
Concept explainers
a.
To construct:a
a.
Answer to Problem 7E
Explanation of Solution
Given information: the
Formula Used:the formulas to be used when constructing a confidence interval for a mean response and when constructing a prediction interval for an individual response.
Let
Here, the critical value
Let
Here, the critical value
the predicted value corresponding to
The t table corresponding t-value for the given confidence interval
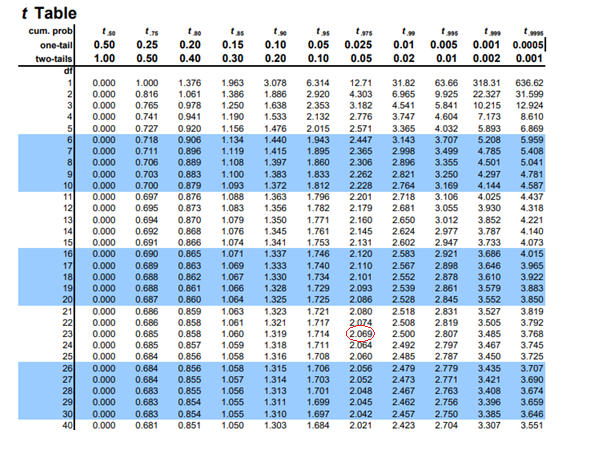
Now to construct prediction interval for the mean response.
b.
To construct: a
b.
Answer to Problem 7E
Explanation of Solution
Given information: the sample size
Formula Used:the formulas to be used when constructing a confidence interval for a mean response and when constructing a prediction interval for an individual response.
Let
Here, the critical value
Let
Here, the critical value
the predicted value corresponding to
The t table corresponding t-value for the given confidence interval
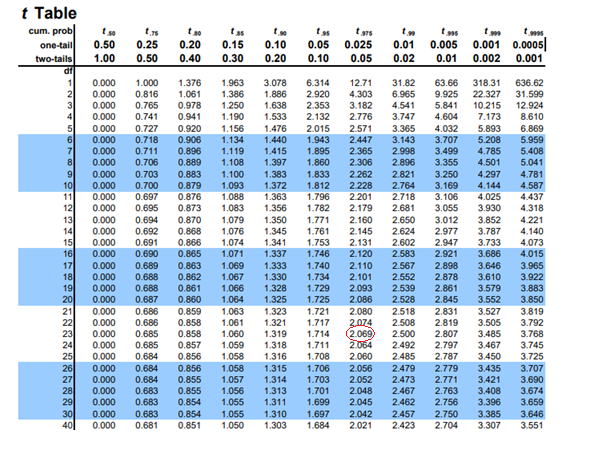
Now to construct prediction interval for the individual response.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition
- Given your fitted regression line, what would be the residual for snake #5 (10 C)?arrow_forwardCalculate the 95% confidence interval around your estimate of r using Fisher’s z-transformation. In your final answer, make sure to back-transform to the original units.arrow_forwardCalculate Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) between temperature and heart rate.arrow_forward
- A researcher wishes to estimate, with 90% confidence, the population proportion of adults who support labeling legislation for genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Her estimate must be accurate within 4% of the true proportion. (a) No preliminary estimate is available. Find the minimum sample size needed. (b) Find the minimum sample size needed, using a prior study that found that 65% of the respondents said they support labeling legislation for GMOs. (c) Compare the results from parts (a) and (b). ... (a) What is the minimum sample size needed assuming that no prior information is available? n = (Round up to the nearest whole number as needed.)arrow_forwardThe table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.05, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? Click on the icon to view the data table. Let Hss, HMS, HLS, Hsuv and Hмy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDs, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? OA. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Ha Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV B. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV = μMV Ha: Hss *HMS *HLS*HSUV * HMV C. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV =μMV = = H: Not all the means are equal. D. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV Ha Hss HMS HLS =HSUV = HMVarrow_forwardQuestion: A company launches two different marketing campaigns to promote the same product in two different regions. After one month, the company collects the sales data (in units sold) from both regions to compare the effectiveness of the campaigns. The company wants to determine whether there is a significant difference in the mean sales between the two regions. Perform a two sample T-test You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. (2 points = 0.5 x 4 Answers) Each of these is worth 0.5 points. However, showing the calculation is must. If calculation is missing, the whole answer won't get any credit.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
