
1.
Troubled debt restructuring
When the unique terms of a debt agreement is encouraged by the financial complications by the debtor (borrower), the new agreement is referred to as a troubled debt restructuring. It includes some allowances on the part of the creditors (issuer).
To Prepare: The
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for gain on disposal of land.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| Land | 3,000,000 | |||||
| Gain on Disposal of Assets | 3,000,000 | |||||
| (To record gain on disposition of assets) | ||||||
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of gain on disposition.
Hence, gain on disposal of assets amount is $3,000,000.
- Land is a non – current asset, and it is increased. Therefore, debit land account for $3,000,000.
- Gain on disposal of asset is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on disposal of asset amount is $3,000,000.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Notes Payable | 20,000,000 | |||
| Interest Payable (2) | 2,000,000 | |||
| Gain on Troubled Debt Restructuring (3) | 6,000,000 | |||
| Land | 16,000,000 | |||
| (To record restructuring of the debt) | ||||
Table (2)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $2,000,000.
(2)
Calculate the amount of gain on troubled debt restructuring.
Hence, gain on troubled debt restructuring amount is $6,000,000.
(3)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $20,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $2,000,000.
- Gain on troubled debt restructuring is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on troubled debt restructuring account for $6,000,000.
- Land is a non – current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit land account for $16,000,000.
(2)(a)
To Prepare: The journal entries to record forgive the interest accrued from last year.
(2)(a)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record forgive the interest accrued from last year of Bank FL.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Notes Payable | 1,000,000 | ||||
| January | 1 | |||||
| Interest Payable (4) | 2,000,000 | |||||
| Gain on Debt Restructuring (5) | 3,000,000 | |||||
| (To record restructuring of the debt) | ||||||
Table (3)
Working notes:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $2,000,000.
(4)
Calculate the amount of gain on troubled debt restructuring.
Hence, gain on debt restructuring amount is $3,000,000.
(5)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $2,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, interest payable account for $2,000,000.
- Gain on debt restructuring is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is increased. Therefore, credit gain on debt restructuring account for $3,000,000.
2 (b)
To Prepare: The journal entry to revise interest payment on December 31, 2018, 2019, 2020 and 2021.
2 (b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record revise interest payment on December 31, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Notes Payable | 1,000,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,000,000 | ||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise interest payment) |
Table (4)
- Notes payable is a long term liabilities, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $1,000,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $1,000,000.
2 (c)
To Prepare: The journal entry to revise principal payment.
2 (c)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to revise the principal payment as on 31st December 2019.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Notes Payable(L–) | 15,000,000 | ||
| December | 31 | |||
| Cash (A–) | 15,000,000 | |||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise principal payment) | ||||
Table (5)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $15,000,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $15,000,000.
(3)
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the restructuring of the debt at January 1, 2016.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
The future payment of debt $27,775,000 is more than the present value of debt $22,000,000
Working note:
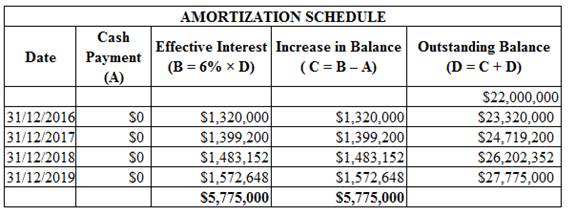
Figure (1)
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2016:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2016 | Interest Expense |
1,320,000 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,320,000 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (6)
Working notes:
Calculate the present value factor.
Hence, present value factor is 0.79208.
Find the interest rate from Table 2 (present value $1) in Appendix.
In row 4 of Table 2, the value of 0.79208 is in 6% column.
Hence, the effective rate of interest is 6%.
Calculate the amount of interest expense.
Hence, interest expense amount is $1,320,000.
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,320,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,320,000.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2017:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2017 | Interest Expense | 1,399,200 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,399,200 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (7)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,399,200.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,399,200.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2018:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2018 | Interest Expense | 1,483,152 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,483,152 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (8)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,483,152.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,483,152.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2019:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Interest Expense | 1,572,648 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable | 1,572,648 | |||||
| (To record interest expense) | ||||||
Table (9)
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $1,572,648.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $1,572,648.
The following is journal entry for restructuring of the debt at December 31, 2019:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Notes Payable (L–) |
20,000,000 | ||||
| December | 31 | |||||
| Interest Payable (6) | 7,775,000 | |||||
| Cash (A–) | 27,775,000 | |||||
| (To record restructuring of the debt to revise interest amount) | ||||||
Table (9)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of interest payable.
Hence, interest payable amount is $7,775,000.
(6)
- Notes payable is a long term liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $2,000,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and it is decreased. Therefore, interest payable account for $7,775,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $27,775,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting w/ Annual Report; Connect Access Card
- Accounting solutionarrow_forwardI need help with accountingarrow_forwardWhat are two double entries the following transaction? Account Receivable. Account payable. Rent Expenses. Cell phone bill, cable, light bill, gas, and monthly income of $4,000.00 what will be your net income after all expenses are paid. Please figure out your own price for each expense.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward
- I need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





