
Concept explainers
Maccoa Soft, a division of Zayer Software Company, produces and distributes an automated payroll software system. A contribution margin format income statement for Maccoa Soft for the past year follows:
| Revenue (12,000 units × $1,200) | $14,400,000 |
| Unit-level variable costs | |
| Product materials cost (12,000 × $60) | (720,000) |
| Installation labor cost (12,000 × $200) | (2,400,000) |
| Manufacturing |
(24,000) |
| Shipping and handling (12,000 × $25) | (300,000) |
| Sales commissions (12,000 × $300) | (3,600,000) |
| Nonmanufacturing miscellaneous costs (12,000 × $5) | (60,000) |
| Contribution margin (12,000 × $608) | 7,296,000 |
| Fixed costs | |
| Research and development | (2,700,000) |
| Legal fees to ensure product protection | (780,000) |
| Advertising costs | (1,200,000) |
| Rental |
(600,000) |
| (300,000) | |
| Other manufacturing costs (salaries, utilities, etc.) | (744,000) |
| Division-level facility sustaining costs | (1,730,000) |
| Allocated companywide facility-level costs | (1,650,000) |
| Net loss | $ (2,408,000) |
- a. Divide the class into groups and then organize the groups into three sections. Assign Task 1 to the first section, Task 2 to the second section, and Task 3 to the third section. Each task should be considered independently of the others.
Group Tasks
- (1) Assume that Maccoa has excess capacity. The sales staff has identified a large franchise company with 200 outlets that is interested in Maccoa’s software system but is willing to pay only $800 for each system. Ignoring qualitative considerations, should Maccoa accept the special order?
- (2) Maccoa has the opportunity to purchase a comparable payroll system from a competing vendor for $600 per system. Ignoring qualitative considerations, should Maccoa outsource producing the software? Maccoa would continue to sell and install the software if the manufacturing activities were outsourced.
- (3) Given that Maccoa is generating a loss, should Zayer eliminate it? Would your answer change if Maccoa could increase sales by 1,000 units?
- b. Have a representative from each section explain its respective conclusions. Discuss the following:
- (1) Representatives from Section 1 should respond to the following: The analysis related to the special order (Task 1) suggests that all variable costs are always relevant. Is this conclusion valid? Explain your answer.
- (2) Representatives from Section 2 should respond to the following: With respect to the outsourcing decision, identify a relevant fixed cost and a nonrelevant fixed cost. Discuss the criteria for determining whether a cost is or is not relevant.
- (3) Representatives from Section 3 should respond to the following: Why did the segment elimination decision change when the volume of production and sales increased?
a1.
Whether Division MS should accept the special order by ignoring the qualitative considerations.
Explanation of Solution
Variable cost: It is also called as production costs that change in extent to the measure of goods that are manufactured. In other words, for each product that is manufactured, variable costs increment by a similar amount.
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost is the forfeit of certain benefits such as cost savings, incomes, which is surrendered by not picking an option. Opportunity costs are applicable in decisions where the acknowledgment of one option disqualifies the likelihood of selecting different alternatives.
Determine the unit-level incremental costs
Therefore the unit-level incremental cost is $592.
From the result obtained above, the fixed costs are irrelevant since they will continue the similar irrespective of whether the special order is accepted. The total unit-level incremental costs that will be incurred if the special order is accepted will be $592. Because the incremental cost per unit of $592 is less than the incremental income of $800 per unit, hence the special order should be accepted.
Therefore the special order should be accepted.
a2.
Whether Division MS should outsource producing the software by ignoring the qualitative considerations.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs
Therefore the total avoidable cost is $5,568,000.
Determine the total avoidable cost per unit
Therefore the avoidable cost per unit is $464.
From the result obtained above, the total avoidable expense per unit is $464. Since the avoidable cost is less than the value required to buy of $600, Division MS would be in an ideal situation to keep on producing the software.
Therefore Division MS should produce the software.
a3.
Whether Company Z should eliminate Division MS.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs at 12,000 units
If the division is eliminated, all expenses with the exception of the assigned companywide facility level expense and the depreciation on manufacturing the equipment or the sunk cost could be avoided.

Table (1)
(Refer excel for workings)
Therefore the total avoidable cost at 12,000 units is -$458,000.
From the result obtained above, the avoidable costs surpass the incremental revenue, the division must be eliminated.
Therefore Division MS should be eliminated.
Whether the answer changes if the sales increase by 1,000 units.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the total avoidable costs at 13,000 units
The additional selling units of 1,000 units would build add up to the total sales of 13,000 units.
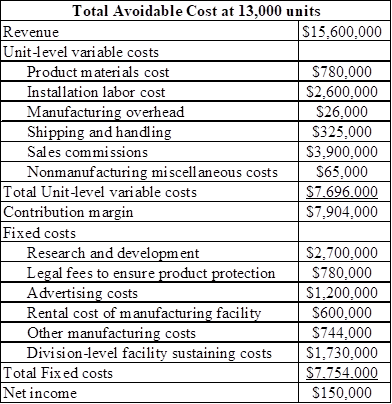
Table (2)
(Refer excel for workings)
Therefore the total avoidable cost at 13,000 units is $150,000.
From the result obtained above, At a sales volume level of 13,000 units, the division must not be eliminated.
Therefore Division MS should not be eliminated.
b1.
Whether the conclusion is valid.
Explanation of Solution
The reason on whether the conclusion is valid is as follows:
All the variable costs are not constantly relevant. For instance, assume that the special order customer move towards the organization openly, in this way eliminating the requirement to pay sales commissions. Under these conditions the sales commissions would not be relevant to a choice with respect to whether the special order should be accepted. The variable costs can be either relevant or irrelevant contingent upon the specific conditions related with the special decision.
b2.
The criteria for determining whether a cost is relevant or not relevant.
Explanation of Solution
The criteria for determining whether a cost is relevant or not relevant are as follows:
The research and development expenditures are applicable on the grounds that they are not incurred if the item is outsourced. The advertising costs are not relevant since they are important to advance the item irrespective of whether it is produced or outsourced. In other words, the costs must vary between the choices and be future arranged.
b3.
The reason on the segment elimination decision changes when the volume of production and sales increased.
Explanation of Solution
The reason on the segment elimination decision changes when the volume of production and sales increased are as follows:
Increases in volume influence the total contribution margin to increment. In like manner, additional margin is accessible to take care of fixed costs or to add to the productivity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Can you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardCalculate company's gross profit for 2022arrow_forwardLee Corporation had a Work-in-Process balance of $95,000 on January 1, 2023. The year-end balance of Work-in-Process was $110,000, and the Cost of Goods Manufactured was $680,000. Use this information to determine the total manufacturing costs incurred during the fiscal year 2023.arrow_forward
- Novus Advisory Group expects its consultants to work 40,000 direct labor hours per year. The company's estimated total indirect costs are $360,000. The direct labor rate is $95 per hour. The company uses direct labor hours as the allocation base for indirect costs. If Novus performs a job requiring 30 hours of direct labor, what is the total job cost?arrow_forwardTONY Corporation makes a product whose direct labor standard are 1.3 hours per unit and $14 per hour. In April, the company produced 5,400 units using 7,440 direct labor hours. The actual direct labor cost was $97,550. The labor rate variance for April is _.arrow_forwardMeryl Manufacturing had a Work-in-Process balance of $168,000 on January 1, 2023. The year-end balance of Work-in-Process was $192,000, and the Cost of Goods Manufactured was $745,000. Use this information to determine the total manufacturing costs incurred during the fiscal year 2023.arrow_forward
- I am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate solution to this financial accounting question using valid calculations.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
 Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting (Text Only)AccountingISBN:9781285743615Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Accounting (Text Only)AccountingISBN:9781285743615Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





