
(Variable-Length Argument List: Calculating Products) Write a
Program Plan:
This header file <stdarg.h>is used for object ap of type va_list is used by macros va_startva_arg and va_end to process the variable-length argument list of function product.
product( int x, ) :This function definition product is using a variable length argument list and calculate the product of a series of integers.
Printf (): used to print the data onto output screen.
Variables i, j, l, m, and n are of integer type which are passed as argument to function.
Total variable of integer type is used to store product of integer value.
Program Description: Purpose of the program is to calculates the series of integers that are passed to function product with several calls, by using a variable length list of arguments list and display result.
Explanation of Solution
Program: Following is Cprogram that calculates the series of integers that are passed to function product with several calls, by using a variable length list of arguments list and display result.
#include<stdio.h>//header file
#include<stdarg.h>///header-file for variable-length argument lists
//Function prototype
int product( int x, ... );
//Start of main
intmain( void )
{
//Initialize the integers
inti = 5;
int j = 4;
int k = 3;
int l = 2;
int m = 1;
//display user the values of integers
printf( "%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n","i = ",
i, "j = ", j,"k = ", k,"l = ", l, "m = ", m );
//display the result of product using the function call to different series of integers
printf( "%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n%s%d\n",
"The Product of i and j is: ", product( 2,i,j ),
"The Product of i, j and k is: ",product(3,i,j,k ),
"The Product of i, j, k and 1 is: ", product(4,i,j,k,l ),
"The Product of i, j, k, 1, and m is: ",product(5,i,j,k,l,m) );
//terminate program succesfully
return0;
}//End of main
//function product in which product of integers is passed as arguments
int product( int x, ... )
{
//Declare and initialize variable total
int total = 1;
//variable to counter loop
intz;
//Stores information needed by va_start and va_end.
/*initialize variable Length argument List*/
va_listarg;
//Stores information needed by va_start.
/*invoke the macros to access the arguments*/
va_start( arg, x );
//Process is running for variable length argument list.
/*evaluate the total using for loop*/
for( z = 1; z <= x ; z++ )
{
total *= va_arg( arg, int);
}/*end of for loop*/
//Clean up variable-length argument list.
/*Perform the housekeeping termination*/
va_end( arg);
/*return the arguments of product*/
returntotal;
}/*end of function Product*/
Explanation:
- Use header file notation
for variable-length list of arguments. - Read different series of integers in function call.
- Assign the value of total equals to 1 and use the argument list including va_list of variable list, next initialize va_start ( ) to invoke the macros so as to access the arguments in function definition.
- Loop for to evaluate the value of product.
- Display the product of a series of integers.
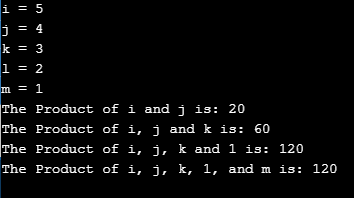
Sample Output:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
C How To Program Plus Mylab Programming With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- Consider the following relational schema. An employee can work in more than one department; the pct_time field of the Works relation shows the percentage of time that a given employee works in a given department. Emp(eid: integer, ename: string, age: integer, salary: real) Works(eid: integer, did: integer, pct_time: integer) Dept(did: integer, budget: real, managerid: integer) Write the following queries in SQL: a. Print the name of each employee whose salary exceeds the budget of all of the departments that he or she works in. b. Find the enames of managers who manage only departments with budgets larger than $1 million, but at least one department with budget less than $5 million.arrow_forwardConsider the following schema: Suppliers(sid: integer, sname: string, address: string) Parts(pid: integer, pname: string, color: string) Catalog(sid: integer, pid: integer, cost: real) The Catalog relation lists the prices charged for parts by suppliers. Write the following queries in SQL: a. Find the sids of suppliers who charge more for some part than the average cost of that part (averaged over all the suppliers who supply that part). b. Find the sids of suppliers who supply a red part or a green part. c. For every supplier that supplies a green part and a red part, print the name and price of the most expensive part that she supplies.arrow_forwardThe following relations keep track of airline flight information: Flights(flno: integer, from: string, to: string, distance: integer, departs: time, arrives: time, price: integer) Aircraft(aid: integer, aname: string, cruisingrange: integer) Certified(eid: integer, aid: integer) Employees(eid: integer, ename: string, salary: integer) Note that the Employees relation describes pilots and other kinds of employees as well; every pilot is certified for some aircraft, and only pilots are certified to fly. Write each of the following queries in SQL.(Additional queries using the same schema are listed in the exercises for Chapter 4) a. Identify the routes that can be piloted by every pilot who makes more than $100,000. b. Print the name and salary of every nonpilot whose salary is more than the average salary for pilots. c. Print the names of employees who are certified only on aircrafts with cruising range longer than 1000 miles and who are certified on some Boeing…arrow_forward
- Need help making python code for this!arrow_forward2.7 LAB: Smallest of two numbers Instructor note: Note: this section of your textbook contains activities that you will complete for points. To ensure your work is scored, please access this page from the assignment link provided in the CTU Virtual Campus. If you did not access this page via the CTU Virtual Campus, please do so now.arrow_forwardI help understanding this question d'y + 4dy +3y = a, Initial Conditions: y(0) = 5 & y'(0)=0 Where a = 10 a) Find y(t) =yh(t) +yp(t) in time domainIs the system over-damped, under-damped, or critical? b) Find y(t) using Laplace Transformsarrow_forward
- Given f(t)=a sin(ßt) a = 10 & ß = 23 Find the Laplace Transform using the definition F(s) = ∫f(t)e-stdtarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardObtain the MUX design for the function F(X,Y,Z) = (0,3,4,7) using an off-the-shelf MUX with an active low strobe input (E).arrow_forward
- I cannot program smart home automation rules from my device using a computer or phone, and I would like to know how to properly connect devices such as switches and sensors together ? Cisco Packet Tracer 1. Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardusing r language for integration theta = integral 0 to infinity (x^4)*e^(-x^2)/2 dx (1) use the density function of standard normal distribution N(0,1) f(x) = 1/sqrt(2pi) * e^(-x^2)/2 -infinity <x<infinity as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 1 for theta set m=100 for the estimate whatt is the estimate theta 1? (2)use the density function of gamma (r=5 λ=1/2)distribution f(x)=λ^r/Γ(r) x^(r-1)e^(-λx) x>=0 as importance function and obtain an estimate theta 2 for theta set m=1000 fir the estimate what is the estimate theta2? (3) use simulation (repeat 1000 times) to estimate the variance of the estimates theta1 and theta 2 which one has smaller variance?arrow_forwardusing r language A continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/56(3x^2+4x^3+5x^4).0<=x<=2 (1) secify the density g of the random variable Y you find for the acceptance rejection method. (2) what is the value of c you choose to use for the acceptance rejection method (3) use the acceptance rejection method to generate a random sample of size 1000 from the distribution of X .graph the density histogram of the sample and compare it with the density function f(x)arrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


