
a.
Prepare a worksheet for statement of
a.
Explanation of Solution
Spreadsheet: A spreadsheet is a worksheet. It is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
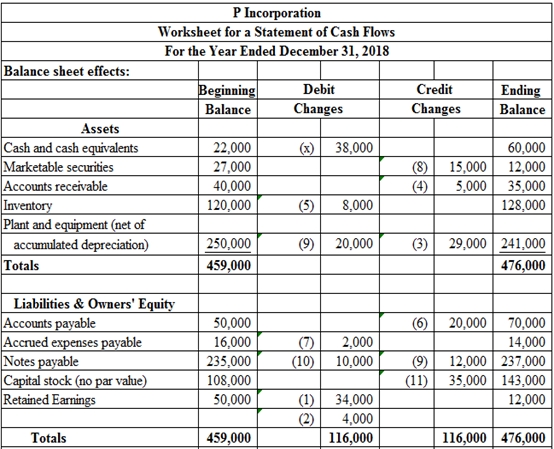
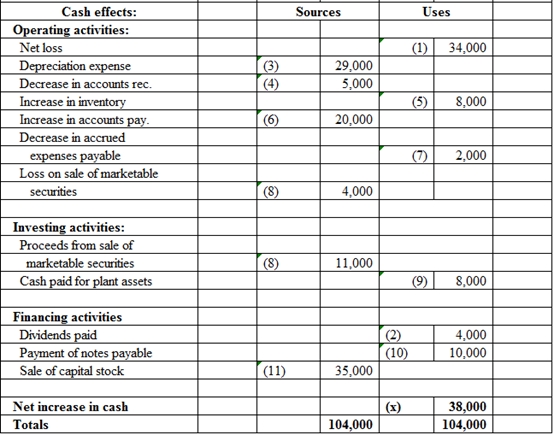
Table (1)
b.
Prepare a formal statement of cash flows for 2018.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows: Statement of cash flows reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
Indirect method: Indirect method uses the accrual basis of accounting, where the Net Income is adjusted to determine the net cash provided from operating activities.
Cash flows from operating activities: Operating activities refer to the normal activities of a company to carry out the business.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from operating activities:
| Cash flows from operating activities (Indirect method) |
| Add: Decrease in current assets |
| Increase in current liability |
| |
| Loss on sale of plant assets |
| Deduct: Increase in current assets |
| Decrease in current liabilities |
| Gain on sale of plant assets |
| Net cash provided from or used by operating activities |
Table (2)
Cash flows from investing activities: Cash provided by or used in investing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes the purchase or sale of equipment or land, or marketable securities, which is used for business operations.
| Cash flows from investing activities |
| Add: Proceeds from sale of fixed assets |
| Sale of marketable securities / investments |
| Deduct: Purchase of fixed assets/long-lived assets |
| Purchase of marketable securities |
| Net cash provided from or used by investing activities |
Table (3)
Cash flows from financing activities: Cash provided by or used in financing activities is a section of statement of cash flows. It includes raising cash from long-term debt or payment of long-term debt, which is used for business operations.
| Cash flows from financing activities |
| Add: Issuance of common stock |
| Proceeds from borrowings |
| Proceeds from sale of |
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
| Deduct: Payment of dividend |
| Repayment of debt |
| Interest paid |
| Redemption of debt |
| Purchase of treasury stock |
| Net cash provided from or used by financing activities |
Table (4)
Non-Cash Transactions:
The transaction, which does not involve any cash dealings, is known as non-cash transactions. In these type transactions there will not be any inflow or outflow of cash. Simply put, the transaction, which does not have an impact on the inflow or outflow of cash, is called as non-cash transactions.
Examples of significant non-cash transactions are stated below:
- Issue of common stock to retire long-term debt.
- Purchase of machinery by issuing notes payable.
- Issuance of common stock for purchase of land.
| P Incorporation | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows - Indirect Method (Partial) | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Details | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||
| Net loss | (34,000) | |
| Adjustment to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||
| Depreciation expense | 29,000 | |
| Decrease in accounts receivable | 5,000 | |
| Increase in inventory | (8,000) | |
| Decrease in accrued expenses | (2,000) | |
| Increase in accounts payable | 20,000 | |
| Loss on sales of marketable securities | 4,000 | 48,000 |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 14,000 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||
| Cash paid to acquire plant assets | (8,000) | |
| Proceeds from sales of marketable securities | 11,000 | |
| Net cash provided by investing activities | 3,000 | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||
| Dividend paid | (4,000) | |
| Payment of note payable | (10,000) | |
| Issuance of capital stock | 35,000 | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 21,000 | |
| Net increase (decrease) in Cash | 38,000 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, January 1, 2018 | 22,000 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, December 31, 2018 | $60,000 | |
| Schedule of Noncash Investing and Financing Activities | ||
| Purchase of plant assets | $20,000 | |
| Less: Portion financed by issuing long-term debt | 12,000 | |
| Cash paid to acquire plant assets | $8,000 | |
Table (5)
Working note:
Prepare a schedule of changes of current assets and liabilities.
| Schedule in the change of current assets and liabilities | ||||
| Details | Amount ($) | Impact | ||
| End of the year | Beginning year |
Increase/ (Decrease) | ||
| Accounts receivable | 35,000 | 40,000 | (5,000) | Add |
| Accounts payable | 70,000 | 50,000 | 20,000 | Add |
| Accrued operating expenses payable | 14,000 | 16,000 | (2,000) | Deduct |
| Increase in inventory | 128,000 | 120,000 | 8,000 | Deduct |
Table (6)
c.
Explain how P incorporation achieved positive cash flows from operating activities.
c.
Explanation of Solution
- The primary reason is P incorporation has involved in liquidating its assets and not paying its debt or bills.
- Most of the accounts receivable are converted into cash. Thus, it helps to reduce the credit sales.
- If the sales are decreased then it reports in the income statement immediately. However, this may take months before its effects (decrease in sales) appear in a statement of cash flows. Therefore, P incorporation achieved positive cash flows from operating activities.
d.
Explain whether the company’s financial position improving or deteriorating.
d.
Explanation of Solution
- P incorporation has more cash balance but the financial condition of the company is declining.
- The marketable security of this company is considered as a highly liquid asset and that is almost gone.
- Increase in accounts payable substantially exceeds the amount of cash in hand.
- Moreover, sales and accounts receivable balance are declining which indicates that the company has an ability to generate cash from operating activities in future. In addition decline in sales affects the liquidity of the company’s inventory.
e.
Explain whether the operation of P Company growing or contracting.
e.
Explanation of Solution
- P incorporation is collapsing in terms of its operations because, the investment made in marketable securities, receivables and plant assets are declining.
- In the income statement shows that operations are affecting the owners’ equity in the business.
- Decrease in sales reduces the cash collected from customers. Therefore, this is the major factor which contributes to a positive cash flow from operating activities.
f.
Explain the management decision and the needed action.
f.
Explanation of Solution
The first decision of the management is whether to attempt it or liquidate it because, the sales volume has declined and it will result in net loss over the period. Moreover, the operating cash flows also turn into negative.
If management has decided to liquidate it, then it should quit quickly because it may affects the future operating losses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GEN COMBO FINANCIAL & MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING; CONNECT ACCESS CARD
- I am looking for a step-by-step explanation of this financial accounting problem with correct standards.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- I need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardThe installment method of revenue recognition is primarily used for_. (a) Service contracts (b) Sales with extended payment terms (c) Construction projects (d) Consignment sales MCQarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





