
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The structure of an given molecular formula C8H16 to be predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
Concept introduction:
The 13CNMR spectrum gives information on the different electronic environments of carbon. As like 1HNMR, the number of signals generated in 13CNMR are predicted by performing symmetry operations (rotation or reflection symmetry). Only chemical shift values are reported in the spectrum but not the multiplicity and integration values because the coupling between two neighboring 13C - 13C nuclei are weakly involved due to the low abundance of 13C isotopes of carbon atom.
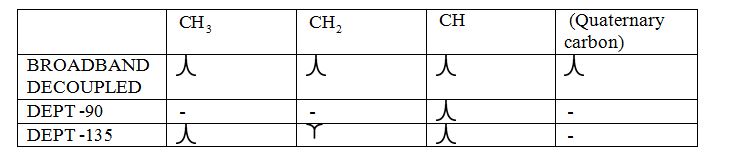
Broadband-decoupled 13CNMR spectrum: The spectra provide information regarding the total number of carbon environments.
DEPT (Distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer):
i) DEPT -90: The spectrum exhibits signal only from CH group and no signals from CH3, CH2, CH and quaternary carbon (carbon with no protons).
ii) DEPT -135: The spectrum exhibits CH3 groups and CH groups as positive signals (pointing up); CH2 groups appear as negative signals (pointing down) and quaternary carbon does not appear.
The signals appear in each type of spectrum:
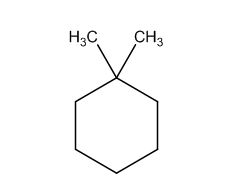
To identify:
The structure of given molecular formula C8H16.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
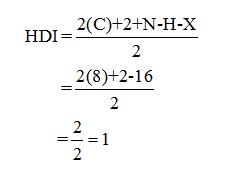
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the presence of a double bond or a ring.
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows five signals whereas the given molecular formula also has eight carbon atoms. Thus all the eight carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The five signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene or Methine groups.
DEPT -90: Spectrum has no signals led to confirmation of no CH group in the structure.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, CH3 and C groups):
ii) The two positive signals indicate the presence of two methyl groups as no signals appear in the DEPT -90 spectrum.
iii) The three negative signals indicate the presence of four methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iv) So far the group of fragments obtained is
Two -CH3, -C-, four -CH2
From the fragments (CH3 + CH3 + (CH2)5 + C = 16 protons) sixteen protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also sixteen.
The possible structures are:
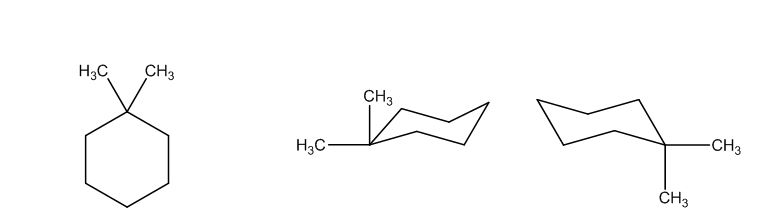
The first structure possesses rotational symmetry and exhibits fewer signals in the spectrum and gets cancelled out.
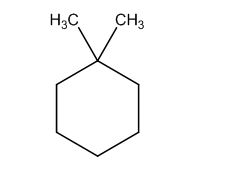
The structure of a given molecular formula C8H16 is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
b)
To identify:
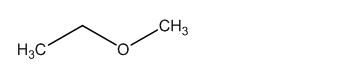
The structure of given molecular formula C3H8O.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
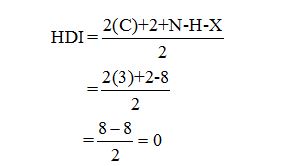
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the absence of a double bond or a ring.
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows three signals whereas the given molecular formula also has three carbon atoms. Thus all the three carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The two signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene groups.
DEPT -90: Spectrum has no signals led to confirmation of no CH group in the structure.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, CH3 groups):
ii) The two positive signals indicate the presence of two methyl groups as no signals appear in the DEPT -90 spectrum.
iii) The one negative signals indicate the presence of methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iv) So far the group of fragments obtained is
Two -CH3, -CH2
From the fragments (CH3 + CH3 + CH2 = 8 protons) eight protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also eight.
The structure of a given molecular formula C3H8O is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
c)
To identify:
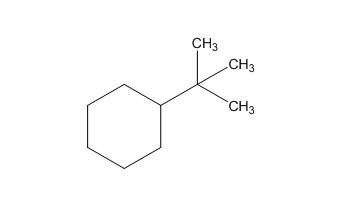
The structure of given molecular formula C10H20.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
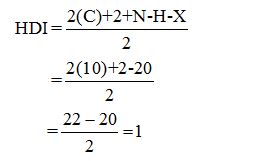
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the presence of a double bond or a ring.
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows six signals whereas the given molecular formula also has ten carbon atoms. Thus all the ten carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The two signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene groups.
DEPT -90: Spectrum has signals led to confirmation of CH group in the structure.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, C, CH3 groups):
ii) The two positive signals indicate the presence of three methyl groups as no signals appear in the DEPT -90 spectrum.
iii) The three negative signals indicate the presence of five methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iv) So far the group of fragments obtained is
Two -CH3, -CH2
From the fragments (CH3)3 + (CH2)5 + CH + C = 20 protons) twenty protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also twenty.
The structure of a given molecular formula C10H20 is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
d)
To identify:
The structure of given molecular formula C6H10.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
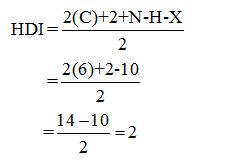
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the presence of a double bond or a ring. (two unsaturated degree).
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows six signals whereas the given molecular formula also has six carbon atoms. Thus all the six carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The two signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene groups.
DEPT -90: Spectrum has signals led to confirmation of CH group in the structure.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, C, CH3 groups):
ii) The four positive signals indicate the presence of two methyl groups as no signals appear in the DEPT -90 spectrum.
iii) The negative signals indicate the presence of methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iv) So far the group of fragments obtained is
Two -CH3, -CH2
From the fragments (CH3)2 + CH2 + (CH)2 + C = 10 protons) ten protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also ten.
The structure of a given molecular formula C6H10 is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
e)
To identify:
The structure of given molecular formula C8H16.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
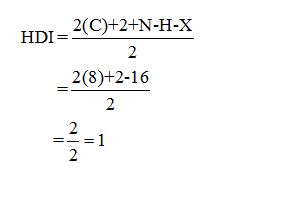
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the presence of a double bond or a ring.
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows four signals whereas the given molecular formula also has eight carbon atoms. Thus all the eight carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The four signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene or Methine groups.
DEPT -90: Spectrum has no signals led to confirmation of CH group in the structure.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, CH3 and CH groups):
ii) The two positive signals indicate the presence of two methyl groups as no signals appear in the DEPT -90 spectrum.
iii) The two negative signals indicate the presence of four methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iv) So far the group of fragments obtained is
Two -CH3, -CH-, four -CH2
From the fragments (CH3 + CH3 + (CH2)4 + (CH)2 = 16 protons) sixteen protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also sixteen.
The structure of a given molecular formula C8H16 is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
f)
To identify:
The structure of given molecular formula C6H10O.
Answer to Problem 48AP
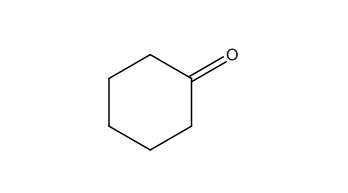
Explanation of Solution
Calculate HDI:
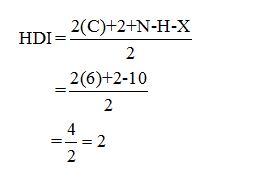
The HDI calculation led to confirm about the presence of a double bond or a ring.
Interpret the given 13CNMR spectrum:
Broadband - decoupled spectrum:
The spectrum shows four signals whereas the given molecular formula also has six carbon atoms. Thus all the six carbons have chemically different electronic environments showing signals.
i) The four signals in the region of 0-50ppm indicate the sp3 hybridized carbon atoms which can be methyl / methylene or Methine groups.
DEPT -135 (gives signals of CH2, C groups):
ii) The two negative signals indicate the presence of four methylene groups; only methylene groups appear negative in the spectrum.
iii) So far the group of fragments obtained is
C=O, -C-, four -ch2
From the fragments (CH2)5 + C = 10 protons) ten protons are obtained whereas the total number of protons from the molecular formula is also ten.
The structure of a given molecular formula C6H10O is predicted using 13CNMR spectra.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Which of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forwardCan I get help drawing my arrows #2arrow_forward
- Can I get some help with my arrows? I have included what the final outcome needs to look like. #3arrow_forwardPlease explain how to calculate the pH.arrow_forwardI'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forward

 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



