
Concept explainers
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (a).
Introduction: A group of skeletal muscles that was supplied by the facial nerves is termed as the facial muscles. They are involved in controlling facial expression. It is also termed as mimetic muscles and it includes zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, platysma, and occipitofrontalis muscle.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
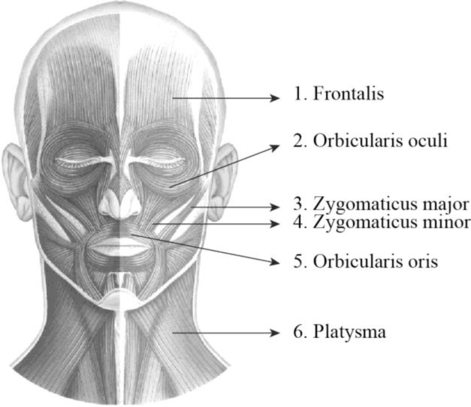
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
3. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
4. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
5. Orbicularis oris: Orbicularis oris is a facial muscle involved in controlling the lip and mouth movements. These muscles are originated from the bones of upper and lower jaw and palates. It is a sphincter muscle that specifically encircles the mouth. These muscles are involved in closing and pursing of lips.
6. Platysma: It is a wide, flat muscle that covers the entire anterior neck and the lower mandible and it ends on the chest. It depresses the mandible and tenses the skin of the neck.
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (c).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
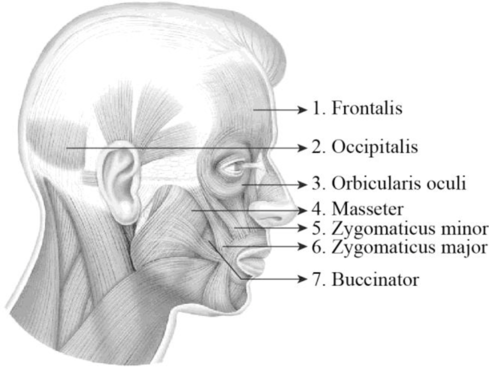
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Occipitalis: It is situated over the inferior portion of the occipital bone. It is innervated by the facial nerve and is involved in the back movement of the skull.
3. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
4. Masseter: The masseter is a facial muscle and it is located in the cheek area and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. It is a rectangular-shaped muscle and is situated in the anterior portion of the ear between the zygomatic arch and posterior part of the mandible. The main function of these muscles is the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
5. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
6. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
7. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (d).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
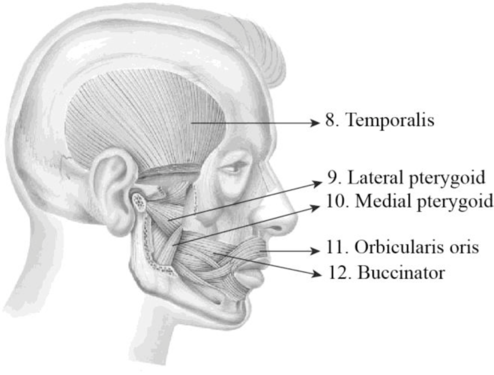
Explanation of Solution
8. Temporalis: The temporalis is a broad, fan-shaped muscle and it is located on each side of the head. It covers most of the temporal bone and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. The main function of these muscles is to move the lower jaw or mandible. It is specifically involved in the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
9. Lateral pterygoid: It is situated superior to the medial pterygoid and deep to masseter. It protracts, depresses, and moves the mandible in it sideways.
10. Medial pterygoid: It is situated inferior to the lateral pterygoid and deep to the masseter. It elevates, protrudes, and moves the mandibles in it sideways.
11. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
12. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion with WileyPLUS Blackboard Card Set
- Please indentify the unknown organismarrow_forwardPlease indentify the unknown organismarrow_forward5G JA ATTC 3 3 CTIA A1G5 5 GAAT I I3 3 CTIA AA5 Fig. 5-3: The Eco restriction site (left) would be cleaved at the locations indicated by the arrows. However, a SNP in the position shown in gray (right) would prevent cleavage at this site by EcoRI One of the SNPs in B. rapa is found within the Park14 locus and can be detected by RFLP analysis. The CT polymorphism is found in the intron of the Bra013780 gene found on Chromosome 1. The Park14 allele with the "C" in the SNP has two EcoRI sites and thus is cleaved twice by EcoRI If there is a "T" in that SNP, one of the EcoRI sites is altered, so the Park14 allele with the T in the SNP has only one EcoRI site (Fig. 5-3). Park14 allele with SNP(C) Park14 allele with SNPT) 839 EcoRI 1101 EcoRI 839 EcoRI Fig. 5.4: Schematic restriction maps of the two different Park14 alleles (1316 bp long) of B. rapa. Where on these maps is the CT SNP located? 90 The primers used to amplify the DNA at the Park14 locus (see Fig. 5 and Table 3 of Slankster et…arrow_forward
- From your previous experiment, you found that this enhancer activates stripe 2 of eve expression. When you sequence this enhancer you find several binding sites for the gap gene, Giant. To test how Giant interacts with eve, you decide to remove all of the Giant binding sites from the eve enhancer. What results do you expect to see with respect to eve expression?arrow_forwardWhat experiment could you do to see if the maternal gene, bicoid, is sufficient to form anterior fates?arrow_forwardYou’re curious about the effect that gap genes have on the pair-rule gene, evenskipped (eve), so you isolate and sequence each of the eve enhancers. You’re particularly interested in one of the enhancers, which is just upstream of the eve gene. Describe an experimental technique you would use to find out where this particular eve enhancer is active.arrow_forward
- For short answer questions, write your answers on the line provided. To the right is the mRNA codon table to use as needed throughout the exam. First letter U บบบ U CA UUCPhe UUA UCU Phe UCC UUG Leu CUU UAU. G U UAC TV UGCys UAA Stop UGA Stop A UAG Stop UGG Trp Ser UCA UCG CCU] 0 CUC CUA CCC CAC CAU His CGU CGC Leu Pro CCA CAA Gin CGA Arg CUG CCG CAG CGG AUU ACU AAU T AUC lle A 1 ACC Thr AUA ACA AUG Mot ACG AGG Arg GUU GCU GUC GCC G Val Ala GAC Asp GGU GGC GUA GUG GCA GCG GAA GGA Gly Glu GAGJ GGG AACASH AGU Ser AAA1 AAG Lys GAU AGA CAL CALUCAO CAO G Third letter 1. (+7) Use the table below to answer the questions; use the codon table above to assist you. The promoter sequence of DNA is on the LEFT. You do not need to fill in the entire table. Assume we are in the middle of a gene sequence (no need to find a start codon). DNA 1 DNA 2 mRNA tRNA Polypeptide C Val G C. T A C a. On which strand of DNA is the template strand (DNA 1 or 2)?_ b. On which side of the mRNA is the 5' end (left or…arrow_forward3. (6 pts) Fill in the boxes according to the directions on the right. Structure R-C R-COOH OH R-OH i R-CO-R' R R-PO4 R-CH3 C. 0 R' R-O-P-OH 1 OH H R-C-H R-N' I- H H R-NH₂ \H Name Propertiesarrow_forward4. (6 pts) Use the molecule below to answer these questions and identify the side chains and ends. Please use tidy boxes to indicate parts and write the letter labels within that box. a. How many monomer subunits are shown? b. Box a Polar but non-ionizable side chain and label P c. Box a Basic Polar side chain and label BP d. Box the carboxyl group at the end of the polypeptide and label with letter C (C-terminus) H H OHHO H H 0 HHO H-N-CC-N-C-C N-C-C-N-GC-OH I H-C-H CH2 CH2 CH2 H3C-C+H CH2 CH2 OH CH CH₂ C=O OH CH2 NH2arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





