
Concept explainers
define keyword is used to define macros
An object-like macros is defined i.e.
#define pi 3.14
A function-like macros is defined i.e.
#define VOL( x ) ( 4.0 / 3 ) * pi * ( x * x * x )
Variable r is declared to store the value of radius.
printf (): used to print the data onto output screen.
Program Description: Purpose of the program is to define macros tofind the volume of sphere for radius values ranging from 1 to 10 in tabular form.
Explanation of Solution
Program: Following is C++ program that defines macros to find the volume of sphere for radius values ranging from 1 to 10.
#include<stdio.h>//header file for input output
//defining macros
#define pi 3.14
#define VOL( x ) ( 4.0 / 3 ) * pi * ( x * x * x )
//start of main
intmain()
{
//defining variable for storing value of radius
int radius;
//tabular reprsentation of data
printf( "Radius\tVolume of sphere\n" );
printf( "\n" );
//for loop to iterate over the value of radius ranging from 1 to 10
for (radius = 1; radius < 11; radius++ )
{
printf( "%d\t%f\n", radius, VOL( radius ) );
}
}//end of main
Explanation:
The given C++ program calculates the volume of sphere.
For declaring the macros statements the define keyword is used for VOL(x) and pi.
Then using the for loop to iterate over the radius variable from 1 to 10 and to print one by one via “\n”. The “\t” is used to print six spaces between the radius and their volume.
Sample Output:
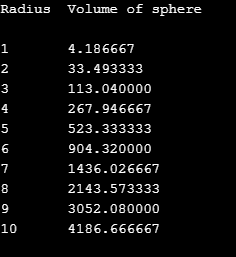
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK C HOW TO PROGRAM
- Please answer this JAVA OOP question that is given below: An Employee has a name, employee ID, and department. An Employee object must be created with all its attributes. The UML diagram is provided below: - name: String - employeeId: String - department: String + Employee(name: String, employeeId: String, department: String) + setName(name: String): void + setEmployeeId(employeeId: String): void + setDepartment(department: String): void + getName(): String + getEmployeeId(): String + getDepartment(): String + toString(): String A faculty is an Employee with an additional field String field: rank Assuming the Employee class is fully implemented, define a Professor class in Java with the following: A toString() method that includes both the inherited attributes and the specializationarrow_forwardPlease answer JAVA OOP question below: An Employee has a name, employee ID, and department. An Employee object must be created with all its attributes. The UML diagram is provided below: - name: String - employeeId: String - department: String + Employee(name: String, employeeId: String, department: String) + setName(name: String): void + setEmployeeId(employeeId: String): void + setDepartment(department: String): void + getName(): String + getEmployeeId(): String + getDepartment(): String + toString(): String A faculty is an Employee with an additional field String field: rank Assuming the Employee class is fully implemented, define a Professor class in Java with the following: Instance variable(s) A Constructorarrow_forwardDevelop a C++ program that execute the operation as stated by TM for addition of two binary numbers (see attached image). Your code should receive two binary numbers and output the resulting sum (also in binary). Make sure your code mimics the TM operations (dealing with the binary numbers as a string of characters 1 and 0, and following the logic to increase the first number and decreasing the second one. Try your TM for the following examples: 1101 and 101, resulting 10010; and 1101 and 11, resulting 10000.arrow_forward
- I need to define and discuss the uses of one monitoring or troubleshooting tool in Windows Server 2019. thank youarrow_forwardI would likr toget help with the following concepts: - Windows Server features - Windows Server versus Windows 10 used as a client-server networkarrow_forwardI need to define and discuss the uses of one monitoring or troubleshooting tool in Windows Server 2019. thank youarrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


