
(a)
Interpretation:
The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information,
The given
The value of
The chemical reaction that happened in the given solution is given by
From, the above information we have eight equations and eight chemical species.
Write the fractional composition expressions
Substitute the above values into the charge balance equation
The value of
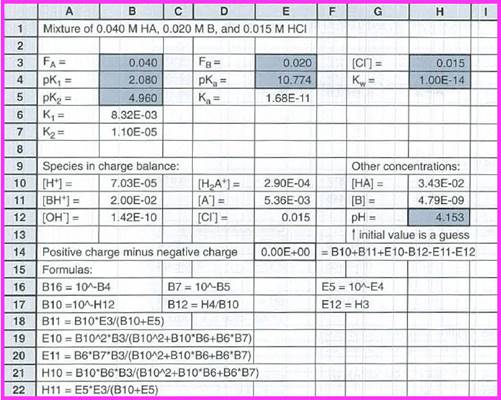
Figure 1
The value of
The concentration of species in the charge balance equation are given below:
The other concentrations are,
(b)
Interpretation:
The fraction of
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information,

Figure 1
The value of
The concentration of species are given below:
The other concentrations are,
The calculated fraction of 2-aminobenzoic acid
The calculated fraction of methylamine
The simple prediction is that
The estimated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Quantitative Chemical Analysis 9e And Sapling Advanced Single Course For Analytical Chemistry (access Card)
- COOEt COOEt Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 COOEt COOEt COOH Step 6 OH Step 4 Step 7 (racemic) cyclizes under conditions (8) OTS Step 5 Step 8 ОН OH (racemic) Frontalin (racemic) Shown above are the steps in one of the several published syntheses of Frontalin, a pheromone of the western pine beetle. From the choices provided, show the reagents and conditions by which step 3 of this synthesis might be accomplished. List the reagent(s) in order that will accomplish this transformation. No more than 4 steps are required. List your answer as a single letter (single-step transformation) or a series of letters (multi-step transformation) with no commas separating them. For example, "ab" corresponds to: 1. Eto Na+ 2. NaOH, H₂O NOTE: The order in which you list your letters matters! Reagents: a. Eto Na* g. NaCN b. NaOH, H₂O h. SOCI₂ c. H3O+, heat i. (CH3)2CuLi, ether, -78°C d. LiAlH4 j. H₂O e. p-TsCI, pyridine k. RCO3H f. Br I. H3O+ 1,024arrow_forwardK ← nationa Login - Paymentivet MapQue Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic acid side product. N 1. excess LiAlH4 2. H₂O ✓ W aarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the alcohol side product. 1. H3O+, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Drawing Qarrow_forward
- Indicate the procedure (reagent Z) to go from compound A1 to compound A2. A1 Z P(C6H5)3 A2arrow_forwardPlease help with this graph.arrow_forwardogin - PaymentN MapQuest 3 Overview - SAP NetW... Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. CI 1. NaBH4 2. H₂O C Clever | Portal Job Op Problem Atoms, Bonds and Rings Draw or tap a new bond toarrow_forward
- 2. Draw the remaining two resonance structures for the carbocation intermediate in the meta nitration of methyl benzoate AND explain why the meta orientation is preferred. Hint: how is the placement of the cation favorable after addition of nitronium relative to the electron withdrawing group? (2 pts) H NO2 CO₂Mearrow_forwardLabel all absorptions over 1500 cm-1. Please be specific and mark IR if needed for explanation. Compound OH sp^3 C-H C=O C-O Triglyceridearrow_forwardIdentify the intermediate that is INITIALLY formed in a saponification reaction (hydrolysis of an ester). III -OH H₂O HO OH HO O || A B C III D IV IVarrow_forward
- Help me answer this practice sheet I found for an answer guidearrow_forwardshow the retrosynthesis of this molecule step by step starting with 1,3-dimethoxy benzene H3CO OH OH OCH 3arrow_forwardConsider the reaction of a propanoate ester with hydroxide ion shown below. A series of four alcohol leaving groups were tested to determine which would be the best leaving group. Based on the pKa values of the alcohols, predict which alcohol would produce the fastest hydrolysis reaction. HO FOR A Alcohol I, pKa =16.0 B Alcohol II, pKa =10.0 C Alcohol III, pKa = 7.2 + ROH D Alcohol IV, pKa = 6.6arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





