
1.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 45% of full manufacturing cost as follows:
Working note (1):
Calculate the total variable cost.
Working note (2):
Calculate the total fixed cost.
Working note (3):
Calculate the total manufacturing cost.
Working note (4):
Calculate the total selling and administrative.
Working note (5):
Calculate the total life cycle cost.
Working note (6):
Calculate the manufacturing cost per unit.
Working note (7):
Calculate the life cycle cost per unit.
2.
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a markup of 25% of full life-cycle cost as follows:
3.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40%.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired gross margin percentage to sales of 40% as follows:
4.
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25%.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the price for the part using a desired life-cycle cost percentage to sales of 25% as follows:
5.
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax
5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate price for the part using a desired before tax return on investment of 15%t as follows:
Working note (8):
Calculate the total investment rate.
6.
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the contribution margin and operation profit for each method and choose the appropriate price as follows:
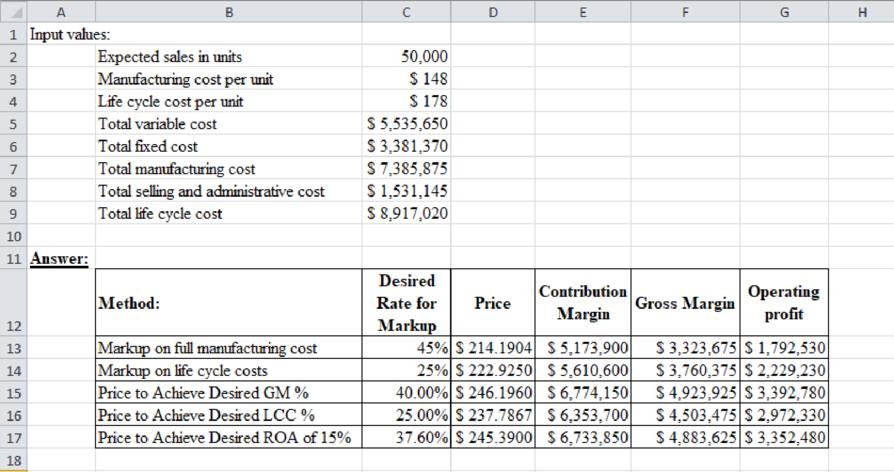
Table (1)
Excel workings:
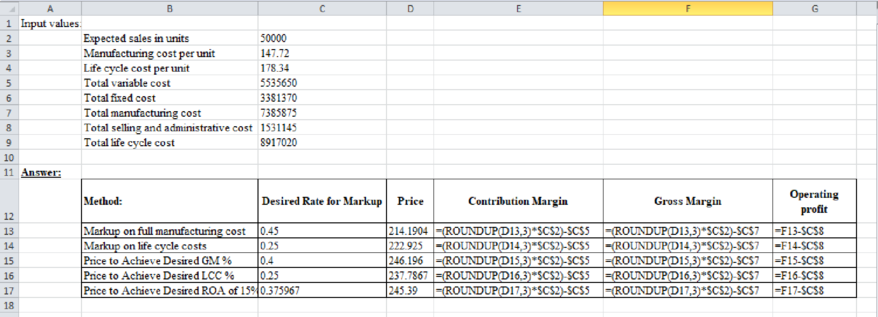
Table (1)
Price to achieve desired ROA of 15% is better price for the company, because the operating profit from this price is more than the other.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
COST MANAGEMENT: CONNECT ACCESS CUSTOM
- I need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardYou are employed by an external audit firm that is hired by JBltd, a privately owned incorporated business. Accounting records are maintained on a computer using proprietary software. You have worked on the audit for three years and this year you are in charge of the audit. Your assistant is a newly recruited business graduate who has done an accounting course but has no practical experience. Because of the small size of the company there is limited opportunity for segregation of duties. You decide, as in previous years, that the appropriate audit strategy is to obtain evidence primarily through the performance of substantive procedures. You also plan to perform the audit around the computer as the proprietary software is known to be reliable and details of all transactions and balances can be readily printed out. On arriving at the company's premises in December 2019 to perform the final audit on the 31 October 2019 financial statements, you obtain a copy of the year end bank…arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





