
Concept explainers
a.
Identify and explain whichof the given modelscan be recommended.
a.
Answer to Problem 66SE
The model with 2 predictors and the model with 3 predictors can be recommended for predicting the pH before addition of dyes.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The MINITAB output shows the best regression option for the data predicted for pH before the addition of dyes using carpet density, carpet weight, dye weight, dye weight as a percentage of carpet and pH after addition of dyes.
Justification:
Mallows
It is used to assess the fit of regression model where the aim to find the best subset of predictors. A relatively small value of
By observing the mallows
By examining the models with three variables,
Hence, the model with two predictorsnamely dye weight and pH after addition of dyes could be considered as a best model subset for predicting pH before the addition of dyes.
Also, a second option would be the model with three predictorsnamely carpet weight, dye weight and pH after addition of dyes could be considered as a best model subset for predicting pH before the addition of dyes.
b.
Test whether the model suggests a useful linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and at least one of the predictors.
b.
Answer to Problem 66SE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and at least one of the predictors dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The MINITAB output for predicting the pH before the addition of dyes using the dye weight
Calculation:
The test hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and the predictors dye weightand pH after the addition of dyes.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and at least one of the predictors dye weightand pH after the addition of dyes.
Conclusion:
The P-value is 0.000 and the level of significance is 0.001.
The P-value is lesser than the level of significance.
That is
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and at least one of the predictors dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes.
c.
Explain whether either one of the predictors could be eliminated from the model given that the other predictor is retained.
c.
Answer to Problem 66SE
No, either one of the predictors could not be eliminated from the model given that the other predictor is retained.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For variable
Testing the hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and dye weightgiven that pH after addition of dyes was retained in the model.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and dye weightgiven that pH after addition of dyes was retained in the model.
From the MINITAB output it can be observed that the P-value corresponding to the t statistic of
Conclusion:
The P-value is 0.000 and the level of significance is 0.001.
The P-value is lesser than the level of significance.
That is
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and dye weight given that pH after addition of dyes was retained in the model.
For variable
Testing the hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and pH after addition of dyes given that dye weight was retained in the model.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and pH after addition of dyes given that dye weight was retained in the model.
From the MINITAB output it can be observed that the P-value corresponding to the t statistic of
Conclusion:
The P-value is 0.000 and the level of significance is 0.001.
The P-value is lesser than the level of significance.
That is
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a use of linear relationship between pH before the addition of dyes and pH after addition of dyes given that dye weight was retained in the model.
Justification:
From the analysis it can be concluded that none of the variables can be eliminated from the model given that the other variable is already present in the model.
d.
Calculate and interpret the 95% confidence interval for the two predictors.
d.
Answer to Problem 66SE
The 95% confidence interval for the estimated slope coefficient
(–0.0000684, –0.0000244).
The 95% confidence interval for the estimated slope coefficient
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The 95% confidence interval is calculated using the formula:
The confidence interval is calculated using the formula:
Where,
n is the total number of observations.
k is the total number of predictors in the model.
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the critical value is given below:
- Click on Graph, select View Probability and click OK.
- Select t, enter 111 as Degrees of freedom, inShaded Area Tab select Probability under Define Shaded Area By and choose Both tails.
- Enter Probability value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:
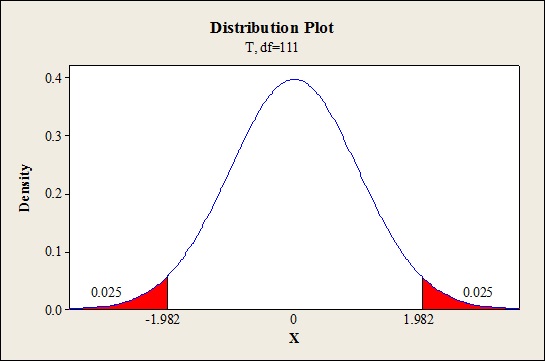
The 95% confidence interval for
Thus, the 95% confidence interval for the estimated slope coefficient
(–0.0000684, –0.0000244).
The 95% confidence interval for
Thus, the 95% confidence interval for the estimated slope coefficient
(0.6417,0.8325).
Interpretation:
For the variable
For one unit increase in the dye weight, it is 95% confident that the estimated value of pH before addition of dyes would decrease between–0.00000684 and–0.0000244 given that pH after addition of dyes is fixed constant.
For the variable
For one unit increase in the pH after the addition of dyes it is 95% confident that the estimated value of pH before addition of dyes would increase between 0.6417 and 0.8325 given that dye weight is fixed constant.
e.
Calculate and interpret the 95% confidence interval for the average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6, respectively.
e.
Answer to Problem 66SE
The 95% confidence interval for the average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6, respectively is (5.250, 5.383)
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The estimated standard deviation for predicting the pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6 is 0.0336.
Calculation:
The average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6 is calculated as follows:
Thus, the average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6 is 5.316.
95% confidence interval for the true response:
The confidence interval is calculated using the formula:
Where,
n is the total number of observations.
k is the total number of predictors in the model.
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the critical value is given below:
- Click on Graph, select View Probability and click OK.
- Select t, enter 111 as Degrees of freedom, in Shaded Area Tab select Probability under Define Shaded Area By and choose Both tails.
- Enter Probability value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:

The 95% confidence interval is given below:
Thus, the 95% confidence interval for the average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6 is (5.250,5.383).
Interpretation:
It is 95% confident that average value of pH before the addition of dyes when the dye weight and pH after the addition of dyes takes 1,000 and 6 would lie between 5.250 and 5.383.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
WEBASSIGN ACCESS FOR PROBABILITY & STATS
- Consider an event X comprised of three outcomes whose probabilities are 9/18, 1/18,and 6/18. Compute the probability of the complement of the event. Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.2/18 C.16/18 D.16/3arrow_forwardJohn and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. What is the simple moving average root mean square error? Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 207.13 B. 20.12 C. 14.39 D. 0.21arrow_forward
- The details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. If the smoothing constant is assumed to be 0.7, and setting F1 and F2=A1, what is the exponential smoothing sales forecast for week 7? Round to the nearest whole number. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 80 clocks B. 60 clocks C. 70 clocks D. 50 clocksarrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. Calculate the value of the simple moving average mean absolute percentage error. Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Part 1 A. 14.39 B. 25.56 C. 23.45 D. 20.90arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
- The accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Develop line charts for each variable and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). What is the line chart for the variable Fossil Fuels Production?arrow_forwardThe accompanying data shows the fossil fuels production, fossil fuels consumption, and total energy consumption in quadrillions of BTUs of a certain region for the years 1986 to 2015. Complete parts a and b. Year Fossil Fuels Production Fossil Fuels Consumption Total Energy Consumption1949 28.748 29.002 31.9821950 32.563 31.632 34.6161951 35.792 34.008 36.9741952 34.977 33.800 36.7481953 35.349 34.826 37.6641954 33.764 33.877 36.6391955 37.364 37.410 40.2081956 39.771 38.888 41.7541957 40.133 38.926 41.7871958 37.216 38.717 41.6451959 39.045 40.550 43.4661960 39.869 42.137 45.0861961 40.307 42.758 45.7381962 41.732 44.681 47.8261963 44.037 46.509 49.6441964 45.789 48.543 51.8151965 47.235 50.577 54.0151966 50.035 53.514 57.0141967 52.597 55.127 58.9051968 54.306 58.502 62.4151969 56.286…arrow_forward
- For each of the time series, construct a line chart of the data and identify the characteristics of the time series (that is, random, stationary, trend, seasonal, or cyclical). Month PercentApr 1972 4.97May 1972 5.00Jun 1972 5.04Jul 1972 5.25Aug 1972 5.27Sep 1972 5.50Oct 1972 5.73Nov 1972 5.75Dec 1972 5.79Jan 1973 6.00Feb 1973 6.02Mar 1973 6.30Apr 1973 6.61May 1973 7.01Jun 1973 7.49Jul 1973 8.30Aug 1973 9.23Sep 1973 9.86Oct 1973 9.94Nov 1973 9.75Dec 1973 9.75Jan 1974 9.73Feb 1974 9.21Mar 1974 8.85Apr 1974 10.02May 1974 11.25Jun 1974 11.54Jul 1974 11.97Aug 1974 12.00Sep 1974 12.00Oct 1974 11.68Nov 1974 10.83Dec 1974 10.50Jan 1975 10.05Feb 1975 8.96Mar 1975 7.93Apr 1975 7.50May 1975 7.40Jun 1975 7.07Jul 1975 7.15Aug 1975 7.66Sep 1975 7.88Oct 1975 7.96Nov 1975 7.53Dec 1975 7.26Jan 1976 7.00Feb 1976 6.75Mar 1976 6.75Apr 1976 6.75May 1976…arrow_forwardHi, I need to make sure I have drafted a thorough analysis, so please answer the following questions. Based on the data in the attached image, develop a regression model to forecast the average sales of football magazines for each of the seven home games in the upcoming season (Year 10). That is, you should construct a single regression model and use it to estimate the average demand for the seven home games in Year 10. In addition to the variables provided, you may create new variables based on these variables or based on observations of your analysis. Be sure to provide a thorough analysis of your final model (residual diagnostics) and provide assessments of its accuracy. What insights are available based on your regression model?arrow_forwardI want to make sure that I included all possible variables and observations. There is a considerable amount of data in the images below, but not all of it may be useful for your purposes. Are there variables contained in the file that you would exclude from a forecast model to determine football magazine sales in Year 10? If so, why? Are there particular observations of football magazine sales from previous years that you would exclude from your forecasting model? If so, why?arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
