
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds cyclohexane and trans-2-hexene are distinguished using NMR spectra is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the trans-2-hexene gives six signals in the NMR spectra. Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds cyclohexane and trans-2-hexene can be distinguished on the basis of NMR signals to be observed in the compound. Both of the compounds contain the same number of hydrogens. The NMR spectra of cyclohexane gives only one signal as all the hydrogens are equivalent in the compound. The trans-2-hexene gives six signals due to the presence of six sets of protons in the compound.
The structure of trans-2-hexene is given below along with six set of protons labeled alphabetically.
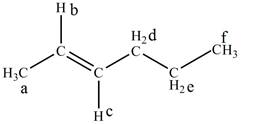
Figure 1
The structure of the cyclohexane along with its all equivalent protons peak data is shown below.
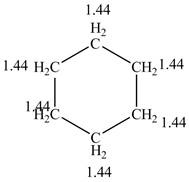
Figure 2
The cyclohexane gives only a single peak for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the trans-2-hexene gives six signals in the NMR spectra.
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds trans-3-hexene and 1-hexene are distinguished using NMR spectra is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The trans-3-hexene gives only three signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the 1-hexene gives seven signals in the NMR spectra. Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds trans-3-hexene and 1-hexene can be distinguished on the basis of NMR signals to be observed in the compound. Both of the compounds contain the same number of hydrogens. The NMR spectra of trans-3-hexene gives only three signals due to the presence of three sets of protons because of being symmetrical compound. The 1-hexene gives seven signals due to the presence of seven sets of protons in the compound.
The structure of trans-3-hexene is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
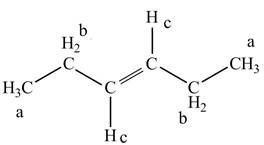
Figure 3
The structure of the 1-hexene is given below along with seven sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
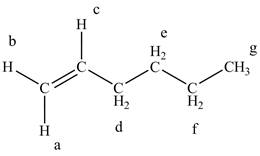
Figure 4
The trans-3-hexene gives only three signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the 1-hexene gives seven signals in the NMR spectra.
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds 1, 1-dichlorohexane, 1, 6-dichlorohexane, and 1, 2-dichlorohexane are distinguished using NMR spectra is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The 1, 6-dichlorohexane gives only three signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the 1, 2-dichlorohexane and 1, 1-dichlorohexane gives six signals in the NMR spectra. These two compounds 1, 2-dichlorohexane and 1, 1-dichlorohexane having same number of signals are distinguished from each other on the basic of peaks at high chemical shift value. All the compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of signals and chemical shift value of signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds 1, 1-dichlorohexane, 1, 6-dichlorohexane, and 1, 2-dichlorohexane can be distinguished on the basis of NMR signals to be observed in the compound. All three compounds contain the same number of hydrogens. The NMR spectra of 1, 6-dichlorohexane gives only three signals due to the presence of three sets of protons because of being symmetrical compound. The 1, 1-dichlorohexane gives the six signals due to the presence of six sets of protons in the compound. The 1, 2-dichlorohexane gives the six signals due to the presence of six sets of protons in the compound.
The two compounds 1, 1-dichlorohexane and 1, 2-dichlorohexane are differentiated from each other from the high chemical shift signals in the NMR spectrum. In the compound, 1, 1-dichlorohexane there is one signal at high chemical value at 5.0 ppm. In the compound, 1, 2-dichlorohexane there are two signals at high chemical shift value for the compound. One at 3.8 ppm and other at 3.0 ppm.
The structure of 1, 6-dichlorohexane is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
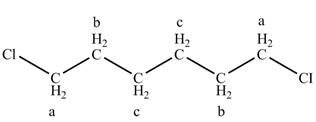
Figure 5
The structure of the 1, 1-dichlorohexane is given below along with six sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
There is one signal at high chemical value at 5.0 ppm in the compound.
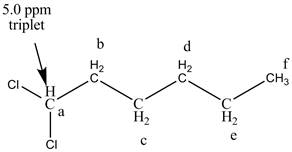
Figure 6
The structure of the 1, 2-dichlorohexane is given below along with six sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
There are two signals at high chemical shift value for the compound. One at 3.8 ppm and other at 3.0 ppm.
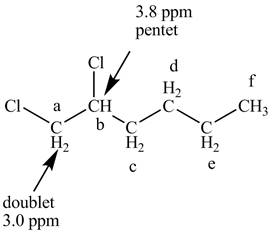
Figure 7
The 1, 6-dichlorohexane gives only three signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the 1, 2-dichlorohexane and 1, 1-dichlorohexane gives six signals in the NMR spectra. These two compounds 1, 2-dichlorohexane and 1, 1-dichlorohexane having same number of signals are distinguished from each other on the basic of peaks at high chemical shift value.
(d)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds tert− butyl methyl ether and isopropyl methyl ether are distinguished using NMR spectra is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The tert− butyl methyl ether gives only two signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the isopropyl methyl ether gives three signals in the NMR spectra. Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds tert− butyl methyl ether and isopropyl methyl ether can be distinguished on the basis of NMR signals to be observed in the compound. Both of the compounds contain a different number of hydrogens. The NMR spectra of tert− butyl methyl ether give only two signals due to the presence of two sets of protons. The isopropyl methyl ether gives three signals due to the presence of three sets of protons in the compound.
The only signal that is different in both the compounds is for the single hydrogen of methane group attached directly to the oxygen. Also, the splitting of the protons methyl groups into doublet occurs for isopropyl group while in tert− butyl group all methyl groups give singlet peak.
The structure of tert− butyl methyl ether is given below along with two sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
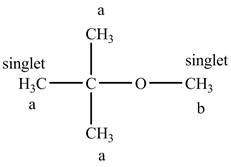
Figure 8
The structure of the isopropyl methyl ether is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
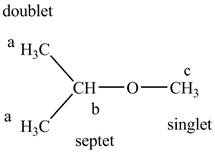
Figure 9
The tert− butyl methyl ether gives only two signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the isopropyl methyl ether gives three signals in the NMR spectra.
(e)
Interpretation:
An explanation as to how the compounds Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 and H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 are distinguished using NMR spectra is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Many nuclei and electrons have spin. Due to this spin magnetic moment arises. The energy of this magnetic moment depends on the orientation of the applied magnetic field. In NMR spectroscopy, every nucleus has a spin. There is an angular momentum related to the spin. The difference between its resonance frequency and that of the reference standard is known as the chemical shift of a nucleus. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as reference.
Answer to Problem 13.37AP
The H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 ether gives only two signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 gives three signals in the NMR spectra.
Both compounds are distinguished on the basis of the number of NMR signals.
Explanation of Solution
The compounds Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 and H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 can be distinguished on the basis of NMR signals to be observed in the compound. Both of the compounds contain the same number of hydrogens. The NMR spectra of H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 give only two signals due to the presence of two sets of protons. The Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 gives the three signals due to the presence of three sets of protons in the compound.
The structure of H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 is given below along with two sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
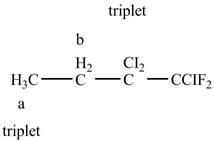
Figure 10
The structure of the Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 is given below along with three sets of protons labeled alphabetically.
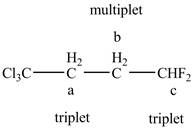
Figure 11
The H3C−CH2−CCl2−CClF2 ether gives only two signals for all the hydrogens in the compounds while the Cl3C−CH2−CH2−CHF2 gives three signals in the NMR spectra.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- 3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardPlease provide a synthesis for the Ester using proponoic acid, thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help with the curved arrow mechanism of this reaction, thank youarrow_forward
- Concentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 Question: Determine the regression equation (a and b coefficients) from first principlesarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forwardNeed help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forward
- Draw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forwardE Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

