
1.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full manufacturing cost as follows:
Working note (1):
Calculate the total variable cost.
Working note (2):
Calculate the total fixed cost.
Working note (3):
Calculate the total manufacturing cost.
Working note (4):
Calculate the total selling and administrative.
Working note (5):
Calculate the total life cycle cost.
Working note (6):
Calculate the manufacturing cost per unit.
Working note (7):
Calculate the life cycle cost per unit.
2.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost as follows:
3.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40%.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40% as follows:
4.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25%.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25% as follows:
5.
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax
5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax return on investment of 15%t as follows:
Working note (8):
Calculate the total investment rate.
6.
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price as follows:
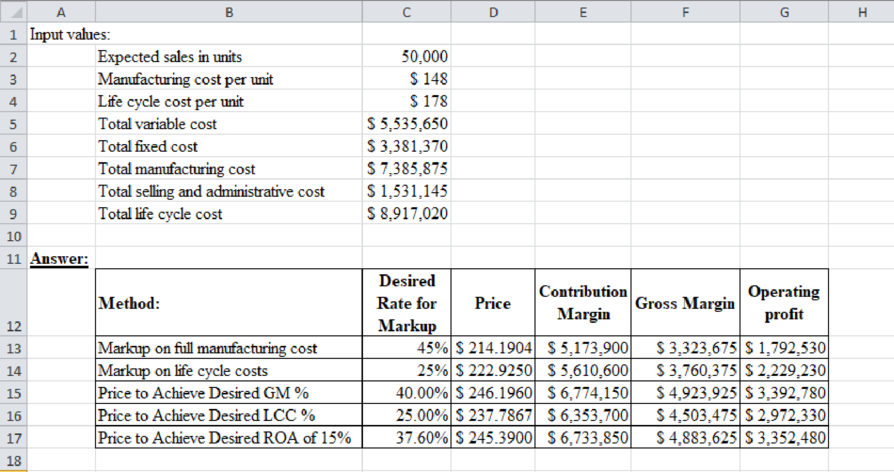
Table (1)
Excel workings:
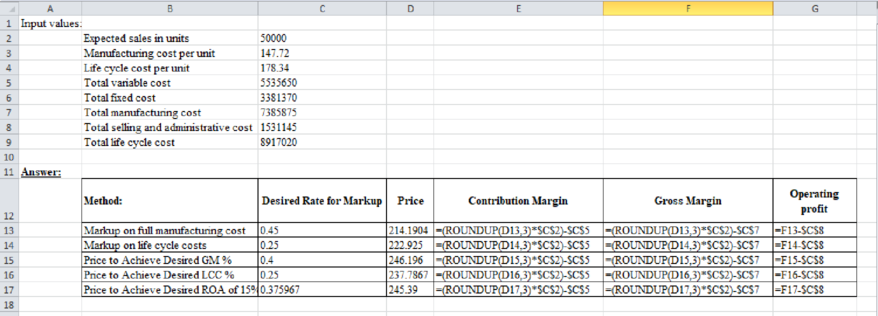
Table (1)
Price to achieve desired ROA of 15% is better price for the company, because the operating profit from this price is more than the other.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardParamount Company uses a standard costing system that allows 2.5 pounds of direct materials for one finished unit. During August, the company purchased 35,000 pounds of direct materials for $175,000 and manufactured 13,200 finished units. The standard direct materials cost allowed for the units manufactured is $132,000. The performance report shows that Paramount has an unfavorable direct materials usage variance of $6,400. Also, the company records any price variance for materials at time of purchase. The number of pounds of direct materials used to produce August's output was__ pounds.arrow_forward
- How does dollar-value LIFO differ from traditional LIFO in accounting records? (A) Uses different cost flow assumption (B) Applies only to specific industries (C) Required for tax purposes (D) Pools inventory by dollars not units Answerarrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardDetermine the number of completed untis manufactured during the year.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





