
1.
Troubled debt restructuring
When the unique terms of a debt agreement is encouraged by the financial complications by the debtor (borrower), the new agreement is referred to as a troubled debt restructuring. It includes some allowances on the part of the creditors (issuer).
To Prepare: The
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for gain on disposal of land.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| Land | 3,000,000 | |||||
| Gain on Disposal of Assets | 3,000,000 | |||||
| (To record gain on disposition of assets) | ||||||
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of gain on disposition.
Hence, gain on disposal of assets amount is $3,000,000.
- Land is a non – current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit land account for $3,000,000.
- Gain on disposal of asset is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on disposal of asset amount is $3,000,000.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Notes Payable | 20,000,000 | |||
| Interest Payable (2) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Gain on Troubled Debt Restructuring (3) | 6,000,000 | |||
| Land | 16,000,000 | |||
| (To record restructuring of the debt) | ||||
Table (2)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $2,000,000.
(2)
Calculate the amount of gain on troubled debt restructuring.
Hence, gain on troubled debt restructuring amount is $6,000,000.
(3)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $20,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $2,000,000.
- Gain on troubled debt restructuring is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on troubled debt restructuring account for $6,000,000.
- Land is a non – current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit land account for $16,000,000.
(2)(a)
To Prepare: The journal entries to record forgive the interest accrued from last year.
(2)(a)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record forgive the interest accrued from last year of Bank FL.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Notes Payable | 1,000,000 | ||||
| January | 1 | |||||
| Interest Payable (4) | 2,000,000 | |||||
| Gain on Debt Restructuring (5) | 3,000,000 | |||||
| (To record restructuring of the debt) | ||||||
Table (3)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $2,000,000.
(4)
Calculate the amount of gain on troubled debt restructuring.
Hence, gain on debt restructuring amount is $3,000,000.
(5)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $2,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, interest payable account for $2,000,000.
- Gain on debt restructuring is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on debt restructuring account for $3,000,000.
2 (b)
To Prepare: The journal entry to revise interest payment on December 31, 2018, 2019, 2020 and 2021.
2 (b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record revise interest payment on December 31, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Notes Payable | 1,000,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,000,000 | ||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise interest payment) |
Table (4)
- Notes payable is a long term liabilities, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $1,000,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $1,000,000.
2 (c)
To Prepare: The journal entry to revise principal payment.
2 (c)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to revise the principal payment as on 31st December 2019.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Notes Payable(L–) | 15,000,000 | ||
| December | 31 | |||
| Cash (A–) | 15,000,000 | |||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise principal payment) | ||||
Table (5)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $15,000,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $15,000,000.
(3)
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the restructuring of the debt at January 1, 2016.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
The future payment of debt $27,775,000 is more than the present value of debt $22,000,000
Working note:
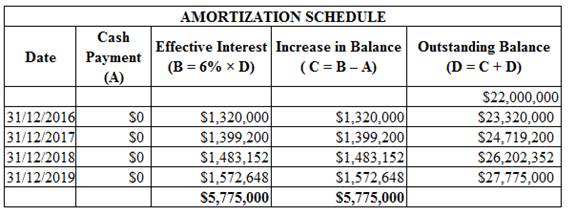
Figure (1)
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2016:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Interest Expense |
1,320,000 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,320,000 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (6)
Working notes:
Calculate the present value factor.
Hence, present value factor is 0.79208.
Find the interest rate from Table 2 (present value $1) in Appendix.
In row 4 of Table 2, the value of 0.79208 is in 6% column.
Hence, the effective rate of interest is 6%.
Calculate the amount of interest expense.
Hence, interest expense amount is $1,320,000.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,320,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,320,000.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2017:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Interest Expense | 1,399,200 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,399,200 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (7)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,399,200.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,399,200.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2018:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2018 | Interest Expense | 1,483,152 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,483,152 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (8)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,483,152.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,483,152.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2019:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Interest Expense | 1,572,648 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,572,648 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (9)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,572,648.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,572,648.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2019:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Notes Payable (L–) |
20,000,000 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable (6) | 7,775,000 | |||||
| Cash (A–) | 27,775,000 | |||||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise interest amount) | ||||||
Table (9)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $7,775,000.
(6)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $2,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, interest payable account for $7,775,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $27,775,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT PLUS
- Portland Pottery Inc. budgeted production of 78,500 vases for the year. Each vase requires glazing. Assume that 9 minutes are required to glaze each vase. If glazing labor costs $16.75 per hour, determine the direct labor cost budget for the year.arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper financial approach.arrow_forwardWhat Is the expected level of operating profits?arrow_forward
- Accurate answerarrow_forwardHello tutor please provide correct answer general accounting question with correct solution do fastarrow_forward33.What characterizes the accounting for involuntary conversions of fixed assets? A. Defer gain if asset is replaced B. Record as regular asset sale C. Recognize loss immediately D. Capitalize insurance proceeds solve thisarrow_forward
- ??arrow_forwardWhat is the ending inventory under variable costing? Financial accountingarrow_forwardDenton Medical Supply receives credit terms of 3/20, net 50 from one of its major suppliers. Assume 365 days in a year. What is the effective annual cost of trade credit if Denton does not take the discount? (Round your answer to two decimal places. Do not round intermediate calculations.)arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





