
1(a)
Financial Ratios: Financial ratios are the metrics used to evaluate the liquidity, capabilities, profitability, and overall performance of a company.
To determine: Return on total assets for five years (20Y4 to 20Y8)
Explanation of Solution
Return on assets determines the particular company’s overall earning power. It is determined by dividing sum of net income and interest expense and average total assets.
Formula:
1(b)
To determine: Return on
1(b)
Explanation of Solution
Formula:
1(c)
To determine: Times interest earned ratio for five years
1(c)
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense. First, determine the sum of income before income tax and interest expense. Then, divide the sum by interest expense.
Formula:
1(d)
To determine: Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity for five years (20Y4 to 20Y8)
1(d)
Explanation of Solution
Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity is determined by dividing liabilities and stockholders’ equity. Liabilities are determined as the difference between ending balance of assets and stockholders’ equity.
Formula:
To Display: The determined ratios in a graph
Explanation of Solution
Return on total assets
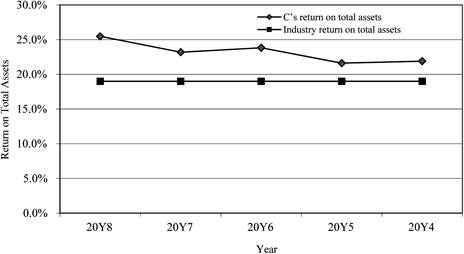
Figure (1)
Return on stockholders’ equity
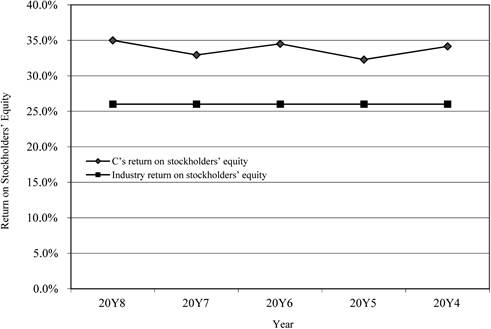
Figure (2)
Times interest earned ratio
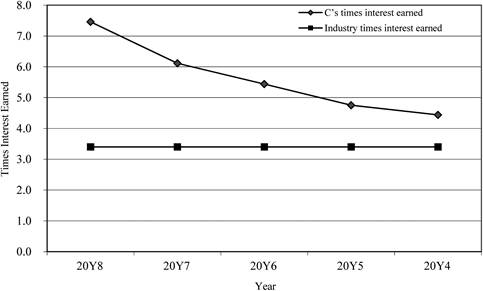
Figure (3)
Ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity
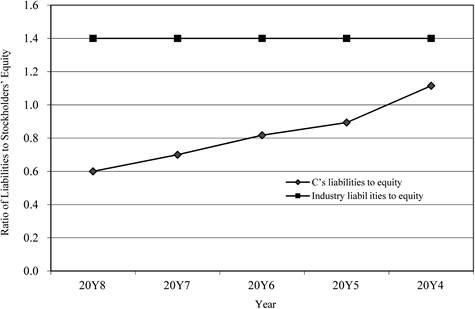
Figure (4)
2.
To prepare: Analysis of graphs
2.
Explanation of Solution
- The return on total assets and return on stockholders’ equity are in increasing trend for the last five years. There is a positive use of leverage. It is evident through the above ratios.
- The ratio of liabilities to stockholders’ equity shows that the proportion of debt to stockholders’ equity is declining over the period.
- The level of debt has been relative to the equity and has improved in the five years.
- The times interest earned ratio is improving
- g when compared to industry average.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting, Loose-Leaf Version
- no aiOne company might depreciate a new computer over three years while another company might depreciate the same model computer over five years...and both companies are right. True Falsearrow_forwardno ai An asset's useful life is the same as its physical life? True Falsearrow_forwardno ai Depreciation Expense reflects an allocation of an asset's original cost rather than an allocation based on the economic value that is being consumed. True Falsearrow_forward
- The purpose of depreciation is to have the balance sheet report the current value of an asset. True Falsearrow_forwardDepreciation Expense shown on a company's income statement must be the same amount as the depreciation expense on the company's income tax return. True Falsearrow_forwardDont use AI Give soln.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





