
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
When 500
Concept introduction
In simple words, Intermolecular forces are termed as the forces acting “between molecules” that is components of a substance. Intramolecular forces are the forces that operate “within a molecule”. The prefix “inter” mean “among” and “intra” mean “within”.
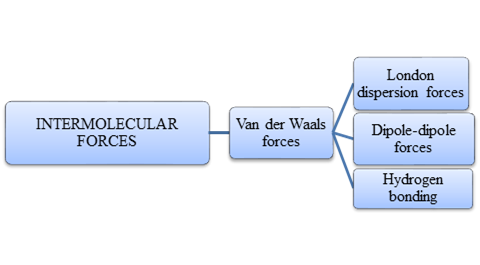
Atoms do combine to form a molecule. Within a molecule, the atoms are held together by intramolecular forces. Many molecules are formed by such instance. Matter is composed of many such innumerable molecules which are held together by intermolecular forces. There are many types of intermolecular forces which is summarizes as follows,
Intramolecular forces are nothing but the type of bonding between them. Ionic compounds have electrostatic force of attraction, the strongest one. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar and non-polar depend upon the polarity of the atoms. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and have two types viz., London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is relatively the strongest one.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- What are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forwardWhat is the reactant that makes the following product of the reaction? Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the reaction proceeds.arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Draw the complete structural formula from each condensed structure. include all hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardDraw the complete structural formula from each condensed structure. Include all hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardIndicate how H2O2 intervenes in the synthesis of K4[Co2(C2O4)4(OH)2]. Write the reactions.arrow_forward
- Explain how, based on physical gas adsorption isotherms, we can determine whether multi-walled C nanotubes are open at their ends. Explain this.arrow_forwardcan somone answer pleasearrow_forwardConstruct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forward
- Indicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forwardConsider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





