
1.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full manufacturing cost as follows:
Working note (1):
Calculate the total variable cost.
Working note (2):
Calculate the total fixed cost.
Working note (3):
Calculate the total manufacturing cost.
Working note (4):
Calculate the total selling and administrative.
Working note (5):
Calculate the total life cycle cost.
Working note (6):
Calculate the manufacturing cost per unit.
Working note (7):
Calculate the life cycle cost per unit.
2.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost as follows:
3.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40%.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40% as follows:
4.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25%.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25% as follows:
5.
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax
5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax return on investment of 15%t as follows:
Working note (8):
Calculate the total investment rate.
6.
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price as follows:
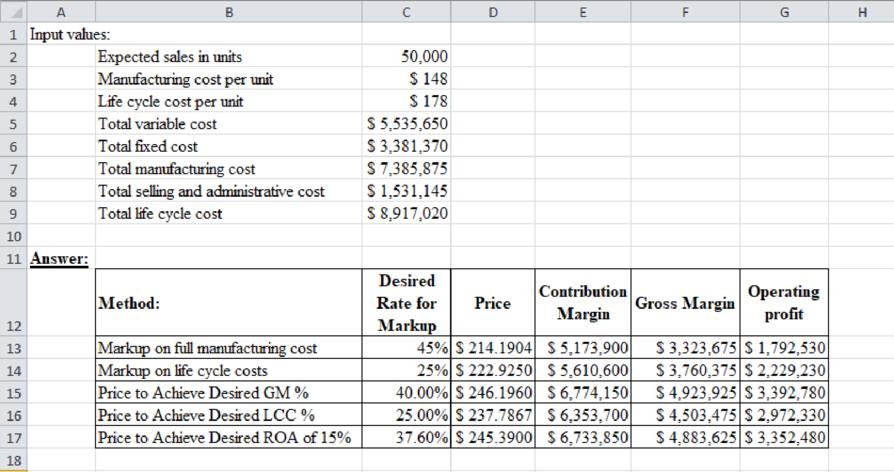
Table (1)
Excel workings:
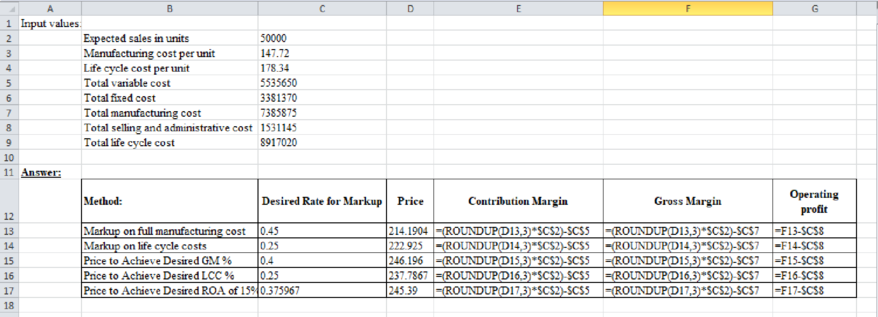
Table (1)
Price to achieve desired ROA of 15% is better price for the company, because the operating profit from this price is more than the other.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
COST MANAGMENT WITH CONNECT ACCESS
- Financial Accounting please give me correct answer this questionarrow_forwardQuestion: What is the formula for computing direct materials price variance? a. actual costs - (actual quantity X standard price) b. actual cost + standard costs c. actual cost - standard costs d. (actual quantity X standard price) - standard costsarrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





