
Concept explainers
A projectile is fired from the origin with angle of elevation α and initial speed v0. Assuming that air resistance is negligible and that the only force acting on the projectile is gravity, g. we showed m Example 13.4.5 that the position
We also showed that the maximum horizontal distance of the projectile is achieved when α = 45° and in this case the range is.
(a) At what angle should the projectile he tired to achieve maximum height and what is the maximum height?
(b) Fix the initial speed is r0 and consider the parabola x2 + 2Ry – R2 = 0, whose graph is shown in the figure at the left Show that the projectile can hit any target inside or on the boundary of the region hounded by the parabola and the x-axis, and that it can't hit any target outside this region.
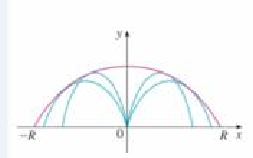
FIGURE FOR PROBLEM 3
(c) Suppose that the gun is elevated to an angle of inclination α in order to aim at a target that is suspended at a height h directly over a point D units downrange (sec the figure below). The target is released at the instant the gun is fired. Show that the projectile always hits the target, regardless of the value v0, provided the projectile docs not hit the ground “before” D.
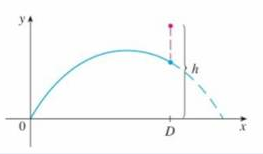
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS
- Suppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forwardLet f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forwardplease do Q3arrow_forward
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
- a -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forwardEvaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning



