
Concept explainers
The scale of the first vertical aerial photograph and the flying height of both the photographs.
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
Take two control points on a vertical aerial photograph:
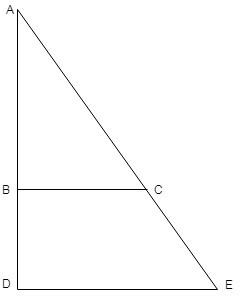
Let the length of DE
We have been given the value of BC
For scale two the value of X is found as follows:
Substituting the values, we get
Now, the value of BC
We have the following formula, for scale first:
Substituting the values, we get
Implying that the scale of the first vertical photograph is
Now, the flying height
Where,
The flying height of the first photograph is,
Now, the flying height
Where,
The flying height of the first photograph is,
Conclusion:
Therefore,the scale of the first vertical photograph is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Traffic And Highway Engineering
- Draw Isometric view of this multiview of object.arrow_forwardREMINDER: The truss must be cut into two different sections. You can choose either one to solve as you will get the same answer. Since there are three equations available, you can't cut more than three members 6.25 Determine the force in members BD, CD, and CE of the truss shown. BO C 36 kips 36 kips D F H 7.5 ft E G 4 panels at 10 ft = 40 ftarrow_forwardCalculate the area of the following polygon using the abscissa and projection method, taking into account the necessary adjustments before calculating the area of the polygon using the compass rule. Latitude Departure Side 930.63 N 930.63 S 1272 E 1271 W AB 122.14 E=12/2-1271-1 cr=-1 680 BC 173.83 length 591 CD 669.13 109.08 DE 139.36 961.1 EA 756.80 201.82 330.63/ 430.65 DEP=L SIN (O) >L DEP/SIN(O) LAT = L COS (0) DEPILATESIN(OYCOS (0)= TAN (0) O TAN-1 (DEP/LAT)= asztan Deptarrow_forward
- Estimate the material quantities (cement, sand, gravel, and steel reinforcement) required for constructing 120 m concrete channel of the following typical cross section, concrete mix of 1:1.5:3 and thickness of 20 cm. Figure (1) Figure (1) 12250- 16300arrow_forwarda) A 14-ft. tall and12-ft.-8-in. long fully grouted reinforced masonry wall is constructed of 8-in.CMU. It is to be analyzed for out-of-plane loading. Construct thenP -nM curves for the wallwith the following three vertical reinforcement scenarios: (1) 10 No. 6 bars at 16 in. spacing,(2) 10 No. 5 bars at 16 in. spacing, and (3) 7 No. 4 bars at 24 in. spacing. The steel is Grade60 with a modulus of elasticity of 29,000 ksi, and the masonry has a compressive strength of2,000 psi. You may use Excel or Matlab to construct the curves. Also, show the maximumnPallowed by the code for each case.(b) For each of the above reinforcement scenarios, determine the maximum axial loads that arepermitted for the tension-controlled condition and transition condition.(c) Discuss how the amount of vertical reinforcement affects thenPn-Mn curve.arrow_forwardYOU HAVE SET YOUR LEVEL UP AND ARE UTILIZING CP-101 ELEVATION FOR YOUR BENCHMARK AND HAVE THE FOLLOWING READING:CP-101=6.02YOUR FORM ELEVATION READINGS ("ATTACHED")( BEGINNING AT THE NORTHEAST BUILDING CORNER)AND WORKING IN A CLOCKWISE DIRECTION CHECKING THE BUILDING CORNER FORMSARE AS FOLLOWS: (CALCULATE THE ELEVATIONS OF 1-6 BELOW) 1. NE COR. = 1.152. SE COR. = 1.153. SW COR. = 1.354. (N) SW COR. = 1.155. INTERIOR = 1.306. NW COR. = 1.15arrow_forward
- a) A 14-ft. tall and12-ft.-8-in. long fully grouted reinforced masonry wall is constructed of 8-in.CMU. It is to be analyzed for out-of-plane loading. Construct thenP -nM curves for the wallwith the following three vertical reinforcement scenarios: (1) 10 No. 6 bars at 16 in. spacing,(2) 10 No. 5 bars at 16 in. spacing, and (3) 7 No. 4 bars at 24 in. spacing. The steel is Grade60 with a modulus of elasticity of 29,000 ksi, and the masonry has a compressive strength of2,000 psi. You may use Excel or Matlab to construct the curves. Also, show the maximumnPallowed by the code for each case.(b) For each of the above reinforcement scenarios, determine the maximum axial loads that arepermitted for the tension-controlled condition and transition condition.(c) Discuss how the amount of vertical reinforcement affects thenPn - Mn curve.arrow_forwardIf you could help me answer these questions in matlab that would be great, I provided an additional picture detailing what the outcome should look like.arrow_forwardA fully grouted reinforced masonry wall is to be constructed of 8-in. CMU. The wall height is 18feet. It is assumed to be simply supported. The wall is to be designed for an out-of-plane seismicload of 52 lbs./ft.2, which can act in either direction. The wall also supports a roof dead load of600 lbs./ft. and a roof live load of 300 lbs./ft. along the wall length. The roof loads have aneccentricity of 2.5 inches. Since there is seismic load, load combinations (6) and (7) in Chapter 2of ASCE 7-22 should be considered. In these two load combinations,horizontal seismic loadhE =andvertical seismic loadvE = . You may ignorevE in this problem for simplicity. The masonryhas a specified compressive strength of 2,500 psi. (a) Use the strength design provisions of TMS402 to determine the size and spacing of the vertical bars needed. Use the P-δ analysis method inSection 9.3.4.4.2 of TMS 402 to determine Mu. (b) Repeat the design using the momentmagnification method in Section 9.3.4.4.3 instead.arrow_forward
- The factor of safety for tipping of the concrete dam is defined as the ratio of the stabilizing moment due to the dam's weight divided by the overturning moment about OO due to the water pressure (Figure 1). Suppose that aa = 5 mm , dd = 2 mm , hh = 7 mm . The concrete has a density of ρconcρconc = 2.5 Mg/m3Mg/m3 and for water ρwρw = 1 Mg/m3Mg/m3arrow_forwardcan you answer both plss, i will give u a likearrow_forward*1-4. The hollow core panel is made from plain stone concrete. Determine the dead weight of the panel. The holes each have a diameter of 100 mm. 200 mm 300 mm 300 mm 300 mm 300 mm 300 mm Prob. 1-4 300 mm 4 marrow_forward
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning





