
Concept explainers
Propose structures for compounds that fit the following 1H NMR data:
(a) C4H6Cl2
2.18 δ (3 H, singlet)
4.16 δ (2 H, doublet, J=7 Hz)
5.71 δ (1 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
(b) C10H14
1.30 δ (9 H, singlet)
7.30 δ (5 H, singlet)
(c) C4H7BrO
2.11 δ (3 H, singlet)
3.52 δ (2 H, triplet, J=6 Hz)
4.40 δ (2 H, triplet, J=6 Hz)
(d) C9H11Br
2.15 δ (2 H, quintet, J=7 Hz)
2.75 δ (2 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
3.38 δ (2 H, triplet, J=7 Hz)
7.22 δ (5 H, singlet)
a)

Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
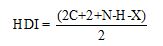
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the 1HNMR spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
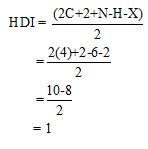
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C10H14 is 6.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.18ppm(3H, singlet)
4.16ppm(2H, doublet, J=7HZ)
5.71ppm(1H , triplet, J=7HZ)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (one level of unsaturation). The total integration value (3+2+1=6 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
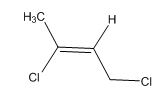
A signal at 2.18ppm with integration of 3H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.
A signal with integration of 2H’s represent a methylene group appears at 4.16ppm rather 5.17ppm, consistent with the value of protons which present at alpha position to vinyl group (C=O) and accounts for the one degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via no reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally three signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of spectrum and DHI calculation.
b)
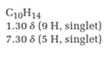
Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
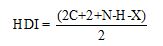
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the 1HNMR spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
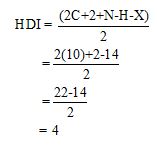
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C10H14 is 14.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
1.30ppm(9H, singlet)
7.30ppm(5H, singlet)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (four level of unsaturation). The total integration value (9+5=14 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
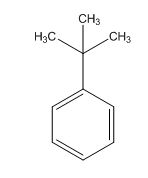
A signal at 1.30ppm with integration of 9H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.
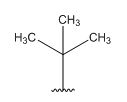
A signal with integration of 5H’s represent a benzene appears at 7.30ppm which present at aromatic group and accounts for the four degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally two signals in 1HNMR spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
c)

Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
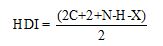
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
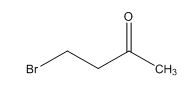
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
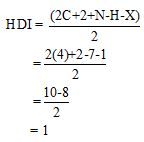
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C4H7Bro is 7.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.11ppm(3H, singlet)
3.52ppm(2H, triplet, J=6HZ)
4.40ppm(2H, triplet, J=6HZ)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (one level of unsaturation). The total integration value (3+2+2=7 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
A signal at 2.11ppm with integration of 3H’s represents methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of isopropyl group.

A two signal with integration of 2H’s represent a methylene group appears at 3.52ppm rather 4.40ppm, consistent with the value of protons which present at alpha position to carbonyl group(C=O) and accounts for the one degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via no reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally three signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
d)
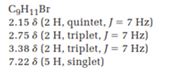
Interpretation:
The proposed structure of the compound to be identified for the given 1HNMR spectrum.
Concept introduction:
HDI calculation:
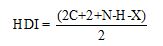
Where
C represent number of carbons.
N represent number of nitrogens.
H represent number of hydrogens.
X represent number of halogens.
Chemical shift: The frequency of the proton signal in the spectrum with reference to the standard compound which may be TMS(Tetramethylsilane) shows signal at 0 ppm(parts per million).
Multiplicity: The number of peaks on the each signal in NMR spectrum is defined as multiplicity; the multiplicity of each signal indicates the neighboring protons. It is generated by coupling of the subjected protons with the neighboring protons (both subjected and neighbor protons are to be chemically not equivalent) separated by either two or three sigma bonds.
Rule: Multiplicity of each signal is calculated using (n+1) rule only when the neighboring protons are chemically equivalent to each other.
(n+1)
where
n indicates number of neighboring protons
Integration value (I): The integration value at the bottom of the spectrum represents the number of protons giving rise to the signal.
To find:
The structure of the compound to be identified for the given molecular formula and 1HNMR spectrum.
Answer to Problem 55GP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI value:
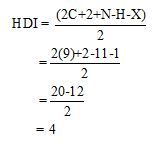
The HDI calculation confirms the presence of an aliphatic ring and double bond
Adjust the relative integration with the number of protons from the molecular formula.
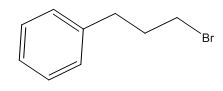
The total number of protons in the molecular formula C9H11Br is 11.
Interpret the given information.
Given information:
Three signals with multiplicity and integration values.
2.15ppm(2H, quintet, J=7HZ)
2.75ppm(2H, triplet, J=7HZ)
3.38ppm(2H, triplet, J=7HZ)
7.22ppm(5H, singlet)
The HDI value confirms the compound has either a ring or a double bond (four level of unsaturation). The total integration value (2+2+2+5=11 protons) is also an exact value with the protons of the molecular formula.
A signal at 2.15ppm with integration of 2H’s represents three methyl groups which are chemically equivalent having one neighboring proton indicates the characteristic pattern of alkyl group.
A signal with integration of 2H’s represent benzylic appears at 2.75ppm which present at aromatic group
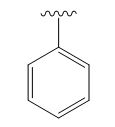
A signal with integration of 5H’s represent benzylic appears at 7.30ppm which present at aromatic group and accounts for the four degree of unsaturation.
The overall predicted structure is:

The methyl groups can be interchanged via reflectional symmetry and the compound gives rise to totally four signals in spectrum.
The structure of the compound is identified using the details of 1HNMR spectrum and DHI calculation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Student Value Bundle: Organic Chemistry, + OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card (NEW!!)
- The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forwardion. A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io : :0: : Cl : - - : :0: ك Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom central O formal charge ☐ top O ☐ right O ☐ bottom O ☐ Cl ☐arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Yes. Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Cl- : 2: :Z: :Z: N—N : 0: C C1: O CO No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". ☑arrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions ΔΗ is (pick one) A This reaction is faster above 103. °C than below. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous only above -9. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) C The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous. AS is (pick one) 18 Ararrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + H CH3CH2OH HCI Drawingarrow_forwardplease explain this in simple termsarrow_forwardK Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward
- (2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forwardDecide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

