
Fundamentals Of Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119573968
Author: David Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 6P
GO In Fig. 13-32, a square of edge length 20.0 cm is formed by four spheres of masses m1 = 5.00 g, m2 = 3.00 g. m3 = 1.00 g, and m4 = 5.00 g. In unit-vector notation, what is the net gravitational force from them on a central sphere with mass m5 = 2.50 g?
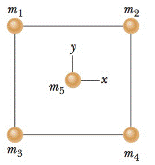
Figure 13-32 Problem 6
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 13 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Physics
Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-21, a central particle of mass M is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2QCh. 13 - In Fig. 13-23, a central particle is surrounded by...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-24, two particles, of masses m and 2m,...Ch. 13 - Prob. 5QCh. 13 - In Fig. 13-26, three particles are fixed in place....Ch. 13 - Rank the four systems of equal- mass particles...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-27 gives the gravitational acceleration...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-28 shows three particles initially fixed...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-29 shows six paths by which a rocket...
Ch. 13 - Figure 13-30 shows three uniform spherical planets...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-31, a particle of mass m which is not...Ch. 13 - ILW A mass M is split into two parts, m and M m,...Ch. 13 - Moon effect. Some people believe that the Moon...Ch. 13 - Prob. 3PCh. 13 - The Sun and Earth each exert a gravitational force...Ch. 13 - Miniature black holes. Left over from the big-bang...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-32, a square of edge length 20.0 cm...Ch. 13 - One dimension. In Fig. 13-33, two point particles...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-34, three 5.00 kg spheres are located...Ch. 13 - SSM WWW We want to position a space probe along a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 10PCh. 13 - As seen in Fig. 13-36, two spheres of mass m and a...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-37a, particle A is fixed in place at...Ch. 13 - Figure 13-38 shows a spherical hollow inside a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 14PCh. 13 - GO Three dimensions. Three point particles are...Ch. 13 - GO In Fig. 13-40, a particle of mass m1 = 0.67 kg...Ch. 13 - a What will an object weigh on the Moons surface...Ch. 13 - Mountain pull. A large mountain can slightly...Ch. 13 - SSM At what altitude above Earths surface would...Ch. 13 - Mile-high building. In 1956, Frank Lloyd Wright...Ch. 13 - ILW Certain neutron stars extremely dense stars...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - Prob. 23PCh. 13 - Two concentric spherical shells with uniformly...Ch. 13 - A solid sphere has a uniformly distributed mass of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 26PCh. 13 - Figure 13-42 shows, not to scale, a cross section...Ch. 13 - Prob. 28PCh. 13 - Prob. 29PCh. 13 - In Problem 1, what ratio m/M gives the least...Ch. 13 - SSM The mean diameters of Mars and Earth are 6.9 ...Ch. 13 - a What is the gravitational potential energy of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 33PCh. 13 - Prob. 34PCh. 13 - GO Figure 13-44 shows four particles, each of mass...Ch. 13 - Zero, a hypothetical planet, has a mass of 5.0 ...Ch. 13 - GO The three spheres in Fig, 13-45, with masses mA...Ch. 13 - In deep space, sphere A of mass 20 kg is located...Ch. 13 - Prob. 39PCh. 13 - A projectile is shot directly away from Earths...Ch. 13 - SSM Two neutron stars arc separated by a distance...Ch. 13 - GO Figure 13-46a shows a particle A that can he...Ch. 13 - a What linear speed must an Earth satellite have...Ch. 13 - Prob. 44PCh. 13 - The Martian satellite Photos travels in an...Ch. 13 - The first known collision between space debris and...Ch. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - The mean distance of Mars from the Sun is 1.52...Ch. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - Prob. 50PCh. 13 - Prob. 51PCh. 13 - The Suns center is at one focus of Earths orbit....Ch. 13 - A 20 kg satellite has a circular orbit with a...Ch. 13 - Prob. 54PCh. 13 - In 1610, Galileo used his telescope to discover...Ch. 13 - In 1993 the spacecraft Galileo sent an image Fig....Ch. 13 - Prob. 57PCh. 13 - Prob. 58PCh. 13 - Three identical stars of mass M form an...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-50, two satellites, A and B, both of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 61PCh. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - SSM WWW An asteroid, whose mass is 2.0 10-4 times...Ch. 13 - A satellite orbits a planet of unknown mass in a...Ch. 13 - A Satellite is in a circular Earth orbit of radius...Ch. 13 - One way to attack a satellite in Earth orbit is to...Ch. 13 - Prob. 67PCh. 13 - GO Two small spaceships, each with mass m = 2000...Ch. 13 - Prob. 69PCh. 13 - Prob. 70PCh. 13 - Several planets Jupiter. Saturn, Uranus are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 72PCh. 13 - Figure 13-53 is a graph of the kinetic energy K of...Ch. 13 - The mysterious visitor that appears in the...Ch. 13 - ILW The masses and coordinates of three spheres...Ch. 13 - SSM A very early, simple satellite consisted of an...Ch. 13 - GO Four uniform spheres, with masses mA = 40 kg,...Ch. 13 - a In Problem 77, remove sphere A and calculate the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 79PCh. 13 - Prob. 80PCh. 13 - Prob. 81PCh. 13 - Prob. 82PCh. 13 - Prob. 83PCh. 13 - Prob. 84PCh. 13 - Prob. 85PCh. 13 - Prob. 86PCh. 13 - Prob. 87PCh. 13 - Prob. 88PCh. 13 - Prob. 89PCh. 13 - A 50 kg satellite circles planet Cruton every 6.0...Ch. 13 - Prob. 91PCh. 13 - A 150.0 kg rocket moving radially outward from...Ch. 13 - Prob. 93PCh. 13 - Two 20 kg spheres are fixed in place on a y axis,...Ch. 13 - Sphere A with mass 80 kg is located at the origin...Ch. 13 - In his 1865 science fiction novel From the Earth...Ch. 13 - Prob. 97PCh. 13 - Prob. 98PCh. 13 - A thin rod with mass M = 5.00 kg is bent in a...Ch. 13 - In Fig. 13-57, identical blocks with identical...Ch. 13 - A spaceship is on a straight-line path between...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
a. Draw all the isomers with molecular formula C6H12 that contain a cyclobutane ring. (Hint: There are seven.) ...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
16. Monica stands at the edge of a circular platform that is slowly rotating on a frictionless axle. She then w...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
A dual-fluid heat exchanger has l0Ibm/s water entering at l00F,20psia and leaving at 50F,20psia . The other flu...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
1. a. At this instant, is the particle in FIGURE Q4.1 speeding up, slowing down, or traveling at constant speed...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
17. Anthropologists are interested in locating areas in Africa where fossils 4-8 million years old might be fou...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Gravitational Force (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxp1Z91S5uQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY