
To discuss:
The anatomy, physiology, and functions of the central nervous system (CNS) with attention to the stimulants effect on its function.
Concept introduction:
The nervous system is a complex network of nerve cells. Nerves are the basic unit of the nervous system. The nervous system is classified into two major divisions’, central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is subdivided into sensory division (afferent) and motor division (efferent).
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
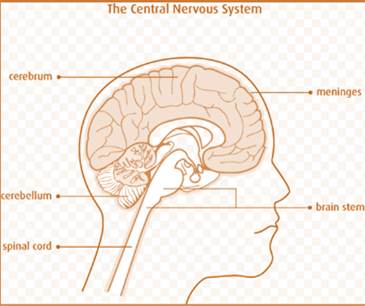
Anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system: Spinal cord and brain are classified under the central nervous system, which is protected by the vertebral column and the cranium. Cranial nerves, peripheral nerves and spinal nerves belong to the PNS, which is protected by connective tissue. The PNS is classified into sensory and motor divisions. Sensory or afferent neurons conduct signal toward the CNS in response to stimuli, such as heat and light. Motor or efferent neurons send signal to the gland cells and the muscle cells.
The cerebellum accepts signals from the sensory systems, spinal cord and other regions of the brain. After receiving the signals, motor movements are regulated by the CNS. Posture, balance, and coordination are regulated by the cerebellum. The anterior region of the brain consists of two hemispheres that are separated by a fissure. It is accountable for sensory as well as neural functions. It co-ordinates the voluntary functions in the body.
The membranous covering of the brain and the spinal cord is known as meninges. This layer along with the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) offers protection to the CNS. Brain stem is the central stalk of the brain, consists of Pons, medulla oblongata, as well as the mid-brain and extends downward to form the spinal cord.
The spinal cord is long, thin and tubular structure. It is made up of support cells and nervous tissue. It spreads from the medulla oblongata present in the brainstem toward the (vertebral column) lumbar region. The major functions of the spinal cord connectthe PNS with the brain and transmission of nerve impulses.
Attention to the stimulant effect over the functions of the CNS:
The drugs that are involved in the stimulation of the spinal cord and the brain are known as stimulant drugs. These drugs work by mimicking the neurotransmitters of the nervous system (sympathetic).
Amphetamine stimulant, Methylphenidate, Phentermine, and Sumatriptan are some of the categories of CNS stimulant drugs. Amphetamine and the caffeine drugs are involved in the stimulation of the cerebral cortex region of the brain. Analeptics and caffeine drugs effects are seen in the brainstem and medulla oblongata. They are involved in the stimulation of the respiration process. Anorexiant group acts partially on the hypothalamus and cerebral cortex for suppressing the appetite.
CNS drugs induce the brain andincrease the rapidity of mental and physical activities. These drugs are used in the treatment of prolonged fatigue, obesity and unnecessary sleep and so on.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Pharmacology and the Nursing Process, 8e
- true or false dark skinned infants should be screened for vitamin D levelsarrow_forwardtrue or false any practice employee is authorized to and should communicate collection guidelines with practice?arrow_forwardrtrue or false equesting a listing of specific creditreferences during patient intake os an acceptable business practice?arrow_forward
- give an overview on the respiratory assessmentarrow_forwardexplain an abdominal exam?arrow_forwardDiscuss β -Lactam antibiotics under the following subheadings Classifications of penicillins Classification of Cephalosporins General Mechanism of Actions Clinical Indications of penicillins and cephalosporins Adverse effects of β-lactamsarrow_forward
- a. Define neoplasm b. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours c. Describe the molecular basis of cancerarrow_forwarddifferentiate the extra heart sounds S3,S4, murmurs and gallopsarrow_forward• Define shock and list types of shock • Discuss pathogenesis of septic shock. • Enumerate the stages of shock. • Define oedema and describe the pathophysiologic mechanisms of oedema with examples.arrow_forward
- Discuss Hypertension under the following headings: Definition Diagnosis Non-pharmacological intervention Drugs Classification Management of a Hypertensive emergencyarrow_forwardExplain how the answer could be 2 or 1.8 WITHOUT changing the questionarrow_forwardoverview of the neurological system, cranial nerves and what part of the body it innervatesarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





