3,000,000.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable account for $52,236.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $3,600,000.
Prepare journal entry to record all subsequent events through July 31, 2016 for Industries B (Borrower).
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on July 31, 2016 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Cash | 3,600 | |||||
| July | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment | 271 | ||||
| Interest Revenue | 3,871 | ||||||
| (To record semi-annual interest revenue) | |||||||
Table (11)
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $3,600.
- Discount on bonds investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, discount on bonds investment account for $271.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $3,871.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on December 31, 2016 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Interest Receivable | 3,000 | |||||
| December | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment | 237 | ||||
| Interest Revenue | 3,237 | ||||||
| (To record interest receivable) | |||||||
Table (12)
Working notes:
Calculation of the interest receivable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest receivable for 5 months amount is $3,000.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable amount is $237.
Calculation of the interest revenue for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest revenue account is $3,237.
- Interest receivable is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit interest receivable account for $3,000.
- Discount on Bond investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, discount on bond investment account is $237.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $3,237.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on January 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Cash | 3,600 | |||||
| January | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment | 47 | ||||
| Interest Receivable | 3,000 | ||||||
| Interest Revenue | 647 | ||||||
| (To record interest revenue) | |||||||
Table (13)
Working notes:
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable amount is $47.
Calculation of the interest revenue for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, interest revenue amount is $647.
- Cash is a current asset, and increased, therefore, debit cash account for $3,600.
- Discount on bonds investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, debit discount on bonds investment account for $47.
- Interest receivable is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest receivable account for $3,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $647.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on July 31, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Cash | 3,600 | |||||
| July | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment | 299 | ||||
| Interest Revenue | 3,899 | ||||||
| (To record semi-annual interest revenue) | |||||||
Table (14)
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $3,600.
- Discount on bonds investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, discount on bonds investment account for $299.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $3,899.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on December 31, 2017:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Interest Receivable | 3,000 | |||||
| December | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment | 261 | ||||
| Interest Revenue | 3,261 | ||||||
| (To record interest receivable) | |||||||
Table (15)
Working notes:
Calculation of the interest receivable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest receivable amount for $3,000.
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable amount is $261.
Calculation of the interest revenue for 5 months as shown below:
Hence, interest revenue amount is $3,261.
- Interest receivable is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit interest receivable account for $3,000.
- Discount on Bond investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, discount on bond investment account is $261.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $3,261.
Prepare the journal entry to record interest on January 31, 2018 as shown below:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2018 | Cash (A+) | 3,600 | |||||
| January | 31 | Discount on Bonds Investment (L–) | 52 | ||||
| Interest Receivable (A–) | 3,000 | ||||||
| Interest Revenue (E–) | 652 | ||||||
| (To record interest revenue) | |||||||
Table (16)
Working notes:
Calculation of the discount on bonds payable for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, discount on bonds payable amount is $52.
Calculation of the interest revenue for 1 month as shown below:
Hence, interest revenue amount is $652.
- Cash is a current asset, and increased, therefore, debit cash account for $3,600.
- Discount on bonds investment is a contra asset, and decreased. Therefore, debit discount on bonds investment account for $52.
- Interest receivable is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest receivable account for $3,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit interest revenue account for $652.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
LooseLeaf Intermediate Accounting w/ Annual Report; Connect Access Card

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





