
Concept explainers
What masses of sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, calcium chloride, potassium chloride, and sodium bicarbonate are needed to produce 1 L of artificial seawater for an aquarium? The required ionic concentrations are (Na+) = 2.56 M, (K+] = 0.0090 M, [Mg2+] = 0.054 M, [Ca2+] = 0.010 M, [HCO3−] = 0.0020 M, [Cl−] = 2.60 M, [SO42-] = 0.051 M.
Interpretation:
Masses of Sodium chloride, Potassium chloride, Sodium sulphate, Calcium chloride, Magnesium chloride and Sodium bicarbonate are required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Mass is the determination of the quantity of the matter in an object. Unit of mass is gram (g) or kilogram (kg). Mass is calculated by multiplying the volume of the compound into its density.
Answer to Problem 13.106QP
Amount of given salts to produce artificial sea water are,
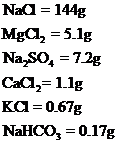
Explanation of Solution
Given data
Required ionic concentrations are,
To calculate the calculation of all ions
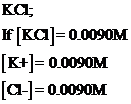
To calculate subtotal of sodium and chloride ion
- The subtotal of chloride ion
Since the required concentration of chloride ion is 2.60M, so the difference is,
- The subtotal of Sodium ion
Since the required concentration of Sodium ion is 2.56M, so the difference is,
By adding the sodium and chloride ions concentration, the subtotal respective ions have calculated.
To calculate mass of the compounds required
By plugging in the value of mass of the given compounds and number of moles of the compound, the mass required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has calculated.
Masses of Sodium chloride, Potassium chloride, Sodium sulphate, Calcium chloride, Magnesium chloride and Sodium bicarbonate are required to produce 1L of artificial sea water has been calculated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- When two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forwardCalculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forward
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




