
Essential University Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134988559
Author: Wolfson, Richard
Publisher: Pearson Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.6, Problem 13.6GI
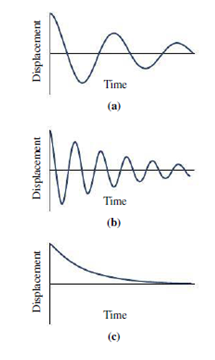
The figure shows displacement-versus-time graphs for three mass-spring systems, with different masses m, spring constants k, and damping constants b. The time on the horizontal axis is the same for all three. (1) For which system is damping the most significant? (2) For which system is damping the least significant?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are tasked with designing a parallel-plate capacitor using two square metal plates, eachwith an area of 0.5 m², separated by a 0.1 mm thick layer of air. However, to increase the capacitance,you decide to insert a dielectric material with a dielectric constant κ = 3.0 between the plates. Describewhat happens (and why) to the E field between the plates when the dielectric is added in place of theair.
Calculate the work required to assemble a uniform charge Q on a thin spherical shell of radiusR. Start with no charge and add infinitesimal charges dq until the total charge reaches Q, assuming thecharge is always evenly distributed over the shell’s surface. Show all steps.
Rod AB is fixed to a smooth collar D, which slides freely along the vertical guide shown in (Figure 1). Point C is
located just to the left of the concentrated load P = 70 lb. Suppose that w= 17 lb/ft. Follow the sign convention.
Part A
Figure
3 ft
-1.5 ft
√30°
1 of 1
Determine the normal force at point C.
Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Η vec
Nc=
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Determine the shear force at point C.
Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.
VC=
ΜΕ ΑΣΦΗ
vec
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
Determine the moment at point C.
Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures.
Mc=
Ο ΑΣΦ Η
vec
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
?
lb
lb
?
lb-ft
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential University Physics
Ch. 13.1 - A typical human heart rate is about 65 beats per...Ch. 13.2 - Two identical mass-spring systems are displaced...Ch. 13.3 - What happens to the period of a pendulum if (l)...Ch. 13.4 - Figure 13.18 shows the paths traced in the...Ch. 13.5 - Two different mass-spring systems are oscillating...Ch. 13.6 - The figure shows displacement-versus-time graphs...Ch. 13.7 - The photo shows a wineglass shattering in response...Ch. 13 - The vibration frequencies of molecules are much...Ch. 13 - What happens to the frequency of a simple harmonic...Ch. 13 - How does the frequency of a simple harmonic...
Ch. 13 - How would the frequency of a horizontal massspring...Ch. 13 - When in its cycle is the acceleration of an...Ch. 13 - One pendulum consists of a solid rod of mass m and...Ch. 13 - Why is critical damping desirable in a cars...Ch. 13 - Explain why the frequency of a damped system is...Ch. 13 - Opera singers have been known to break glasses...Ch. 13 - What will happen to the period of a massspring...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11ECh. 13 - A violin string playing the note A oscillates at...Ch. 13 - The vibration frequency of a hydrogen chloride...Ch. 13 - The top of a skyscraper sways back and forth,...Ch. 13 - A hummingbirds wings vibrate at about 45 Hz. Whats...Ch. 13 - A 200-g mass is attached to a spring of constant k...Ch. 13 - An automobile suspension has an effective spring...Ch. 13 - A 342-g mass is attached to a spring and undergoes...Ch. 13 - A particle undergoes simple harmonic motion with...Ch. 13 - How long should you make a simple pendulum so its...Ch. 13 - At the heart of a grandfather clock is a simple...Ch. 13 - A 622-g basketball with 24.0-cm diameter is...Ch. 13 - A meter stick is suspended from one end and set...Ch. 13 - A wheel rotates at 600 rpm. Viewed from the edge,...Ch. 13 - The x- and y-components of an objects motion are...Ch. 13 - A 450-g mass on a spring is oscillating at 1.2 Hz....Ch. 13 - A torsional oscillator of rotational inertia 1.6...Ch. 13 - Prob. 28ECh. 13 - The vibration of a piano string can be described...Ch. 13 - A massspring system has b/m = 0/5, where b is the...Ch. 13 - A cars front suspension has a natural frequency of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 32ECh. 13 - Prob. 33ECh. 13 - Prob. 34ECh. 13 - Example 13.2: Repeal the preceding problem, now...Ch. 13 - Example 13.5: A mass–spring system is oscillating...Ch. 13 - Prob. 37ECh. 13 - Example 13.5: A sample pendulum is swinging with...Ch. 13 - Example 13.5: A simple pendulum of muss m is...Ch. 13 - A simple model for carbon dioxide consists of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 41PCh. 13 - The human eye and muscles that hold it can be...Ch. 13 - A mass m slides along a frictionless horizontal...Ch. 13 - Prob. 44PCh. 13 - A physics student, bored by a lecture on simple...Ch. 13 - A pendulum of length L is mounted in a rocket....Ch. 13 - The protein dynein powers the flagella that propel...Ch. 13 - A mass is attached to a vertical spring, which...Ch. 13 - Derive the period of a simple pendulum by...Ch. 13 - A solid disk of radius R is suspended from a...Ch. 13 - A thin steel beam is suspended from a crane and is...Ch. 13 - A cyclist turns her bicycle upside down to repair...Ch. 13 - An object undergoes simple harmonic motion in two...Ch. 13 - The muscles that drive insect wings minimize the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 55PCh. 13 - If Jane and Tarzan are initially 8.0 m apart in...Ch. 13 - A small mass measuring device (SMMD) used for...Ch. 13 - A thin, uniform hoop of mass M and radius R is...Ch. 13 - A mass m is mounted between two springs with...Ch. 13 - Prob. 60PCh. 13 - Show that the potential energy of a simple...Ch. 13 - The total energy of a massspring system is the sum...Ch. 13 - A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is mounted...Ch. 13 - A mass m is free to slide on a frictionless track...Ch. 13 - A 250-g mass is mounted on a spring of constant k...Ch. 13 - A harmonic oscillator is underdamped if the...Ch. 13 - A massless spring with k = 74 N/m hangs from the...Ch. 13 - A meter stick is suspended from a frictionless rod...Ch. 13 - A particle of mass m has potential energy given by...Ch. 13 - Two balls with the same unknown mass m are mounted...Ch. 13 - Two mass-spring systems with the same mass are...Ch. 13 - Two mass-spring systems have the same mass and the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 73PCh. 13 - A 500-g block on a frictionless, horizontal...Ch. 13 - Repeat Problem 64 for a small solid ball of mass M...Ch. 13 - A disk of radius R is suspended from a pivot...Ch. 13 - Youre a structural engineer working on a design...Ch. 13 - Show that x(t) = a cos t bsin t represents simple...Ch. 13 - Youre working for the summer with an ornithologist...Ch. 13 - While waiting for your plane to take off, you...Ch. 13 - Youre working for a playground equipment company,...Ch. 13 - The pendulum in an antique clock consists of a...Ch. 13 - This problem explores the nonlinear pendulum...Ch. 13 - Physicians and physiologists are interested in the...Ch. 13 - Physicians and physiologists are interested in the...Ch. 13 - Physicians and physiologists are interested in the...Ch. 13 - Physicians and physiologists are interested in the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The distances you obtained in Question 3 are for only one side of the ridge. Assuming that a ridge spreads equa...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
For the reaction shown, find the limiting reactant for each of the initial quantities of reactants. 4Al(s)+3O2(...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R with total charge Q, centered at the origin inthe xy-plane. Find the electric field (as a vector) at a point on the z-axis at a distance z above thecenter of the ring. Assume the charge density is constant along the ring.arrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wx fuc, then use equation Vs VA + Ve/athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) 0.5 m B 1 m 60° A 45° vc = 3 m/sarrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wxf, then use equation V, VA + Va/Athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) f-3marrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward14. A boy is out walking his dog. From his house, he walks 30 m North, then 23 m East, then 120 cm South, then 95 m West, and finally 10 m East. Draw a diagram showing the path that the boy walked, his total displacement, and then determine the magnitude and direction of his total displacement.arrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward12. A motorboat traveling 6 m/s, West encounters a water current travelling 3.5 m/s, South. a) Draw a vector diagram showing the resultant velocity, then determine the resultant velocity of the motorboat. b) If the width of the river is 112 m wide, then how much time does it take for the boat to travel shore to shore? c) What distance downstream does the boat reach the opposite shore?arrow_forwardLake Erie contains roughly 4.00⋅10114.00⋅1011 m3 of water. Assume the density of this water is 1000. kg/m3 and the specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg˚C. It takes 2.31x10^19 J of energy to raise the temperature of that volume of water from 12.0 °C to 25.8 ˚C. An electric power plant can produce about 1110 MW. How many years would it take to supply this amount of energy by using the 1110 MW from an electric power plant?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY