The moment about point A.
The moment about point B.
The moment about point C.
Answer to Problem 13.1P
The moment about point A is
The moment about point B in member BA is
The moment about point B in member BC is
The moment about point C is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The supports
The girder has thickness of
Concept Used:
Write the expression for fixed end moments.
Here, uniform distributed load is
Write the expression for absolute stiffness factor for member
Here, stiffness factor for member
Write the expression for absolute stiffness factor for member
Here, stiffness factor for member
Write the expression for distribution factor for member
Write the expression for distribution factor for member
Write the expression for distribution factor for member
Since the supports
Write the expression for distribution factor for member
Since the supports
Calculation:
The diagram of the beam is shown below.
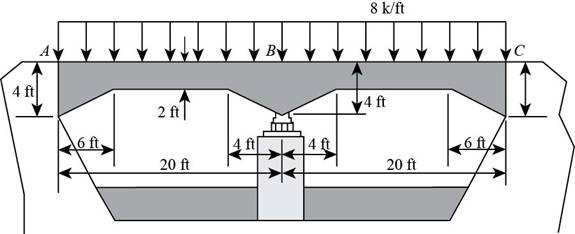
Figure (1)
Consider Figure (1).
Length of span is
Length of haunch at end
Length of haunch at end
Calculate ratio of length of haunch at end
Calculate ratio of length of haunch at end
Calculate ratio for rectangular cross-sectional area at end
Calculate ratio for rectangular cross-sectional area at end
Calculate ratio of length of haunch at end
Calculate ratio of length of haunch at end
Calculate ratio for rectangular cross-sectional area at end
Calculate ratio for rectangular cross-sectional area at end
Determine the carry over factor of member
Determine carry over factor of member
Determine carry over factor of member
Determine carry over factor of member
Determine stiffness factor of member
Determine stiffness factor of member
Determine stiffness factor of member
Determine stiffness factor of member
Calculate absolute stiffness factor for member
Substitute
Calculate absolute stiffness factor for member
Substitute
Calculate fixed end moment for member
Determine coefficients from straight haunches-constant width table.
Substitute
Calculate fixed end moment for member
Determine coefficients from straight haunches-constant width table.
Substitute
Calculate fixed end moment for member
Determine coefficients from straight haunches-constant width table.
Substitute
Calculate fixed end moment for member
Determine coefficients from straight haunches-constant width table.
Substitute
Calculate distribution factor for member
Substitute
Calculate distribution factor for member
Substitute
The moment distribution table is shown below.
| Joint | A | B | C | |
| Member | AB | BA | BC | CB |
| K | | | ||
| D.F. | | | | |
| C.O.F. | | | | |
| F.E.M. | ||||
| DIST | | | ||
| SUM | ||||
Table (1)
Conclusion:
The moment about point A is
The moment about point B in member BA is
The moment about point B in member BC is
The moment about point C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Structural Analysis, Student Value Edition
- 1. (20 Points) Determine the critical depth in the trapezoidal drainage ditch shown below. The slope of the ditch is 0.0016, the side slopes are 1V:2.5H, the bottom width is b = 14', and the design discharge is 500 cfs. At this discharge the depth is y = 4.25'. Also, determine the flow regime and calculate the Froude number. Ye= ? Z barrow_forward3. (20 Points) A broad crested weir, 10 feet high, will be constructed in a rectangular channel B feet wide. The weir crest extends a length of B = 120 feet between the banks with 2 - 4 foot wide, round nosed piers in the channel. The width of the weir crest is 8 feet. If H = 6', determine the design discharge for the weir.arrow_forwardParking Needs vs. Alternative Transportation Methods for presentation slides include images and graphsarrow_forward
- Please explain step by step and show formulararrow_forwardBeam ABD is supported and loaded as shown. The cross-section of the beam is also shown. The modulus of elasticity of the beam is 200 GPa. 6.0 kN/m Cross-section: 330 mm 4.5 kN 8.0 kNm 40 mm 2.5 m 1.5 m 20 mm Set up the discontinuity moment function in terms of x. List all the appropriate boundary conditions. Determine the slope function in terms of x. Determine the deflection function in terms of x. Determine the support reactions. Determine the maximum deflection. 290 mmarrow_forwardDraw the Shear Force Diagram and Bending Moment Diagram for the beam shown in Fig.1. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope Deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardText Book Problem 7.82 (page 261) Consider the total head-loss in the system forthis flow is 18.56 ft (head-losses in first and second pipe are 13.83 ft and 4.73 ftrespectively). Please show numerical values for EGL/HGL at the beginning/end/intermediatechange point. (Point distribution: elevation determination 5 points, EGL, HGL lines 4points).(I think we are just using the values provided for head losses to solve this problem)arrow_forwardCalculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method, and draw the Shear force diagram and Bending moment diagram for the beam shown. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardThank you for your help if you would also provide the equations used .arrow_forwardThe sectors are divided as follows:top right = 1, top left = 2, middle = 3, bottom = 4.(a) Determine the distance yˉ to the centroid of the beam’s cross-sectional area.Solve the next questions by building a table. (Table format Answers) (b) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the x′ axis. (c) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the y-axis.arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





