
Concept explainers
In Fig. 13-21, a central particle of mass M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distance d or distance d/2 along the perimeter of the square. What are the magnitude and direction of the net gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles?
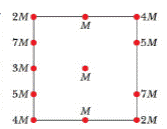
Figure 13-21 Question 1.
To find:
The magnitude and direction of the net gravitational force acting on the central particle due to the other particles
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
The net gravitational force acting on the central particle due to the other particles is
and is directed towards left.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Observing the figure, we can cancel out the equal and opposite forces. The sum of the remaining forces will be the net force acting on the central particle M.
2) Given:
Thefigure of system of particles is given.
3) Formulae:
The Gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses M and m separated by distance R is,
4) Calculations:
From the given figure, we can infer that the gravitation force due to each particle on one of the sides of the square is cancelled by the gravitational force due to one of the particles on the opposite side of the square with the same mass except particle 3M. Particle 3M would exert force on M, but there is no force on the opposite side which can cancel this force.
So, the net force acting on the central particle M is due to the particle 3M which is
As we know the gravitational force is an attractive force, the force on particle M by particle 3M is pointing towards the left.
Conclusion:
Using the formula for gravitational force, we can find the net force acting on the particle due to the system of particles.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS (LLF)+WILEYPLUS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- A 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward12. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which will cause more damage? (think about which collision has a larger amount of kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment? I m II III A. I B. II C. III m m v brick wall ע ע 0.5v 2v 0.5m D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them) 2marrow_forward
- 11. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which brings the car of mass (m) on the left to a halt? I m II III m m ע ע ע brick wall 0.5v 2m 2v 0.5m A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them)arrow_forwardHow can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?arrow_forwardYou want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the process to form the inlet and outlet. Square Cross Sectionarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





