
(A)
Introduction:
Fixedmanufacturing
To choose:
Predetermine fixed manufacturing overhead rate.
Answer to Problem 13.30C
Machine hour rate = 3.25 per hr.
Explanation of Solution
Machine hour rate
(B)
Introduction:
Fixed overhead cost means that expense which have been incurred in past and these expenses will not change even production increase or not.
To choose:
Draw a graph of a fixed manufacturing expense.
Explanation of Solution
Fixed overhead always same except some condition
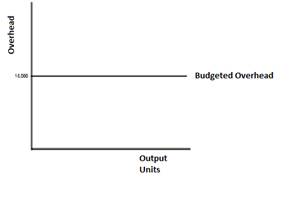
(C)
Introduction:
Variable overhead varies with the production unit, because these expenses will be change with production. If production unit increase then variable expense also be increased and vice-versa
To choose:
Draw a graph of a variable manufacturing expense
Answer to Problem 13.30C
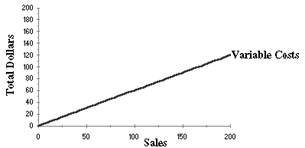
Explanation of Solution
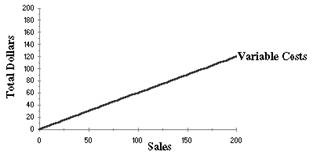
(D)
Introduction:
Raw material consumed means the material which has been specially used for the manufacturing process for output the final product.
To choose:
Prepare"T space" ledger account. Explain the relationship between raw material purchased and raw material consumed.
Answer to Problem 13.30C
Consumed raw material = 252000
Explanation of Solution
Raw material consumed account
| Date | Particular | Amount ($) | Date | Particular | Amount ($) |
| To Balance b/d To customer (purchase) | 39,000 240,000 | By Consumed raw material(bal. fig) By balance c/d | 252000 29000 |
Raw material purchase means total raw material purchase during the last year for the consumption purpose, but this is not compulsory that this raw material must be used in the current period.
Raw material consumed means this is material which has been used for the manufacturing process out of raw material purchased during the current year or form the opening stock.
Raw material consumed = opening stock + purchased − closing stock.
(E)
Introduction:
Manufacturing expense applied on the work in process, because those goods which have not in complete form. On these good some all types' expense has been incurred.
To choose:
Calculate the variable manufacturing expense on the applied work in process.
Answer to Problem 13.30C
For opening working in process = $33000
For closing working in process = $51500
Explanation of Solution
Total variable cost incurred =
Total goods manufacturing = $233500
Total manufacturing goods = total variable cost
$233500 = $180000
So, calculate for $1 goods =
So this is the cost for opening work in progress
For opening working in process = $33000
For closing working in process = $51500
(F)
Introduction:
Fixed overhead expense means that expense has been incurred before starting the production these expenses not changed with the production. This applied on the product at the basic rate. This rate is calculated by the absorption method. Some time called black rate method.
To choose:
Calculate the fixed manufacturing expense on the applied work in process.
Answer to Problem 13.30C
For opening finished goods = $104000
For closing finished goods = $122000
Explanation of Solution
Total fixed cost incurred =
Total manufacturing goods = total variable cost
$312000= $215500
So, calculate for $1 goods =
So this is the cost for opening work in progress
For opening finished goods = $104000
For closing finished goods = $122000
(G)
Introduction:
Work in process means that some goods has been manufacturing but yet not complete up to final product.
To choose:
Prepare T-accounts for work in process to calculate the cost of goods manufacturing
Answer to Problem 13.30C
Cost of goods manufacturing $233500
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-account for the work in process tocalculate the cost of goods manufacturing
Work in process
| Particular | Amount | Particular | Amount |
| To Balance b/d To cost of material consumed | 33,000 252000 285000 | By cost of goodsmanufacturing (Balfig) By Balance c/d | 233500 51500 285000 |
(H)
Introduction:
Cost of goods sold means those goods that have completed all stage and ready to sale. For those goods company calculate the cost of goods sold applied all type of expense which incur for the manufacturing form the raw material to finished goods.
To choose:
Prepare a T-accounts for finished goods to calculate the cost of goods sold.
Answer to Problem 13.30C
Cost of goods sold = $215500
Explanation of Solution
T-accounts for finished goods to calculate the cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold for finished goods
| Particular | Amount | Particular | Amount |
| To Balance b/d To cost of goods manufacturing | 104000 233500 285000 | By cost of goods sold (Bal fig) By Balance c/d | 215500 122000 285000 |
(i)
Introduction:
Fixed overhead expense means that expense has been incurred before starting the production these expenses not changed with the production. This applied on the product at the basic rate. This rate is calculated by the absorption method. Some time called black rate method.
To choose:
What is the treatment of used hour in the
Answer to Problem 13.30C
Unfavorable fixed cost variance is going to income statement account, which is $26000
Explanation of Solution
As per the company data which is provided in the question, company used the machine for 96,000 hours, but due to some reasons company used only 88000 hours, company total fixed expenditure $312,000 for 96000 hours but company used the machine only 88000 hours.
This is a variance of fixed cost
As per the budget total fixed cost = $312,000 for 96000 hours.
Fixed cost per hour =
As per the given information in the question machine only works 88000 hours
So, the expense will be only = 88,000 hour
= $286,000
Extra expense will be going to financial profit and loss = $312,000 - $286,000
= $26,000
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Accounting: What the Numbers Mean
- Treadway Equipment acquired manufacturing machinery at the beginning of the year at a cost of $86,000. The machinery has an estimated residual value of $5,500 and an estimated useful life of 5 years. Determine the second-year depreciation using the straight-line method.arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forwardThe ending balance of the direct materials inventory is $_.arrow_forward
- What are adjusting journal entries and why are they necessary? Meedarrow_forwardno ai What are adjusting journal entries and why are they necessary?arrow_forwardLawrence Industries plans to produce 30,000 units next period at a denominator activity of 45,000 direct labor hours. The direct labor wage rate is $16.00 per hour. The company's standards allow 2.2 yards of direct materials for each unit of product; the material costs $8.50 per yard. The company's budget includes a variable manufacturing overhead cost of $3.25 per direct labor hour and fixed manufacturing overhead of $270,000 per period. Using 45,000 direct labor hours as the denominator activity, compute the predetermined overhead rate and break it down into variable and fixed elements.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





