
Concept explainers
Inventory Write-Down and Recovery
Cub Company, a calendar−year entity, had 2,100 geothermal healing pumps in its beginning inventory for 20X1. On December 31, 20X0, the heating pumps had been adjusted down to $850 per unit from an actual cost of $920 per unit. It was the lower of cost or market. Cub purchased no additional units during 20X1. The following additional information is provided for 20X1:
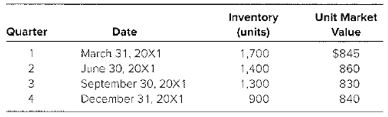
Required
Respond to the following two independent as requested.
- Case 1: The company does not have sufficient experience with the seasonal market for geo thermal pumps and assumes that any reductions in market value during the year will he permanent.( (1) Determine the cost of goods sold for each quarter.
(2) Verify the total cost of goods sold by computing annual cost of goods sold on a lower-of-cost-or-market bush.
b. Case 2: The company has prior experience with the seasonal market for geothermal pumps and expects that any reductions in market value during the year will be only temporary andwill recover by year end.
(1) Determine the cost of goods sold for each quarter.
(2) Verily the total cost of goods sold by computing annual cost of goods sold on a lower-of-cost-or-market basic.
a
Introduction: The losses in inventory due to a decrease in market value is recognized in the period of decline, and recoveries in the subsequent period must also be recognized as recoveries of losses in the prior period of the fiscal year, any gain in market value is not recognized. In addition to that, the temporary decline in market price which is expected to be recovered is also not recognized.
The cost of goods sold in each quarter and verify total cost of goods sold by computation of annual cost of goods sold on a lower of cost or market value basis when company does not have prior experience with seasonal market.
Answer to Problem 13.5E
Cost of goods sold quarterly
- $348,500
- $246,500
- $111,000
- $323,000
Annual basis $1,029,000
Explanation of Solution
Case 1 Market reduction
| Qtr. | Cost of units sold | Adjustment +/(-) | Cost of goods sold |
| 1 | Write down to $840 | $348,500 | |
| 2 | Recovery to $850 | $246,500 | |
| 3 | Write down to $830 | $111,000 | |
| 4 | Recovery to $840 | $323,000 | |
| Total | $1,029,000 | ||
| Annual basis | Write down to $840 | $1,029,000 |
b
Introduction: The losses in inventory due to a decrease in market value is recognized in the period of decline, and recoveries in the subsequent period must also be recognized as recoveries of losses in the prior period of the fiscal year, any gain in market value is not recognized. In addition to that, the temporary decline in market price which is expected to be recovered is also not recognized.
The cost of goods sold in each quarter and verify total cost of goods sold by computation of annual cost of goods sold on a lower of cost or market value basis when company have prior experience with seasonal market.
Answer to Problem 13.5E
Cost of goods sold quarterly
1. $340,000
2. $255,000
3. $85,000
4. $340,000
Annual basis $1,029,000
Explanation of Solution
Case 2 Market reduction
| Qtr. | Cost of units sold | Adjustment +/(-) | Cost of goods sold |
| 1 | $340,000 | ||
| 2 | $255,000 | ||
| 3 | $85,000 | ||
| 4 | Write down to $840 | $340,000 | |
| Total | $1,020,000 | ||
| Annual basis | Write down to $840
| $1,029,000 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Advanced Financial Accounting
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

